13
FebMicrosoft Azure Virtual Network Explained
Azure Virtual Network (VNet) allows you to create a private network in the cloud that mirrors a traditional datacenter network, but using Azure's infrastructure. It provides a secure, isolated environment where your Azure resources can communicate with each other, the internet, and on-premises systems.It simplifies the concept of the Internet. This enables the provisioning and management of various virtual private networks (VPNs)to establish an isolated and highly secure network. Azure skills are projected to boost your earning potential by 20% in the next 3 years. Enroll now in our Azure Fundamental Free Course with Certification!
It also supports configuring connections between different VNets. These interconnected networks resemble a set of connected systems and servers that can communicate with each other, but are not accessible via the internet. Resources, such as virtual machines within a virtual network, can only respond to requests originating from that network. Access to these virtual machines or web applications deployed in virtual private networks requires a special VPN key.
In this Azure Tutorial, we’ll explore the key architecture, components, and benefits of Azure Virtual Network. You'll learn how to create VNets using the Azure Portal and PowerShell, set up subnets, apply Network Security Groups (NSGs), and integrate services like Load Balancer, Application Gateway, and VPN Gateway—helping you build a solid foundation in Azure networking.
What is Azure Virtual Network
Azure Virtual Network is a cloud service offering from Microsoft that represents a virtual network in the cloud. In general, Azure Virtual Networks are used to secure development and deployment environments against various types of network attacks and data leaks. Virtual machines, web apps, databases, load balancers, etc., should always be kept inside the Virtual network. With Azure, it is very easy to create and configure highly secure private networks with the help of network security groups.
Read More: Top 50 Azure Interview Questions and Answers
Azure Virtual Network Architecture
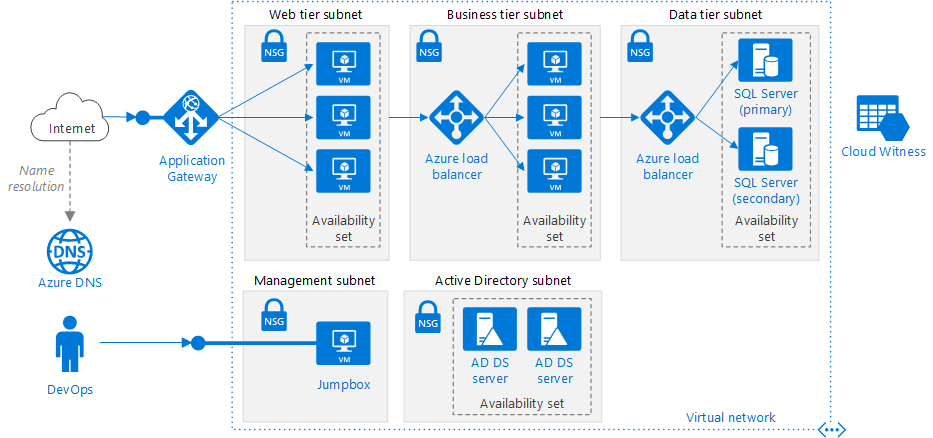 source: https://docs.microsoft.com
source: https://docs.microsoft.comThe above is a typical architecture of a virtual Network for a n-tier application architecture. The entire virtual network has been subdivided into different subnets based on workloads, like the web tier, which contains the User interface, the Business tier that operates the business logic and data tier that hosts the data source. The idea to create and bind each group of Virtual machines into different subnets is useful in a way that we can assign one Network Security Group (NSG) to each subnet and control the traffic flows between the tiers. For example, an HTTP request from the internet should not directly reach to data tier subnet.
We can assign access policy to the Network Security Group of Subnet attached with data tier which only allows incoming requests from business tier subnet. Any other requests trying to reach data tier with any protocol other than business tier will be denied. Similarly, we can assign an access policy on NSG of business tier subnet that the incoming request source IP address should fall in the range of web tier subnet. Additionally, we can also control the traffic requests to the Active Directory by putting that in a separate Subnet inside a Virtual Network.
