06
FebWhat is Expressions in C++ | Types of Expressions in C++ ( With Examples )
Expressions in C++ Programming: An Overview
Do you want to learn a programming language that can help build user-friendly projects? C++ is an excellent choice because it's a powerful, flexible language - and with the right instruction through C++ Full Course Free, it can be easier to learn than you think! Expression in programming is a value that executes in a way that ends up being another value. A value is one of the unique features of programming. It is basically a syntactic entity that determines the value of that program.
What is Expression in C++ Programming?
C++ Expression is a particular entity that contains constants, operators, and variables and arranges them according to the rules of the C++ language. If the question is what is an expression in C++ then it can be answered that the c++ expression contains function calls that return values. Every expression generates some values that are assigned to that particular variable with the help of the assignment operator.
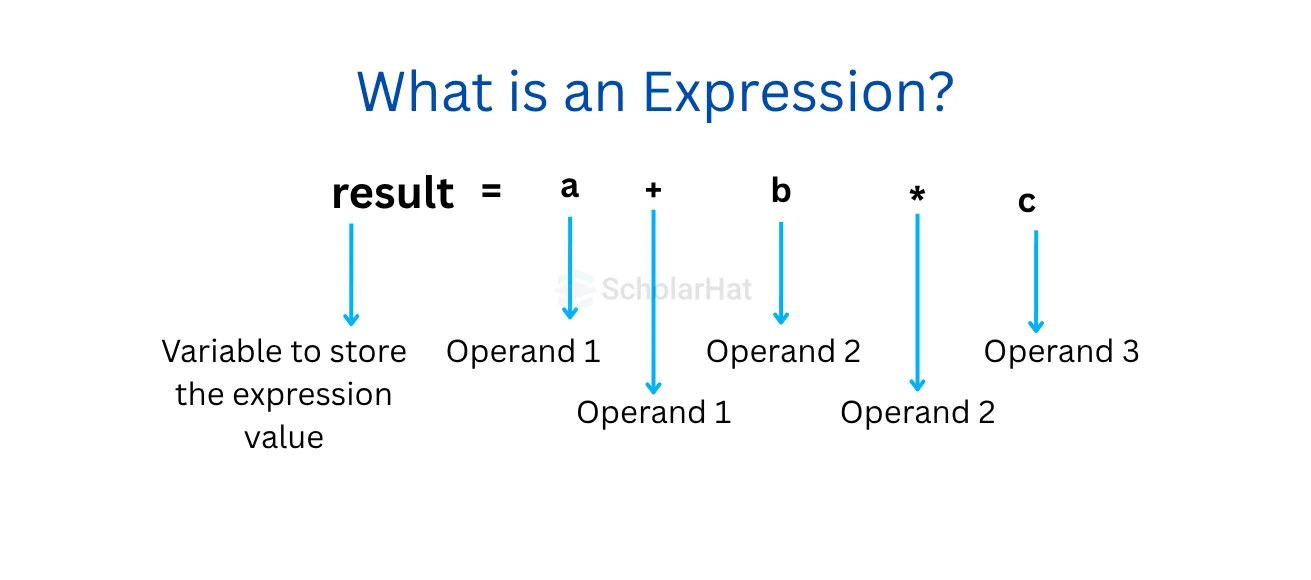
Example of what is an expression in C++:
