30
JanWhat is Angular?
Angular is an open-source JavaScript-based web application framework that provides a comprehensive solution for front-end development with tools for routing, form handling, and HTTP services. It is developed by Google for building dynamic and scalable single-page applications.The word Angular is a buzzword in the market, and most people in the tech world are talking about the framework.
The demand for Angular developers is soaring. Angular isn’t just a framework; it's a gateway to high-paying and future-ready job roles like Angular Developer, Front-End Engineer, and Full-Stack Developer. Mastering this framework can significantly enhance your job prospects.
In this Angular tutorial, we will learn about different Angular types such as components, directives, services, and modules that help in building structured and dynamic web applications.
What is Angular?
Angular is a client-side JavaScript framework developed by Google that follows the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern. It is now open-source, so anyone can contribute. Angular is mainly used to build Single Page Applications (SPAs), where everything runs on one web page. It also allows us to create apps for different platforms using the same framework.
- Web application
- Desktop-based application
- Mobile-based application
Read More:How long will it take to learn Angular?
Why learn Angular?
It’s been a decade since Angular was invented, and so far many developers around the globe have learned Angular. Angular is very demanding in terms of skill because most of the organizations moved their project into Angular and they are considering their product to become enterprise shortly. Let us know more point
- Widely used by enterprises for scalable apps.
- Powers many Single Page Applications (SPAs).
- Supported by Google and large open-source community.
- Integrated with modern stacks (MEAN, JAMstack, etc.).
- Strong tooling via Angular CLI, RxJS, and TypeScript.
Prerequisites to Learn Angular
You have the basic knowledge on HTML, CSS and OOPS concepts. In addition to this, it will be very helpful, if you have a profound knowledge on TypeScript and JavaScript.
The version history of Angular
As we have discussed earlier in this guide, Angular is evolving and teams are working hard to introduce new and crunchy features to improve performance and stability for the user.
Below is the complete Angular version history in a tabular format.
| Version | Release Date | Key Highlights |
| Angular 2 | Sep 2016 | Complete rewrite in TypeScript; component-based architecture introduced |
| Angular 4 | Mar 2017 | Smaller and faster apps; improved *ngIf and *ngFor; skipped v3 for router sync |
| Angular 5 | Nov 2017 | Build optimizer; improved compiler speed |
| Angular 6 | May 2018 | Angular CLI updates, RxJS 6, and Angular Elements |
| Angular 7 | Oct 2018 | CLI prompts; virtual scrolling; drag and drop |
| Angular 8 | May 2019 | Ivy preview; differential loading for faster apps |
| Angular 9 | Feb 2020 | Ivy renderer by default; better performance |
| Angular10 | Jun 2020 | New default browser config; optional strict typing |
| Angular 11 | Nov 2020 | Improved Hot Module Replacement; updated logging |
| Angular 12 | May 2021 | Nullish coalescing; Ivy Everywhere; Webpack 5 support |
| Angular13 | Nov 2021 | No support for View Engine; improved TypeScript support |
| Angular14 | Jun 2022 | Typed reactive forms; standalone components (preview) |
| Angular15 | Nov 2022 | Fully stable standalone APIs; simplified code |
| Angular16 | May 2023 | Signals introduced; improved hydration for SSR |
| Angular17 | Nov 2023 | Deferrable views; declarative control flow |
Angular CLI
Angular CLI (Command Line Interface) is a powerful tool for setting up, developing, scaffolding, and managing Angular applications. It includes a set of commands for streamlining the development process and automating repetitive tasks. Some examples of usual Angular CLI commands are:
- ng generate
- ng new
- ng build
- ng serve
- ng test
- ng update
- ng deploy
- ng doc
Core Concepts of Angular
- Component: The core building unit of an Angular application's UI, consisting of a view (template), logic (class), and styling.
- Directive: A setof instructions that enhance the functionality of an HTML element by manipulating the DOM based on specifications.
- Module: A unified block of code that organizes components, directives, pipelines, and services.
- Routing: Routing is the system that governs how the program responds to various URL pathways, deciding which component to display.
- Class: A class is a blueprint for building objects with properties (data) and methods (actions).
- Pipe: A function that modifies data before rendering it in an Angular template.
- Service: A reusable class that provides business logic and data access capability to components.
- Enum: A collection of named constant values that represent a fixed set of possibilities, improving code readability.