Important Virtual Network Terminologies:
1. Resource Group
A Resource Group is a logical container for all related resources. Generally, all the Azure resources created for a particular environment, like a test environment, can be put in a single resource group and assigned access to users as needed. For any application architecture, all resources (like VMs, VNets, IP, App Service, Azure Functions, etc.) that combine to make a complete system need to be replicated for each environment, like Dev, Test, UAT, Pre-Prod, and Prod. So, we can have different resource groups for each environment and create all required resources within the corresponding resource group. Then, we can provide access to the test team to the test resource group only and the dev team to the dev resource group only.
2. Public IP
Resources like websites, API apps, Load balancers, and Application gateways will require a public IP address in order to receive requests from the internet and that is achieved by a public IP address. We can also have a public IP address for the Virtual Machines, but it is not recommended as it can allow malicious attacks. Subnet: A subnetwork, or simply subnet, is a range of IP addresses within a Virtual Network. It can be considered that all the machines in a particular project of an organization have separately identifiable IP addresses corresponding to a particular range. Now, we can assign a network security group to this range of IP addresses (Subnet) in order to allow some RDP connections to project-specific machines. Different tiers of an application architecture are also placed in different subnets to isolate them from each other.
3. Network Security Group
A network security group is a set of rules or policies for incoming and outgoing requests. A network security group is generally attached at the subnet level. The advantage of applying network security groups to Subnets is that we can control the data flow. This is important in terms of network security. With an NSG, we can define the IP range for the source of incoming requests.
How Virtual Networking Works in Azure
Virtual networking enables connections between resources and services within the Azure cloud, creating a secure and isolated environment. It provides capabilities such as private IP addressing, network security groups, and routing tables, functioning independently from your on-premises infrastructure.
Key Components of Azure Virtual Networking
1. Virtual Networks (VNets): A virtual network in Azure is a logically isolated space where you can host virtual machines and other resources. It forms the foundation for securely managing and organizing resources.
2. Subnets: Subnets divide a virtual network into smaller segments. Resources within a subnet can be grouped based on function, security level, or other criteria. Subnets also help manage and filter incoming traffic to applications.
3. Routing: Azure uses routing to control the flow of network traffic between resources within a virtual network and across connected networks.
4. VPN and ExpressRoute: To connect on-premises networks to Azure, you can use a VPN (Virtual Private Network) for a secure connection over the internet, or ExpressRoute for a dedicated, private connection that bypasses the public internet.
Advantages of Using Azure Virtual Network
There are many benefits of using Azure Virtual Network, which are as follows:
- Connectivity Options- There are many connectivity options in Azure Virtual Network like site-to-site VPN, point-to-site VPN, Azure ExpressRoute, and virtual network peering.
- Scalability- Azure Virtual Network is scalable enough to handle large workloads and growing infrastructure requirements.
- Isolation and Segmentation- It gives total control of the resources and enhanced security by creating an isolated and segmented network environments.
- Network Security- The security of Azure virtual network is much more enhanced due to its features like Network Security Groups (NSGs).
- Traffic Routing and Load Balancing- The network performance can be highly optimized and workloads are evenly distributed with the help of advanced traffic routing and load balancing techniques.
- Hybrid Cloud Integration- Using Azure Virtual Network, it becomes easy to connect on-premises network with the help of cloud. Large workloads can also be easily moved between your servers and Azure.
Read More: How to Build a Career with Microsoft Azure Fundamentals Certification?
