Data Types in C++
What is a C++ data type?
A data type in C++ describes the type of data that a variable can hold. The format and size of values that can be stored in a variable are defined.
Different Data Types in C++
There are 3 different Data types in C++, which are:
- Primitive Data Type
- Derived Data Type
- User-Defined or Abstract Data Type
Primitive Data Type
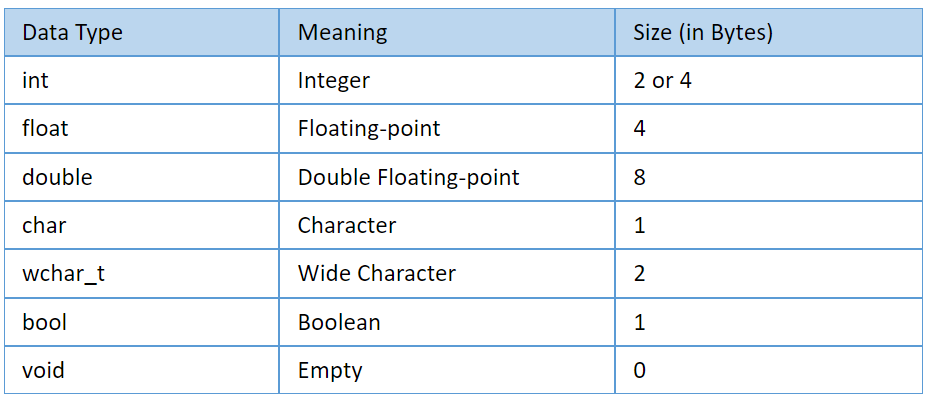
In C++, primitive data types are built-in data types that can be used directly by the user when declaring variables. Some of the primitive data types in C++ are:
- Integer
- Character
- Boolean
- Floating Point
- Double Floating Point
- Valueless or Void
- Wide Character
Integer
Integer data types describe whole numbers that do not contain any fractions or decimal parts. They may be signed (positive, negative, or zero) or unsigned (only positive or zero).
Character
Character data types represent specific characters from a character set, such as ASCII or Unicode. In C++, the term 'char' is widely used to represent characters.
Boolean
Boolean data types represent binary values, which are commonly used for true (1) or false (0) conditions. In C++, 'bool' is used to represent Boolean data.
Floating Point
Floating-point data types represent numbers that contain a fractional portion. In C++, 'float' refers to a single-precision floating-point type.
Double Floating Point
Double-precision floating-point data types are used to represent numbers with a wider range and more precision than 'float'. In C++, the term 'double' is often used.
Void
In C++, the void data type is used to indicate that a function returns no value or to specify generic pointers that do not refer to a specific data type.
Wide Character
Wide character data types, such as 'wchar_t', are used to represent characters from expanded character sets, such as Unicode characters, which take up more storage than a conventional 'char'.
Derived Data Type
In C++, the primitive data type gives rise to the derived data type. There are some derived data types in the C++ language.
- Function
- Array
- Pointer
- Reference
Function
A function is a reusable part of code that completes a certain task. It is a derived data type because it allows you to construct functions that interact with other data types and can even return results of multiple data types.
Array
An array is a derived data type that represents a collection of identical data pieces stored in contiguous memory regions. The elements can be accessed using their indexes.
Pointer
A pointer is a derived data type that contains the memory address of another data type. Pointers are commonly used for dynamic memory allocation as well as direct memory access.
Reference
A reference is a derived data type that serves as an alias or alternate name for an existing variable. It allows you to directly manipulate the original variable, which cannot be null or reseated to another variable after initialization.
User-defined or Abstract Data Types
Users define abstract data types in the C++ programming language. It is like to define a class in structure or C++. This data type has a few variations, which are:
- Class
- Structure
- Union
- Enumeration
- Typedef defined Datatype
Class
A class is a user-defined data type that provides a blueprint for generating things. It encapsulates both data (attributes) and the functions (methods) that work with it. Classes are used to represent real-world entities and to construct bespoke data structures.
Structure
A structure is a user-defined data type that combines variables from many data types under a single name. Structures are useful for grouping related data components.
Union
A union is a user-defined data type that enables you to store many data kinds in the same memory region. Unlike structures, which allot memory to all members, unions distribute memory among their members.
Enumeration
An enumeration is a user-defined data type made up of a collection of named integer constants. It allows you to define symbolic names for values, which improves code readability.
Typedef Defined Data Type
typedef is a keyword that allows you to define aliases for existing data types, improving code readability and abstraction. It is not a new data type, but rather a method of creating different names for existing ones.
What are Data Type Modifiers in C++?
In C++, data type modifiers are used to change the behavior and storage properties of basic data types. C++ has four modifiers. These modifiers can be used to modify data types such as integers, doubles, and characters. They are as follows:
- Signed
- Unsigned
- Short
- Long
Signed
The signed modifier indicates that a variable can have both positive and negative values. However, most built-in integer types (such as int) are signed by default in C++. As a result, using the signed keyword directly is rarely necessary.
Unsigned
The unsigned modifier indicates that a variable can only have non-negative values (zero or positive). It is commonly used when you know that a variable should not contain negative values and want to save memory by avoiding storing negative numbers.
Short
The short modifier indicates that a variable should be stored with fewer bits than the normal data type. This is commonly used to save memory when you know a variable's value will fall inside a narrower range.
Long
The long modifier indicates that a variable should be stored with more bits than the usual data type. This is used for storing larger values that do not fit within the range of a standard data type.
Advantages of Data Types in C++
- Data types allow you to categorize and organize data in a program, making it easier to comprehend and handle.
- Each data type has a limited range of values that it can store, providing for more precise control over the type of data being stored.
- Data types help to prevent errors and faults in a program by setting strict constraints on how data can be used and modified.
- C++ supports a wide selection of data types, allowing developers to select the most appropriate type for a given task.
Disadvantages of Data Types in C++
- Using the wrong data type might cause unexpected behavior and mistakes in a program.
- Some data types, such as long doubles or char arrays, can consume a significant amount of memory and have a negative influence on performance if utilized in excess.
- Beginners may find it challenging to learn and use C++ due to its complex type system.
- Data types can increase a program's complexity and verbosity, making it more difficult to comprehend and understand.