Features of Angular
The Features of Angular are explained as follows:
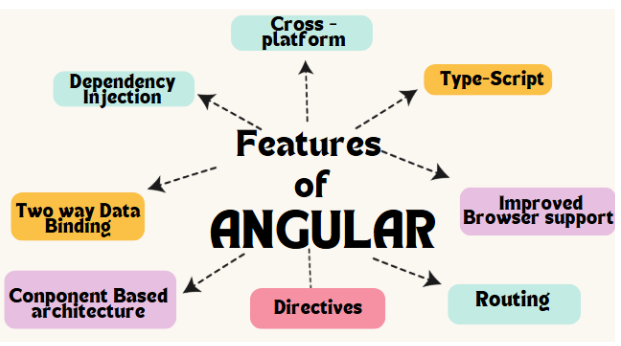
- Cross-Platform: Angular applications may be deployed across multiple platforms, including the web, mobile native apps, and desktop apps.
- Improved Dependency Injection: Dependency injection is a mechanism for introducing dependencies into a component or service. Angular simplifies dependency injection, making it easier to develop maintainable code.
- Improved Data Binding: Angular employs two-way data binding, which automatically synchronizes model data with the view. This makes development easier and eliminates the need to write a lot of boilerplate code.
- Improved Browser Support: Angular is compatible with the most recent versions of Chrome, Firefox, Safari, Edge, and Internet Explorer 11.
- Mobile Development: Angular may be used to create cross-platform mobile applications with frameworks such as Ionic.
- TypeScript: Angular apps are written in TypeScript, a superset of JavaScript with optional static typing. TypeScript helps to detect mistakes early in the development process and makes code more maintainable.
- Routing: Routing is the method for switching between views in an Angular application. Angular includes a built-in router that makes it simple to design routes and manage navigation events.
- Directives: Directives are DOM element markers that change the behavior of the DOM or a component. Angular includes several pre-built directives, as well as the ability to construct your own.
Difference Between AngularJS vs Angular?
| Feature | AngularJS | Angular (2+) |
| Release Year | 2010 | 2016 |
| Language | JavaScript | TypeScript |
| Architecture | MVC (Model-View-Controller) | Component-based architecture |
| Performance | Slower (due to watchers and digest cycle) | Faster with AOT compilation and improved change detection |
| Modularity | Limited modularity | Strong modular structure using NgModules |
| Form Handling | Simple forms | Template-driven and Reactive Forms |
| Tooling (CLI) | Basic or manual setup | Powerful Angular CL |
| Data Binding | Two-way data binding | Mostly one-way (supports two-way with [( )]) |
| Community & Support | Deprecated (End of support in 2021) | Actively maintained and updated by Google |
Configuration to get started with Angular
To start building Angular applications, you need to set up your development environment properly. Here’s a simple step-by-step configuration guide:
1. Install Node.js and npm (Node Package Manager)
- Download and install the latest stable version of Node.js from https://nodejs.org.
- npm comes bundled with Node.js and is required to install Angular CLI.
2. Install Angular CLI (Command Line Interface)
- Open your terminal or command prompt.
- Run the following command:
npm install -g @angular/cli3. Create a New Angular Project
- To create a new project, run:
ng new your-project-name4. Navigate into the Project Folder
cd your-project-name5. Serve the Application
- Start the Angular development server by running:
ng serve| Must Read Articles: |
| A Roadmap to Become an Angular Developer |
| Top Angular Interview Questions and Answers |
Angular Job Role and Salary:
| Job Role | Avg Salary (India) | Avg Salary (USA) | Required skills |
| Frontend Developer | ₹4 – ₹10 LPA | $80k – $120k/year | Angular, HTML, CSS, JavaScript, REST APIs |
| Angular Developer | ₹5 – ₹12 LPA | $85k – $130k/year | Angular 2+, TypeScript, RxJS, Angular CLI, NgRx |
| FullStack Developer | ₹6 – ₹15 LPA | $100k – $140k/year | Angular + Node.js, Express, MongoDB, RESTful APIs |
| UI/UX Engineer (Angular) | ₹4 – ₹9 LPA | $75k – $110k/year | Angular, SCSS, Figma, Responsive Design |
| Software Engineer (Angular) | ₹5 – ₹11 LPA | $90k – $135k/year | Angular, Git, TypeScript, Performance optimization |
| Tech Lead – Angular | ₹12 – ₹25 LPA | $130k – $160k/year | Angular, Architecture Design, DevOps, Agile, Micro Frontends |
| MEAN Stack Developer | ₹7 – ₹18 LPA | $100k – $145k/year | MongoDB, Express.js, Angular, Node.js, Docker |
Conclusion
In conclusion, Angular is a powerful framework that helps you build fast, dynamic, and single-page web applications. It offers useful features like components, services, and routing, making development easier and more organized. With support from Google and a strong community, Angular is a great choice for modern web development.
Additionally, we'll also delve into an Angular Certification Course and provide a comprehensive Angular Tutorial to help you enhance your skills.
FAQs
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.