13
FebWhat is Angular Services - Types of services in Angular with Examples
Angular Services are a core part of Angular used to write and manage shared logic, such as fetching data from APIs, handling user authentication, or managing application state. Services help you avoid repeating code by allowing multiple components to use the same logic. By using services with Angular's Dependency Injection (DI) system, your app becomes more structured, efficient, and easier to maintain.
Angular Services promote the "Separation of Concerns"—meaning your UI components focus only on displaying data, while the services handle the actual logic. This design makes large applications easier to build, debug, and grow over time.
In the Angular tutorial, let's understand Angular Services properly and in an easier way.
What are Angular Services?
Angular Services are special classes in Angular that are used to hold common or reusable code. Instead of writing the same logic in many components, you can write it once in a service and use it wherever needed. This makes your app cleaner, more efficient, and easier to manage.
- Services are used to share data or logic across components.
- They help in fetching data from APIs or handling background tasks.
- Services support Dependency Injection, so Angular provides them automatically when needed.
- They promote clean code by keeping logic separate from the UI.
- Services can be singletons, meaning one shared instance is used across the app.
- Easy to test and improves app performance and maintainability.
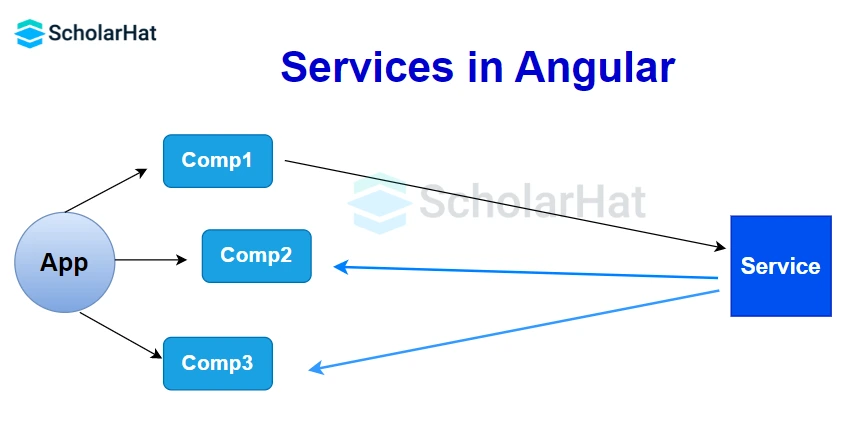
The component is meant to provide the data to view. When I say view, it means providing the data to respective HTML whatever is required. It is not a good practice to make an API call directly from the component. Services give the benefit of separation of concerns and you can say the single responsibility principle as well.
Read More: Top 50+ Angular Interview Questions & Answers
Let's see Services in Action
- Create an angular project: go to VS Code integrated terminal
Run - ng new ServiesTest - Run this newly created project by using the below command
ng serveOnce you run this command you must see the below page at
http://localhost:4200/
- Create a service by using the below command
ng g s DateTime - Now go to the DateTimeService.ts file you will find below the code
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; @Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class DateTimeService { constructor() { } }If you notice it has the @Injectable decorator similar to the @Component decorator which we used to have in an angular component. @Injectable means it can participate in dependency injection.@Injectable accepts metadata objects. So here you can have providedIn value as root, which means this service can be injected into any of the classes across the project.
- Now let us write the code to consume the actual service. So here I am trying to call a real-time RestFul API which is from
https://www.jsontest.com/ - We will call an API located at :
http://date.jsontest.comSo here is the code for the same:import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; @Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class DateTimeService { public apiURL:string="http://date.jsontest.com"; constructor() { } getDateTime () { return this.httpClient.get(this.apiURL) .pipe( map(res => res), catchError( this.errorHandler) ); } }So my code is complaining about httpClient, map, catchError, and errorHandler.
So let us do the import for these complaints.
import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http';For httpClient inject in the constructor like below:
constructor(private httpClient:HttpClient) { } import { map, catchError } from 'rxjs/operators'; For map, catchError Now it's time to fix errorHandler. So write one method like below: errorHandler(error: Response) { console.log(error); return throwError(error); }Lastly, do this import :
import {throwError} from 'rxjs'So finally service code looks like this:
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; import {throwError} from 'rxjs' import { map, catchError } from 'rxjs/operators'; @Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class DateTimeService { public apiURL:string="http://date.jsontest.com"; constructor(private httpClient:HttpClient) { } getDateTime () { return this.httpClient.get(this.apiURL) .pipe( map(res => res), catchError( this.errorHandler) ); } errorHandler(error: Response) { console.log(error); return throwError(error); } }If any error while calling the service it will be logged in the console and an error will be thrown to the subscriber. Now is the time to consume this service from the component. So here you go.
