13
FebPartial Views and View Components in ASP.NET Core
Partial Views and View Components in ASP.NET Core: An Overview
In the MVC (Model-View-Controller) pattern, the view is one of the most important layers since it is used to represent the data of the application including user interactions. A view is an HTML template that is embedded with Razor markup syntax. In ASP.NET Core, the file extension is .cshtml in which C# programming language is used mainly. ASP.NET powers 35% of modern web applications. Don’t miss out—join our Free ASP.NET MVC Course today.
In standard practice, view files are grouped in a folder name according to the controller’s name. These folders are normally stored within the views folder. Typically, views can be categorized into three different sections as follows:
Layouts
Layout is used to maintain consistency in web pages and reduce repetitive code. Normally, the layout mainly contains header, navigation, menu elements, or footer sections.
Partial Views
Partial views mainly reduce code duplicates by maintaining reusable parts of the views.
View Components
It is pretty similar to the partial view in terms of reusability and reduced code repetition.
Views help us to establish a SOC Design (Separation of Concerns) within the MVC application. It separates the user interface from other parts of the application. In this way, we make the application modular which gives us several benefits –
The application can be easily maintained since it is now better organized. Because views are normally grouped by the application features.
The application became loosely coupled. We can build or update the application views separately from the business logic and data access sections.
It is effortless to perform tests on the user interface since it is a separate unit.
Upskill for Higher Salary with ASP.NET Core Programming Courses |
| Training Name | Training Mode | Get Free Demo!! |
| ASP.NET Core Training | Live Training | Book a FREE Live Demo! |
| ASP.NET Core Course | Self Paced | Book a FREE Live Demo! |
Partial Views
Partial Views are just views that can be reused across the web application. So, They can act as a pluggable reusable block that we can call from anywhere in the application, and the content of the partial view is displayed. Whenever we use Partial Views, they must be rendered as child views. They are beneficial as a reusable component or when splitting a large interface into small parts.
We can create a partial view just like regular views, and this view can be returned from the controller using ViewResult. The main difference is that the partial view does not run _ViewStart.cshtml Before the rendering and also, the partial view is rendered within another view.
A partial view is usually rendered in the main views using. @Html.Partial() Method. The partial view passes the partial's name and optionally can pass model data. The partial view always removes repetition because we can use the same partial view in several places in the applications.
We can also design our layout view using partial views, similar to content views. In the normal scenario, the view engine always searches for partial views either in the current folder or a shared folder. The partial view can access the parent view's ViewData dictionary since it can obtain a copy of the view data.
Rendering Partial Views
Partial views can be included in an application's parent page in several ways. The below command is used to call the partial view from the parent interface –
@Html.Partial("_navigationbar")
@Html.Partial() helper method always renders the partial view in the application. This method always takes one argument as a string in which we normally specify the partial view name as a string and it returns the view content as MvcHtmlString type value. It always returns the content of the views as HTML and this gives us the facility to change or modify the HTML part before rendering.
The @Html Helper Objects also have 3 more methods namely PartialAsync, RenderPartial, and RenderPartialAsync which are mainly used for rendering the content of the partial UI. The method name contains Async will be rendered for the asynchronous code. The Render methods result needs to be written directly to the response.
If we want to Create a Partial View, then we need to right-click on the view folder > click on the folder > select Add > click on View.
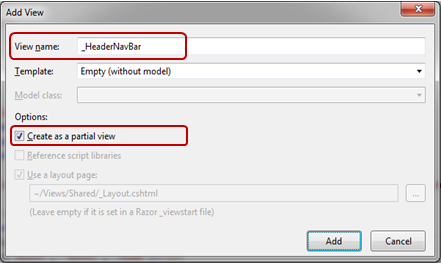
Now, the folks familiar with Angular 1. x might be in dilemma about what is actual difference between Component and Directives Right!? The major difference between both of them is Directives add behavior to existing DOM elements while Components create their view with attached behavior.
