20
FebAngular Component Lifecycle Hooks Explained
Angular Lifecycle Hooks are essential tools for building responsive, dynamic web apps. If you're working with Angular components, understanding these hooks—like ngOnInit, ngOnDestroy, and others—is crucial to writing optimized, maintainable code. In this guide, you'll explore each Angular lifecycle method with practical examples. Let us now dive into an insightful Angular tutorial and discuss Angular Component Lifecycle Hooks, Stages of Angular Component Lifecycle, eight lifecycle hooks, and why we need Angular lifecycle hooks.
What are Angular Lifecycle Hooks?
Lifecycle hooks are Angular methods that are executed at certain points during a component's lifecycle. These methods allow you to tap into the Angular component lifecycle and apply custom logic or operations at specified points in time. Angular lifecycle hooks give you precise control over your component’s behavior at different stages of its existence.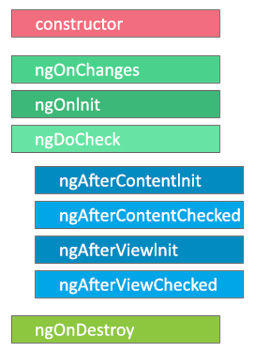
Angular Component Lifecycle Stages
Each Angular component goes through a series of lifecycle stages, and Angular provides hooks you can implement to execute logic at each one. Here's a brief, explanation of each Angular lifecycle phase.
1. Creation Phase
- Angular instantiates the component class and initializes input properties.
- constructor() sets up dependencies.
- ngOnChanges() responds to input changes.
- ngOnInit() is ideal for data fetching and one-time setup.
2. Change Detection & View Rendering Phase
- Angular checks for changes and updates the DOM accordingly.
- Hooks like ngDoCheck() let you add custom detection logic.
- Content and view hooks (ngAfterContentInit(), ngAfterViewInit(), etc.) trigger when rendering completes.
3. Destruction Phase
- Called just before the component is removed from the DOM.
- ngOnDestroy() is used for cleanup tasks like unsubscribing and removing listeners.
- Skipping this can lead to memory leaks and performance issues.
8 Lifecycle Hooks in Angular (with Code Examples)
Angular has many lifecycle hooks that allow you to inject code at precise times in a component's or directive's life cycle. These hooks function similarly to checkpoints, allowing you to conduct specified tasks based on the current state of the component. In Angular, there are eight lifecycle hooks: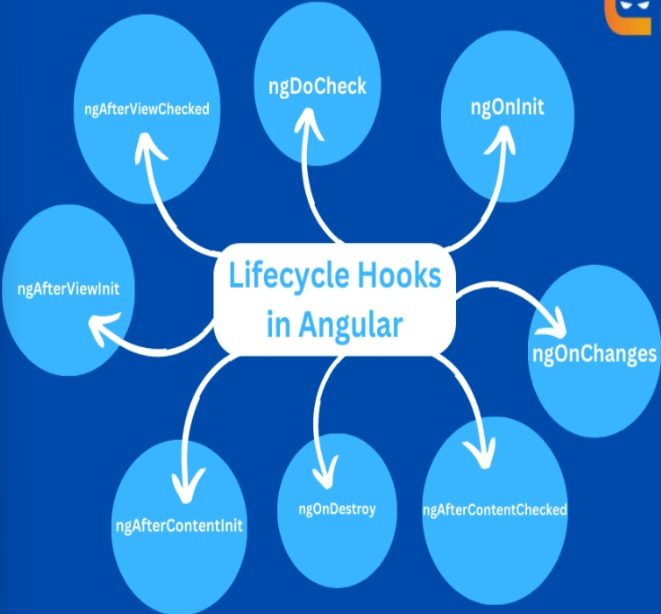
- ngOnChanges
- ngOnInit
- ngDoCheck
- ngAfterContentInit
- ngAfterContentChecked
- ngAfterViewInit
- ngAfterViewChecked
- ngOnDestroy
1. ngOnChanges
When the value of an input binding to the component changes, this hook is called.Example of ngOnChanges
ngOnChanges(changes: SimpleChanges) {
if (changes['data']) {
this.processData(changes['data'].currentValue);
}
}2. ngOnInit
Once the component has been initialized and its input bindings have been handled, this hook is invoked.Example of ngOnInit
ngOnInit() {
this.initialData = this.getData();
}3. ngDoCheck
Every change detection cycle ends with a call to this hook. Because of the performance ramifications, it is frequently regarded as an anti-pattern.Example of ngDoCheck
ngDoCheck() { if (this.element.clientWidth !== this.lastWidth) { this.adjustLayout(); this.lastWidth = this.element.clientWidth; }}4. ngAfterContentInit
After the projected content (content projected into the component with <ng-content>) has been initialized, this hook is invoked.Example of ngAfterContentInit
ngAfterContentInit() { this.content = this.contentElement.nativeElement.textContent;}5. ngAfterContentChecked
This hook is invoked at the end of each change detection cycle for the projected content.Example of ngAfterContentChecked
ngAfterContentChecked() { if (this.content) { this.analyzeContent(this.content); }}6. ngAfterViewInit
After the component's view (including its children) has been fully initialized, this hook is called.Example of ngAfterViewInit
ngAfterViewInit() { this.canvas = this.canvasElement.nativeElement; this.drawChart(this.data);}7. ngAfterViewChecked
This hook is invoked at the end of each change detection cycle for the component's view.Example of ngAfterViewChecked
ngAfterViewChecked() { if (this.isScrolling) { this.updateScrollPosition(); }}8. ngOnDestroy
When the component is destroyed, this hook is called.Example of ngOnDestroy
ngOnDestroy() { this.unsubscribeFromEvents();}Angular Lifecycle Hooks Summary Table
| Lifecycle Hook | Called When | Technical Purpose |
| ngOnChanges() | On input property change | Respond to changes in @Input() bindings using SimpleChanges |
| ngOnInit() | Once after first ngOnChanges | Initialize data, fetch from APIs, setup default states |
| ngDoCheck() | On every change detection run | Custom change detection logic |
| ngAfterContentInit() | After content projected via <ng-content> is initialized | Interact with projected content |
| ngAfterContentChecked() | After each check of projected content | Perform post-check operations |
| ngAfterViewInit() | After component’s view (and child views) initialized | Access ViewChild or ViewChildren, manipulate DOM |
| ngAfterViewChecked() | After every check of the view | React to changes in the view or child views |
| ngOnDestroy() | Before component is destroyed | Unsubscribe from observables, clear intervals, avoid memory leaks |
Why Are Angular Lifecycle Hooks Important?
Angular components go through different stages — like being created, shown, updated, and destroyed. Angular lifecycle hooks are essential for managing the behavior of components and directives at various stages of their existence. Lifecycle hooks let you run code at each of these moments.
| Reason | What Hook Helps |
| Run logic after creation | ngOnInit() |
| Respond to input changes | ngOnChanges() |
| Customize change detection | ngDoCheck() |
| Work with content projection | ngAfterContentInit() |
| Work with the view/DOM | ngAfterViewInit() |
| Cleanup to prevent leaks | ngOnDestroy() |
Summary
Component creation, update, & destruction all involve angular magic.Angular Lifecycle hooks enable checkpoints for injecting code at certain stages in the app's lifecycle, improving app functionality and speed. Make good use of these hooks for a smooth and efficient Angular experience.
FAQs
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.