Create a Virtual Network using the Azure Portal
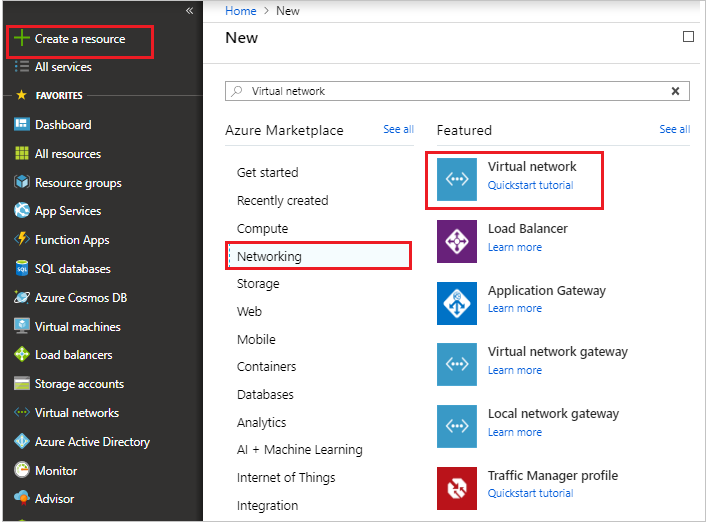
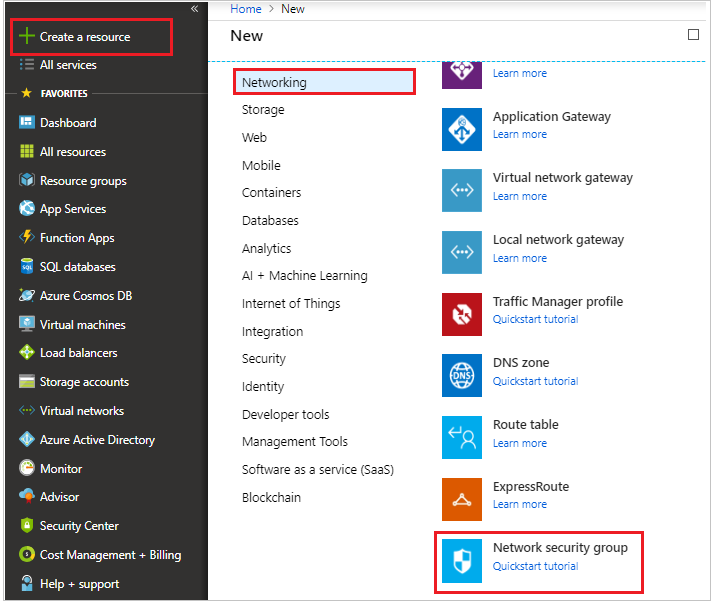
Login to the Azure portal portal.azure.com and click on Create a resource.
On the Marketplace select Networking tab and click on Virtual network as shown below.
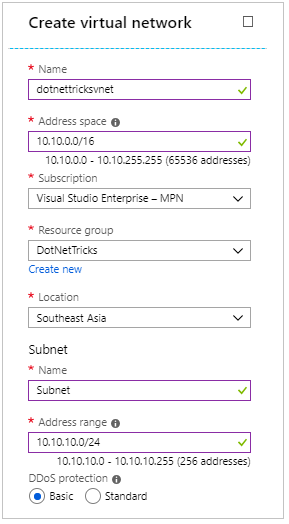
In the Create VNet screen, provide a name to the virtual network and an address space. Choose subscription, resource group and location.
Additionally, also provide a subnet name and address space which should fall within the range of address space of virtual network and click on Create button.
From the top right corner notification tab, click on Go to resource button.
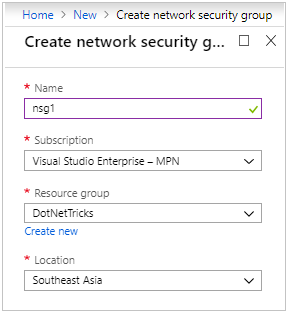
Let’s create a network security group. Click on Create a resource and select Networking tab and click on Network Security group.
Provide name, subscription, resource group and location.
Click on create button.