Now, we need to look at the HTML part of the partial view as per our requirements like below –
<div class="navbar navbar-inverse navbar-fixed-top">
<div class="container"<
<div class="navbar-header">
<button type="button" class="navbar-toggle" data-toggle="collapse" data-target=".navbar-collapse">
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
<span class="icon-bar"></span>
</button>
@Html.ActionLink("Sample Project", "Index", "Home", new { area = "" }, new { @class = "navbar-brand" })
</div>
<div class="navbar-collapse collapse">
<ul class="nav navbar-nav">
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Home", "Index", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("About Us", "About", "Home")</li>
<li>@Html.ActionLink("Contact", "Contact", "Home")</li>
</ul>
</div>
</div>
</div>
Then we can call the Partial view into the main view.
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8" />
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>@ViewBag.Title – ASP.NET Core Application</title>
@Styles.Render("~/Content/css")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/modernizr")
</head>
<body>
@{
Html.RenderPartial("_HeaderNavBar");
}
<div class="container body-content">
@RenderBody()
<hr />
<footer>
<p>© @DateTime.Now.Year – ASP.NET Core Application</p>
</footer>
</div>
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/jquery")
@Scripts.Render("~/bundles/bootstrap")
@RenderSection("scripts", required: false)
</body>
</html>
View Component
View Components is one of the newly introduced features in ASP.NET Core MVC by Microsoft. It is very much similar to the partial view but it is much powerful compared to the partial view. View components do not use model binding. But, it works only with the data provided when we call it.
Like Partial View, View components do not depend on controllers. It has its class to implement the logic to develop the component’s model and razor markup view page. The most important thing is that View Components can utilize dependency injection, which makes them very powerful and testable. A View Components has the following features –
View Components supports SOC (Separation-Of-Concerns)
It can have its business logic as well as parameter
It is always invoked from the Layout Page
It always renders a chunk rather than a whole process.
View Components can be implemented in any part of the web application where there are some possibilities of code duplicates like the Navigation Pane, Login Panel, Menu, Shopping Cart, etc. So, in simple words, View Components behave like a web part that contains both business logic and UI design to create a web part package that can be reused in the multiple parts of the web application.
So, when we want to create a standard ASP.Net MVC page, it involves processing by both a Controller Class and a View. Similarly, View Components also involve processing by both a view component class and a View. The View Component class must be derived from the View Componentd class.
In ASP.Net Core, we have two processes for declaring a view component. One is to create a class with a name and then append the ViewComponent, or we can decorate our class with the ViewComponent attribute by setting our view component's name through the attribute’s name property.
public class EmployeeViewComponent: ViewComponent
{ }
[ViewComponent(Name = "Employee")]
public class EmployeeInfo: ViewComponent
{}
We can store these class files in any folder in our application. But, since the main point of view component is to create something that can be used in multiple places in our application, it makes sense to put these files related to view components in the view folders called Shared folder.
Now, we have already created our view components class and view. So, now it’s just a matter of time to add the methods to our class and put Razor markup in the view. In our view component class, we must define one method and it must be –
Have the name InvokeAsync
Must return a Task object type to IViewComponentResult
Must be decorated with the Async Keyword
Must accept a single parameter (of any type)
The async attribute will take care of wrapping the object that we return from our InvokeAsync method inside a Task object. Currently, the View method is the only method in the ViewComponent class whose return type is IViewComponentResult.
public async Task InvokeAsync(string EmployeeCode) {
Employee objEmployee;
//...retrieve or build Employee object for a specified Employee
return View(objEmployee);
}
Now, of course, creating a view component is not much if we can’t invoke that view component from any part of the web application. So, to invoke a view component from any other view, we need to use @Component.InvokeAsync() as below:
@Component.InvokeAsync("EmployeeViewComponent",<anonomous type containing params>)
These parameters will be passed to the InvokeAsync method. Suppose, I want to fetch the employee details of code A001. For that, the invoking state will be look like this –
@await Component.InvokeAsync("EmployeeViewComponent", "A001")
View Components are normally invoked from views. But, we can invoke the view components from a controller method. Despite view components does not define any endpoints like controllers, but still we can easily implement a controller action method that can return the content of a ViewComponentResult as in the below example:
public IActionResult EmployeeView()
{
return ViewComponent("EmployeeViewComponent", "A001");
}
SUMMARY
View Component is an essential feature of ASP.NET Core. It is very similar to the Partial View. In this article, we have discussed how to create and use the View Component in ASP.NET Core. You can also consider doing our ASP.NET Core Online Training from Scholarhat to upskill your career.
FAQs
Take our Aspnet skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.