13
FebIf Statements in C: Syntax, Examples, and Best Practices
If Statement in C
What is the If Statement in C?
The if statement in C is a decision-making tool that executes specific code blocks based on whether a condition is true or false. Let’s break it down step by step:
Flowchart:
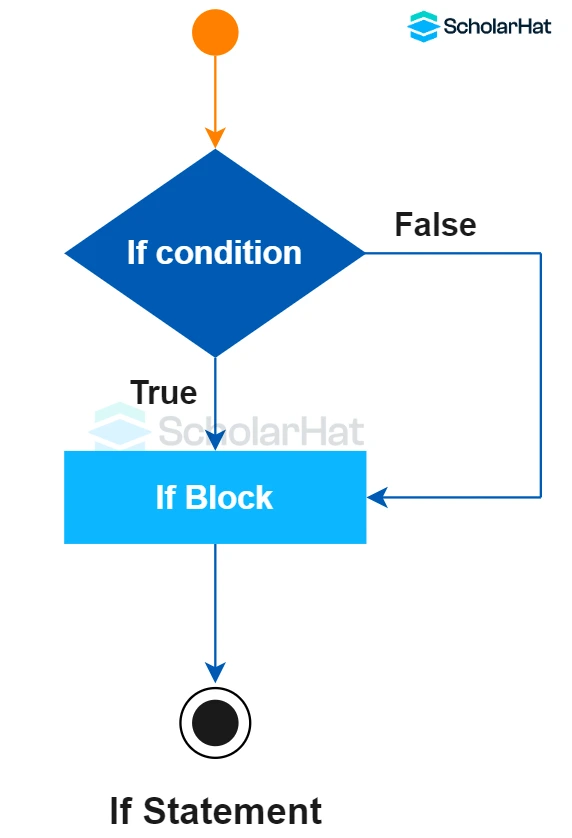
Syntax and Structure of If Statement
This is how the structure of an if statement looks like:
if (condition)
{
// code to execute if the condition is true
} How ‘if’ statement Work in C?
The if statement in C is a decision-making tool that executes specific code blocks based on whether a condition is true or false. Let’s break it down step by step:
Step 1: Condition Evaluation
The condition inside the parentheses ( ) is evaluated. It can be a logical or relational expression like x > 5 or a == b. The result must be either true (non-zero) or false (zero).
Step 2: Decision Making
If the condition is true, the block of code inside the curly braces { } is executed. If false, the block is skipped.
Step 3: Execute the Code Block (if true)
Here’s an example:
int x = 10;
if (x > 5) {
printf("x is greater than 5\n");
} Since x > 5 is true, the output will be:
x is greater than 5
Step 4: Skip the Code Block (if false)
If the condition is false, the program moves to the next statement after the if block:
int x = 2;
if (x > 5) {
printf("x is greater than 5\n");
}
printf("This always runs\n"); Output:
This always runs Step 5: Nested Conditions (Optional)
You can nest if statements to check multiple conditions:
int age = 20;
if (age > 18) {
if (age < 25) {
printf("Eligible for the program\n");
}
} Step 6: Alternative Paths (else or else if)
For handling different actions based on the condition, use else or else if:
int x = 10;
if (x > 15) {
printf("x is greater than 15\n");
} else {
printf("x is 15 or less\n");
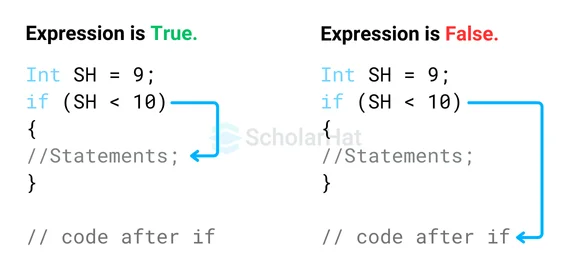
} When using the if statement, 'condition' is something the computer evaluates. If it's true, the code inside the curly braces is executed. If it's false, the code inside the braces is skipped.