- (a-b) + c
- (x*y) -z
- 4a2 - 5b +c
- (a+b) / (x+y)
Read More - C++ Interview Interview Questions and Answers
Different types of expressions in C++
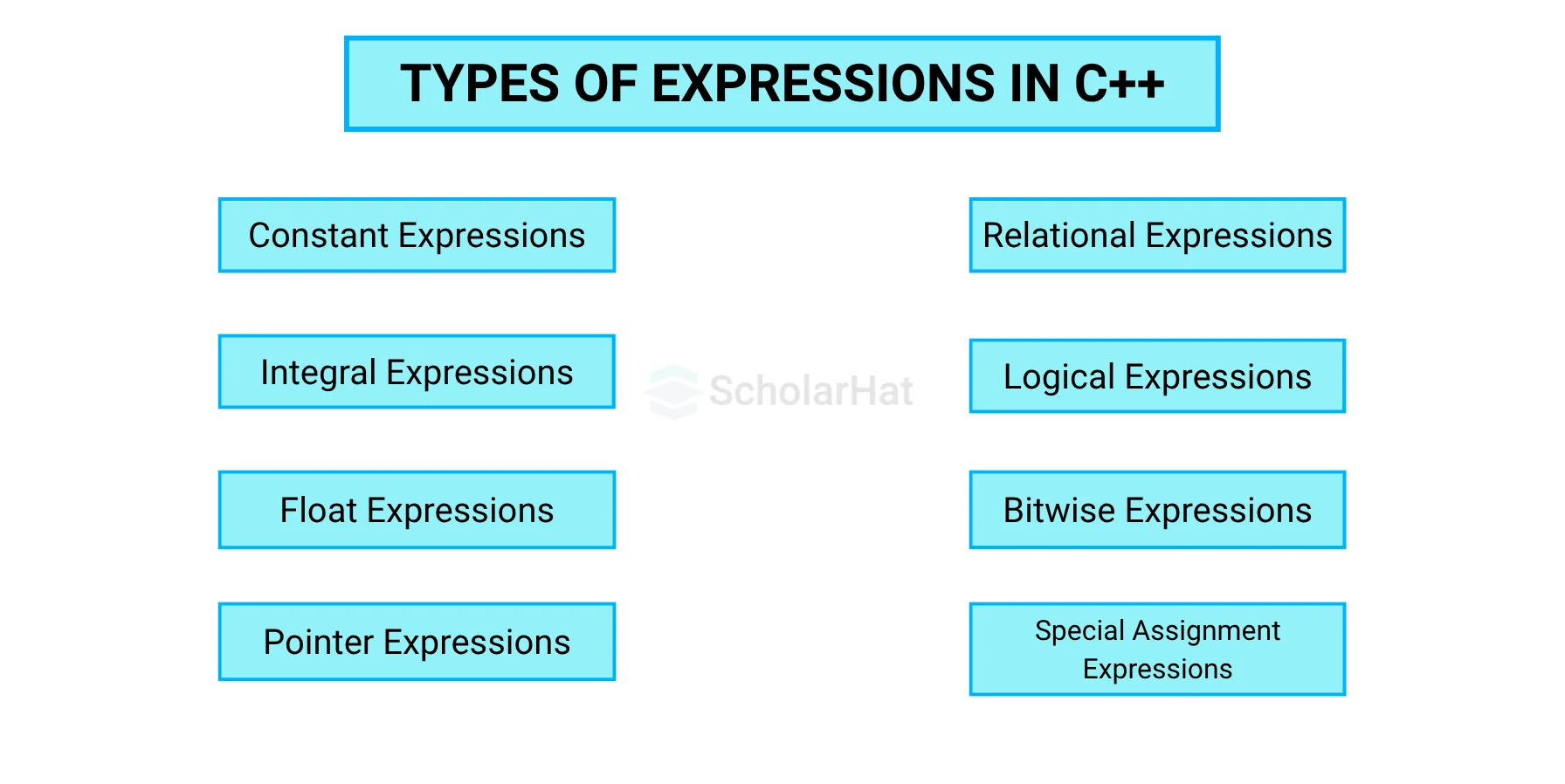
There are different types of expression in C++ programming language is generated, which are:
- Constant expressions
- Integral expressions
- Float expressions
- Pointer expressions
- Relational expressions
- Logical expressions
- Bitwise expressions
- Special assignment expressions
1.) Constant Expression in C++
What is constant in C++ programming language can be explained as this is an expression that contains only constant values. The value of this expression is determined in compile time but it is evaluated in run time. Constant definition in C++ can be composed of integer, floating point, character, and enumeration constants.
- A constant can be used in the following situations,
- It can be used in the declarator of the subscript for describing the array bound.
- It can be used after the keyword, case in the switch statement.
- It can be used as a numeric value in an “enum”
- It helps to specify a bit-field width.
