Microservices: Database Patterns
Database Patterns in Microservices
Microservices database patterns address distributed architecture's problems with consistency and data management.
Database Per Service
Encapsulate data in microservices by giving each service a private database that can only be accessed via the API that it has been assigned.

Shared Database
Shared databases, typically best suited for modernizing legacy apps, possibly support a small number of microservices but run the risk of growth and autonomy issues.
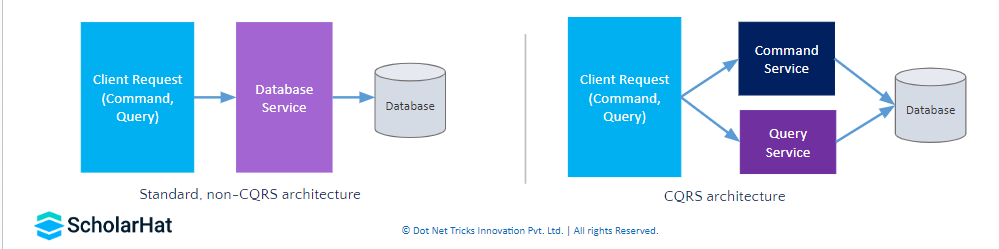
Command Query Responsibility Segregation (CQRS)
CQRS, or Command and Query Responsibility Segregation, is a pattern that divides a data store's read and update processes. You may optimize your application's scalability, security, and performance by implementing CQRS.
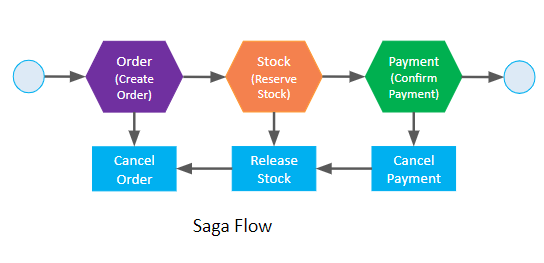
Saga Pattern
The saga pattern is a failure management technique that assists in coordinating transactions across several microservices to preserve data consistency and aids in establishing consistency in distributed systems.
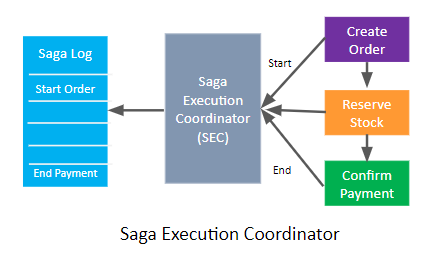
Saga Execution Coordinator
Upon SEC recovery, logs are used to identify and compensate components in reverse chronological order. The Saga Execution Coordinator (SEC) is responsible for monitoring a Saga log, identifying impacted components, and compensating transaction sequences in the event of failure.