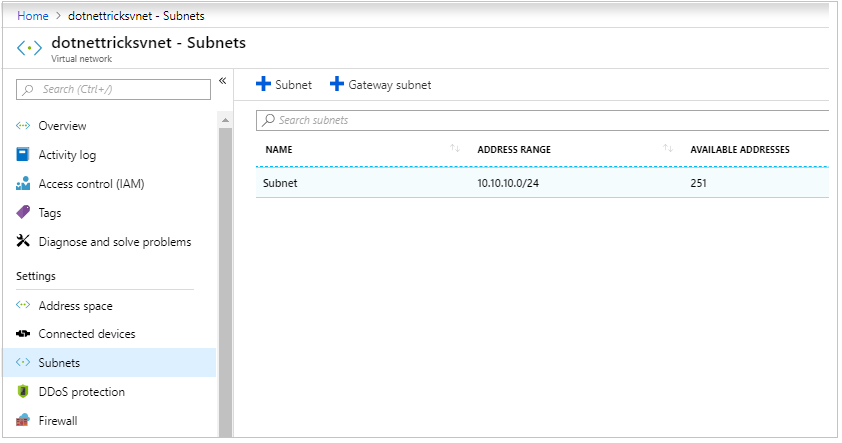
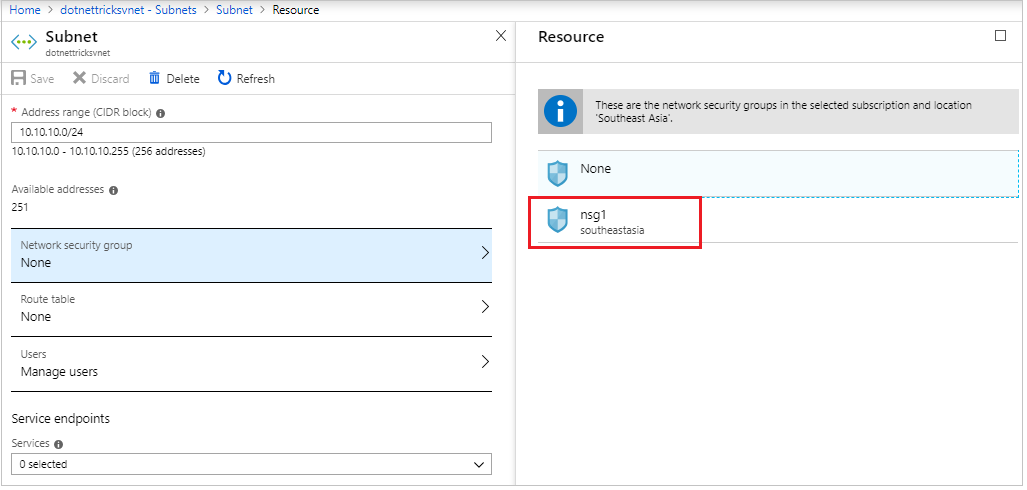
Go back to the virtual network and click on subnets.
Select the subnet and open its details.
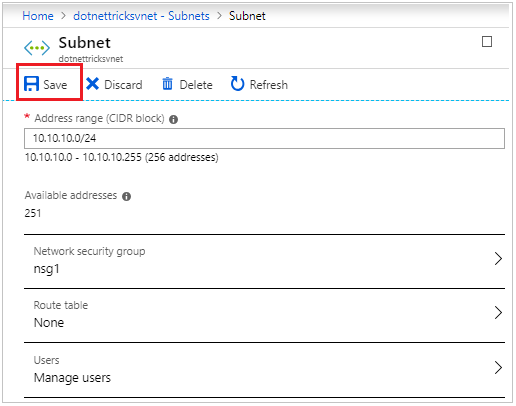
We can attach the network security group to the subnet and save.
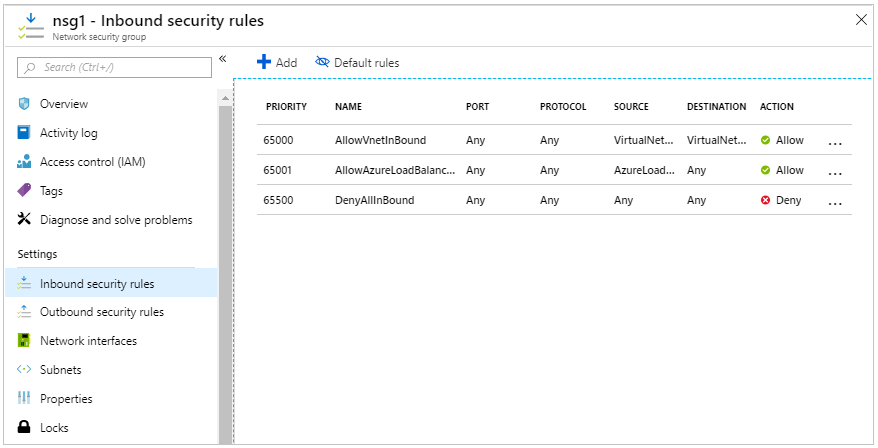
Go to the network security group and click on Inbound security rules.