Go to app.module.ts and importimport { HttpClient,HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http';Use this import in an import array like this
imports: [ BrowserModule,HttpClientModule ],First of all, you need to inject this service into components like this:
constructor(private dateTimeService:DateTimeService){}So here now by using this dateTimeService injector, we will call the service method like this
ngOnInit() { this.dateTimeService.getDateTime() .subscribe((result) => { this.globalResponse = result; }, error => { //This is error part console.log(error.message); }, () => { // This is Success part console.log("Date time fetched sucssesfully."); console.log(this.globalResponse); } ) }Here we are calling the getDateTime method from the service, which will call
http://date.jsontest.comand return us the output in the below format.{ "time": "03:53:25 AM", "milliseconds_since_epoch": 1362196405309, "date": "03-02-2013" }We are subscribing to the service response here in the component. Similarly, in this way, you can consume this service in any of your components because the service is injected in the root. So in my component, as you can see I am storing the service response in the global response. Since we have logged the service response in the console, you can see the response in the console something like this.

Let us bind this variable to HTML. Go to app.component.html and paste this code :
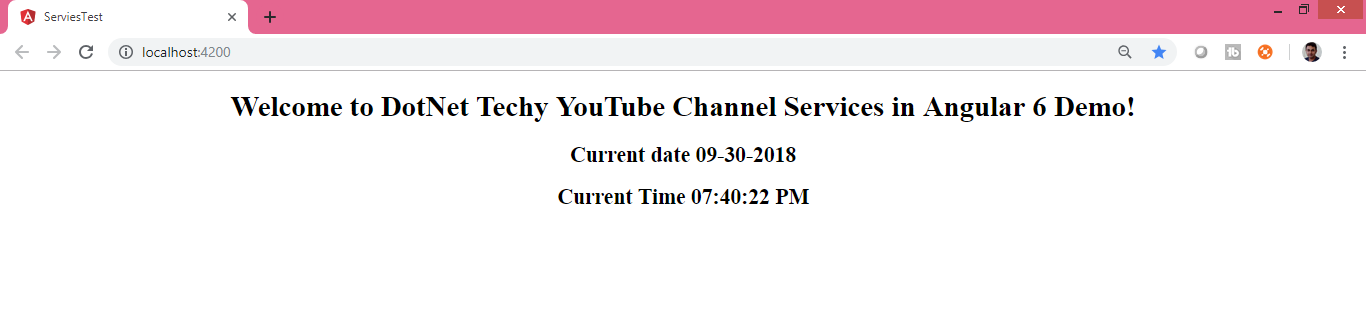
<div style="text-align:center"> <h1> Welcome to {{ title }}! </h1> <h2>Current date {{globalResponse.date}}</h2> <h2>Current Time {{globalResponse.time}}</h2> </div>Run the project, your output will be like this
Now let me give all required files source code:
App.module.ts
import { BrowserModule } from '@angular/platform-browser'; import { NgModule } from '@angular/core'; import { HttpClient,HttpClientModule } from '@angular/common/http'; import { AppComponent } from './app.component'; @NgModule({ declarations: [ AppComponent ], imports: [ BrowserModule,HttpClientModule ], providers: [], bootstrap: [AppComponent] }) export class AppModule { }date-time.service.ts
import { Injectable } from '@angular/core'; import { HttpClient } from '@angular/common/http'; import {throwError} from 'rxjs' import { map, catchError } from 'rxjs/operators'; @Injectable({ providedIn: 'root' }) export class DateTimeService { public apiURL:string="http://date.jsontest.com"; constructor(private httpClient:HttpClient) { } getDateTime () { return this.httpClient.get(this.apiURL) .pipe( map(res =>res), catchError( this.errorHandler) ); } errorHandler(error: Response) { console.log(error); return throwError(error); } }app.component.ts
import { Component,OnInit } from '@angular/core'; import { DateTimeService } from './date-time.service'; @Component({ selector: 'app-root', templateUrl: './app.component.html', styleUrls: ['./app.component.css'] }) export class AppComponent implements OnInit { title = 'DotNet Techy YouTube Channel Services in Angular 6 Demo'; public globalResponse: any; constructor(private dateTimeService:DateTimeService){} ngOnInit() { this.dateTimeService.getDateTime() .subscribe((result) => { this.globalResponse = result; }, error => { //This is error part console.log(error.message); }, () => { // This is Success part console.log("Date time fetched sucssesfully."); console.log(this.globalResponse); console.log("Thanks to DotNet Techy Youtube channel who taught me, how to create services in Angular 6."); } ) } }app.component.html
<div style="text-align:center"> <h1> Welcome to {{ title }}! </h1> <h2>Current date {{globalResponse.date}}</h2> <h2>Current Time {{globalResponse.time}}</h2> </div>
Read More:
- Angular Developer Skills
- Angular Developer Salary In India
- Angular Roadmap to Become an Angular Developer
Conclusion
In conclusion, Angular Services play an important role in building clean, organized, and scalable applications. They allow you to write reusable logic and share it across multiple components without repeating code. By using services with Dependency Injection, Angular apps become easier to maintain, test, and grow. Learning how to use services effectively is key to mastering Angular development.
In-depth exploration of services and their implementation is a crucial aspect covered in Angular Training.
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.