Here is how it works:
- Condition Checking- Firstly, you need to write the ‘if’ keyword followed by a condition inside the parenthesis. This condition is like a question the program will ask itself.
- Making a Decision- If the condition turns out to be true, meaning the answer to the question is “yes”, the code inside the curly braces ‘{}’ following the ‘if’ statement is executed. But if, in case, the condition turns out to be false, the code inside the curly braces is skipped, and the program continues to the next statement after the ‘if’ block.
Example in C Compiler
Here is a simple example that will make you understand the working of ‘if’ statement better:
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number = 10;
// Check if the number is positive
if (number > 0) {
printf("The number is positive.\n");
}
return 0;
} In the above example, the program checks if the variable ‘number’ holds a positive value or not. If the condition ‘number > 0’ is true, meaning ‘number’ is greater than 0, the program prints “The number is positive.” Otherwise, if the condition turns out to be false, nothing will be printed, and the program will end.
Output
The number is positive. Real-Time Examples of if Statements in C
Example 1: Temperature Check for a Heater
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int temperature = 25;
if (temperature < 20) {
printf("Turning on the heater.\n");
} else {
printf("Heater is off.\n");
}
return 0;
} Explanation: This program checks if the room temperature is below 20°C. If it is, the heater is turned on.
Example 2: User Login Authentication
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string.h>
int main() {
char username[20] = "admin";
char password[20] = "1234";
char inputUser[20];
char inputPass[20];
printf("Enter username: ");
scanf("%s", inputUser);
printf("Enter password: ");
scanf("%s", inputPass);
if (strcmp(username, inputUser) == 0 && strcmp(password, inputPass) == 0) {
printf("Login successful!\n");
} else {
printf("Invalid username or password.\n");
}
return 0;
} Explanation: This program authenticates a user by checking if the entered username and password match the predefined ones.
Example 3: Odd or Even Number Check
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int number;
printf("Enter a number: ");
scanf("%d", &number);
if (number % 2 == 0) {
printf("The number is even.\n");
} else {
printf("The number is odd.\n");
}
return 0;
} Explanation: The program determines whether the input number is odd or even using the modulo operator.
Example 4: Age Validation for Driving License
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int age;
printf("Enter your age: ");
scanf("%d", &age);
if (age >= 18) {
printf("You are eligible for a driving license.\n");
} else {
printf("You are not eligible for a driving license.\n");
}
return 0;
} Explanation: This program checks if a user is eligible for a driving license based on their age.
Example 5: Bank ATM Withdrawal Limit
#include <stdio.h>
int main() {
int balance = 5000;
int withdrawal;
printf("Enter amount to withdraw: ");
scanf("%d", &withdrawal);
if (withdrawal <= balance) {
balance -= withdrawal;
printf("Withdrawal successful. Remaining balance: %d\n", balance);
} else {
printf("Insufficient funds.\n");
}
return 0;
} Explanation: The program checks if the withdrawal amount is less than or equal to the available balance. If yes, the amount is withdrawn; otherwise, it displays an error.
Advantages of if statement:
- With the "if" statement, you can execute specific blocks of code based on whether a certain condition is true or false.
- "If" statements allow for flexible program flow.
- "If" statements are instrumental in error handling and validation.
- As your program grows in complexity, "if" statements remain scalable and adaptable.
Disadvantages of the if statement in C:
- As the number of nested "if" statements increases, code readability may decrease.
- When dealing with multiple "if" statements that perform similar actions based on different conditions, there's a risk of code duplication.
Summary
Finally, the 'if' statement in C enables conditional code execution based on a defined condition. The program analyzes the condition in the parenthesis and executes the code within the curly braces '{}' if it is true. If the condition is false, the code in the 'if' block is bypassed, and the program proceeds to the next sentence.To learn C programming from scratch, consider enrolling in our C Certification Course.










