15
FebWhat is Lazy Load in Angular With Example?
Lazy loading in Angular is a design pattern that loads feature modules only when they are needed, rather than loading everything at the start. This is particularly beneficial for large applications with many features and modules, as it reduces the initial bundle size and speeds up the application's startup. It will load the elements when you are about to scroll them, thus saving bandwidth and load time.
In this Angular tutorial, we'll learn this important technique thoroughly. We'll see what lazy loading is, why use lazy loading, the implementation of lazy loading, lazy loading components, benefits of lazy loading, use cases of lazy loading, etc., along with the comparison of lazy loading and eager loading. So, go along with us and understand the concept.
Read More: Top 50+ Angular Interview Questions & Answers
What is Lazy Loading?
Lazy loading is a performance optimization technique commonly used in web development. The core idea is simple: instead of loading all the resources or components of an application at once, lazy loading allows you to load them only when they are needed.
Why Use Lazy Loading?
- By loading only, the modules needed for the first view, lazy loading makes the initial application load faster, providing a better user experience.
- The main bundle remains small because additional feature modules are downloaded on demand — this helps with app scalability.
- Less memory is used because unnecessary parts of the app aren’t loaded unless needed.
- It prevents unnecessary downloading of heavy components that users may never access.
- As everything doesn't load at the beginning the application loads fast.
- Only required modules and components are loaded hence less memory consumption.
- There is modularity in the code hence easy to maintain.
Example
- Products
- User Profile
- Admin Dashboard
Use Case :
- Break down your application into feature modules (e.g., user management, shopping cart).
- If a feature is complex or rarely accessed (e.g., admin dashboard), lazy load it to reduce initial load time.
- Load content based on user interaction (e.g., clicking a tab to display a specific section).
- Lazy loading modules help break down the overall application bundle for faster build and development cycles
Angular performs lazy loading by using the Angular Router. When a user navigates to a specific route associated with a lazy-loaded module, Angular fetches and loads that module immediately
To lazy load Angular modules, use loadChildren in your AppRoutingModule routes configuration as follows.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: 'items',
loadChildren: () => import('./items/items.module').then(m => m.ItemsModule)
}
]; Add a route for the component in the lazy-loaded routing module.
const routes: Routes = [
{
path: '',
component: ItemsComponent
}
]; Don't forget to remove the ItemsModule from the AppModule.
How to Implement Lazy Loading in Angular?
Prerequisites
- Node.js must have been installed.
- Basic knowledge of Angular
1. Create an Angular Project
Use the Angular CLI to create your project. Install the CLI using npm by running the command:
npm install -g @angular/cli
Now create a project named Lazy Loading Example
ng new lazy-loading-example --routing
The Angular project named Lazy Loading Example was created. The src/app folder contains the code for your app. The main routing file, app-routing.module.ts is located in this folder.
2. Create a Feature Module with Routes
This feature module will load lazily. Run the command
ng generate module blog --route blog --module app.module
This command creates a module named BlogModule, along with routing. You can see this in src/app/app-routing.module.ts:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
const routes: Routes = [ { path: 'blog', loadChildren: () => import('./blog/blog.module').then(m => m.BlogModule) }];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forRoot(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class AppRoutingModule { }
In the above code, the following line defines the routes for lazy loading:
const routes: Routes = [ { path: 'blog', loadChildren: () => import('./blog/blog.module').then(m => m.BlogModule) }];
The module defines its child routes, such as blog/**, in its routing.module.ts file. The blog module you generated looks like this:
import { NgModule } from '@angular/core';
import { RouterModule, Routes } from '@angular/router';
import { BlogComponent } from './blog.component';
const routes: Routes = [{ path: '', component: BlogComponent }];
@NgModule({
imports: [RouterModule.forChild(routes)],
exports: [RouterModule]
})
export class BlogRoutingModule { }
The above routing file contains a single route, ''. This resolves for /blog and points to the BlogComponent. You can add more components and define those routes in this file.
For example, to add a component that would pull details about a particular blog post, you could create the component with this command:
ng generate component blog/detail
This generates the component for the blog detail and adds it to the blog module. To add a route for it, you can add it to your routes array:
const routes: Routes = [{ path: '', component: BlogComponent },
{path:"/:title",component: DetailComponent}];
Verify Lazy Loading
You can easily check whether lazy loading is working or not. For this, run the below command:
ng serve
You will get the following output
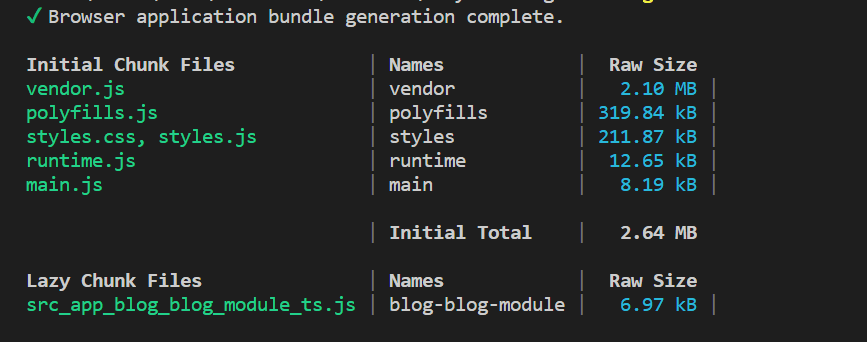
You can observe in the above output that Initial Chunk Files are loaded when the page first loads. Lazy Chunk Files are lazy-loaded. The blog module is listed in this part.
Lazy Loading Vs. Eager Loading
| Parameters | Lazy Loading | Eager Loading |
| Resource Initialization Timing | Delays initialization until needed | Initializes or loads resources as soon as code is executed or page is loaded, regardless of immediate requirement. |
| Impact on Performance | Reduces initial load times, ideal for speed and responsiveness, but may introduce delay when accessing resources for the first time | Ensures immediate availability of resources, smoother post-load experience, but longer initial load times |
| Bandwidth and Memory Usage | loads only required resources, beneficial for mobile users or limited bandwidth | Consumes more bandwidth and memory upfront by loading all resources, which is less efficient for limited resources. |
| Complexity and Maintenance | More complex logic for on-demand loading, increasing code maintenance complexity | Simpler to implement, with no additional loading logic, but may need optimization for the initial resource load |
| Application Scenarios | Suited for applications with many features/content, ideal for mobile devices or varying network conditions | Appropriate for smaller applications where all resources are essential from the start, like certain desktop applications. |
Summary
FAQs
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.