We can add/ delete more security rules to enhance network security.
Creating a Virtual Network using PowerShell
Launch cloud shell from the top on the portal.
Alternatively, open PowerShell command prompt locally on the system. Check for the latest version of AzureRM module. To continue, the version should be 5.4.1 or later. Run the below command to check for version
Get-Module -ListAvailable AzureRMLogin to Azure with the following command :
Connect-AzureRmAccountCreate a resource group by running the following command :
New-AzureRmResourceGroup -Name DNTResourceGroup -Location EastUSCreate a Virtual Network in the same location where resource group is and attach the Vnet with the resource group
$virtualNetwork = New-AzureRmVirtualNetwork ` -ResourceGroupName DNTResourceGroup ` -Location EastUS ` -Name DNTVirtualNetwork ` -AddressPrefix 10.10.0.0/16Create a subnet within the virtual network
$subnetConfig = Add-AzureRmVirtualNetworkSubnetConfig ` -Name default ` -AddressPrefix 10.10.0.0/24 ` -VirtualNetwork $virtualNetworkNow that our Virtual Network is ready, we can assign this virtual network to Virtual machines. Let’s create a VM with the following command :
New-AzureRmVm ` -ResourceGroupName " DNTResourceGroup " ` -Location "East US" ` -VirtualNetworkName "DNTVirtualNetwork" ` -SubnetName "default" ` -Name "DNTVm1" ` -AsJobGet the IP address of VM with the help of following command
Get-AzureRmPublicIpAddress -Name DNTVm1 -ResourceGroupName DNTResourceGroup | Select IpAddressUsing the IP from the above command, run the below command to download the RDP file and use it to connect the VM.
mstsc /v:<publicIpAddress>
Examples of Virtual Networking in Azure
1. Azure Load Balancer:
Function: Distributes incoming traffic across multiple virtual machines within a virtual network.
Usage: Often works in tandem with Azure Application Gateway to route traffic efficiently to various applications or microservices, ensuring high availability and responsiveness.
2. Azure Application Gateway:
Function: Acts as a Layer 7 (HTTP/HTTPS) load balancer.
Usage: Routes traffic based on URL path or host headers, enabling advanced features like SSL termination, session affinity, and Web Application Firewall (WAF) for securing web applications.
3. Azure VPN Gateway:
Function: Acts as a virtual device that establishes secure connections between on-premises networks and Azure Virtual Networks.
Usage: Utilizes VPN technology and the IPSec protocol to create a secure tunnel, enabling encrypted communication between on-premises infrastructure and resources hosted in Azure.
4. Azure Network Security Groups (NSGs):
Function: Control inbound and outbound traffic to network interfaces, VMs, and subnets.
Usage: Define rules to allow or deny specific traffic, such as allowing HTTP traffic only to a web subnet and blocking all other traffic.
5. Azure Firewall:
Function: Serves as a cloud-based network security solution that safeguards resources within an Azure Virtual Network.
Usage: Inspects and filters both application- and network-level traffic, enforcing policies that ensure only authorized communications are allowed, thereby protecting the environment from potential threats.
Summary
Azure Virtual Network is a core component of cloud infrastructure in Microsoft Azure, enabling secure, isolated, and scalable networking for your cloud resources. By segmenting applications into subnets and applying Network Security Groups, you can control traffic flow and enhance security across each tier. Whether you're deploying VMs, integrating VPNs, or managing traffic with load balancers and firewalls, Azure VNet provides the flexibility and control needed for modern cloud architectures.
In the next 3 years, 75% of developer roles will require Azure expertise. Don’t lag behind. Join our Azure Developer Course now!
FAQs
Take our Azure skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.