Arrays in C
What is an Array in C?
An array is a collection of related data items stored in contiguous memory locations, and its elements can be accessed at random using array indexes. They can hold a collection of primitive data types, such as int, float, double, and char.
Properties of an Array in C
- Declaration: In C, arrays are declared by defining the data type and number of items.
- Indexing: Access elements by index; the initial element index is always zero.
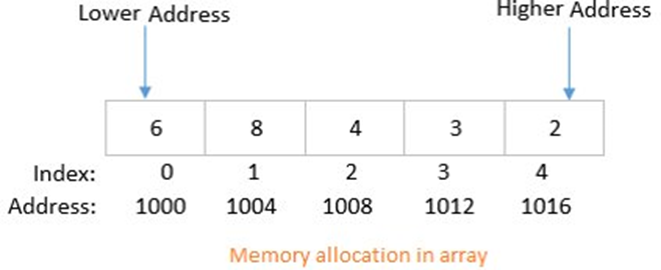
- Memory Allocation: Contiguous memory allocation occurs at declaration; size equals elements multiplied by element size.
- Initialization: Arrays can be initialized before or after declaration.
- Size: The size of an array is equal to the number of elements; to calculate the size, use the sizeof() operator.
- Manipulation: Manipulate arrays using loops, functions, and other programming constructs.
Declaration of an Array
Before we can use an array in C, we must define it just like any other variable. An array can be declared by defining its name, element type, and dimensions. When we declare an array in C, the compiler assigns the memory block of the specified size as the array name.
Initialization of an Array
An array's elements can be initialized one at a time or with a single command. The number of values between braces {} is limited to the number of elements declared in the array between square brackets [].
Types of Arrays
C has two types of arrays:
- Single Dimensional Array
- Multi-dimensional array
Single Dimensional Array
In C, a single-dimensional array is a collection of elements of the same data type that are stored in contiguous memory locations and can be accessed using only one index. It is stated by providing the data types and sizes of its members.
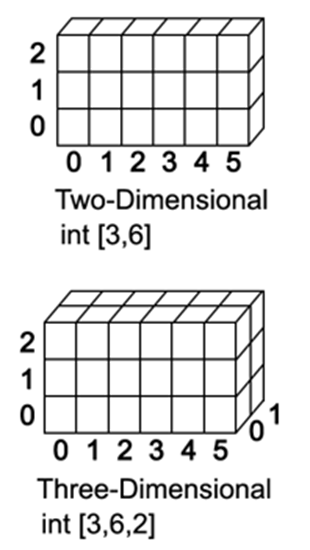
Multi-dimensional array
A multidimensional array in C is an array of arrays that stores elements in a tabular manner with rows and columns. It is declared by defining the data type of its members as well as the dimension sizes. 2D arrays, 3D arrays, and 4D arrays are all examples of multidimensional arrays.
Array Traversal in C
In C, array traversal involves iterating through each element of an array and sequentially accessing and processing its data via loops or recursion.
Array Insertion in C
In C, array insertion refers to adding elements to an existing array, either at a specific index or at the end, which necessitates relocating elements to make place for the new ones.
Array Deletion in C
Array deletion in C is the process of eliminating elements from an array, either by shifting existing components to fill the space or by marking the removed element as invalid, depending on the requirements.
Passing Arrays to Functions
In C, an array is always provided as a collection of pointers to functions. When we attempt to send an array to a function, it decays to a pointer, which is then passed as a pointer to the first element of the array.
Pointer to an array
You can construct a pointer to an array's first element by simply providing the array name without an index.
Returning an array from a function in C
In C, functions can only return one value. Pointers are required for returning multiple values or elements. A function can return an array by passing a pointer to the first element of the array.
Advantages of an Array in C
- Efficient Memory Usage: Arrays use contiguous memory, which allows for efficient allocation and access.
- Easy Access: Elements can be accessible using an index, making it easier to get specific data.
- Better Performance: Index-based access is faster than linked lists or trees because it uses direct memory access.
- Flexibility: Arrays can store a variety of data kinds (integers, characters, and strings).
- Algorithm Implementation: Many algorithms make use of arrays, which simplifies C implementation.
- Compatibility: In complicated implementations, arrays function well with other data structures (stacks, queues).
- Function Passing: You can easily pass arrays to functions for quick data management.
Disadvantages of an Array in C
- Fixed-size: The array size is set at declaration; there is no dynamic resizing.
- Memory Allocation: Contiguous memory allocation; big arrays may experience allocation problems.
- No Bounds Checking: C lacks bounds checking, which increases the danger of memory access mistakes.
- Limited Flexibility: Fixed size and dimensions limit adaptation to changing needs.
- Inefficient for Insertion/Deletion: Insertion and deletion are inefficient for big arrays since they involve rearranging items.
- Not Suitable for Non-Numeric Data: While arrays are suitable for numeric data, they do not accept non-numeric data.