- It is used as the pre-processor in the if statement
| Expression containing constant | Constant value |
| x = (2/5) * 4 | (2/5) * 4 |
| extern int y = 89 | 89 |
| int z = 21 | 21 |
| static int a = 60 | 60 |
Example in C++ Editor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a; // variable declaration.
a = (4 / 3) + 2; // constant expression
cout << "The value of a is: " << a; // displaying the value of a.
return 0;
}
Output
The value of a is: 3
2.) Integral Expression in C++
An integral expression is a type of expression in C++ that helps to produce the integer as output after doing all the implicit and explicit conversions.
Example of integral expression in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a; // variable declaration.
int b; // variable declaration
int c; // variable declaration
a=8;
b=9;
c = a + b;
cout << "\nValue of c is: " << c; // displaying the value of c.
return 0;
}
Output
Value of c is:17
3.) Float Expression in C++
Float expressions produce floating point values as an output of a program after doing all the explicit and implicit conversions.
Example of float expression in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
float a = 8.9; // variable initialization
float b = 5.6; // variable initialization
float c; // variable declaration
c = a + b;
cout << "The value of c is: " << c << endl; // displaying the value of c.
return 0;
}
Output
The value of c is:14.5
4.) Pointer Expression in C++
This particular pointer expression in C++ produces an address value as an output of the program.
Example of pointer expression in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int X[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}; // array initialization
int *ptr; // pointer declaration
ptr = X; // assigning the base address of the array to the pointer ptr
ptr = ptr + 1; // incrementing the value of the pointer
cout << "Value of the second element of an array: " << *ptr << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
value of the second element of an array: 2
5.) Relational Expression in C++
This Relational expression produces a particular type of value that can be either true or false which is also known as a boolean expression. If any arithmetic expressions are used on both sides of the Relational operator then the arithmetical expression will evaluate first then it will compare the results.
Example of relational expression in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int X = 45; // variable declaration
int Y = 78; // variable declaration
bool Z = X > Y; // relational expression
cout << "The value of Z is: " << Z << endl; // displaying the value of Z.
return 0;
}
Output
The value of Z is : 0
6.) Logical Expression in C++
Logical expression in C++ combines two or more relational expressions to produce a Boolean type of value.
Example of logical expression in C++ Online Compiler
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 2;
int y = 7;
int z = 4;
cout << ((x > y) || (x > z));
return 0;
}
Output
0
7.) Bitwise Expression in C++
Bitwise expressions are used to manipulate data at a bit level for shifting it to bits.
Example of bitwise expression in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int A = 5; // variable declaration
cout << (A >> 1) << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
2
8.) Special assignment Expression in C++
Special assignments in C++ can be classified depending on the value of the variable that is assigned
- Chained assignment expressions- in chained assignment expression assigns the same values more than once by using only one statement
Example-1
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x; // variable declaration
int y; // variable declaration
x = y = 80; // chained assignment
cout << "Values of 'x' and 'y' are: " << x << "," << y << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Values of 'x' and 'y' are : 80,80
- Embedded assignment expressions- In this embedded assignment expression one expression is enclosed within another assignment expressions
Example-2
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x; // variable declaration
int y; // variable declaration
x = 10 + (y = 90); // embedded assignment expression
cout << "Value of 'x' is " << x << endl;
return 0;
}
Output
Values of 'x' is 100
9.) Compound assignment expressions-
This particular assignment operator combines the assignment operator and binary operator.
Example of compound assignment expressions in C++ Online Compiler
#include <iostream>
#include
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int x = 10; // variable declaration
x += 10; // compound assignment
cout << "The value of x is: " << x << endl; // displaying the value of x.
return 0;
}
Output
The value of x is: 20
Summary
This article contains what an expression is in the C++ programming language, including different types of expressions in the C++ language with examples. With these expressions, you can make your C++ programming more efficient and concise, which can be beneficial when obtaining a C++ certification. We hope you have enjoyed learning about expressions in C++ programming.
React.js is powering apps like Netflix and Instagram. Don’t miss out—join our React JS online course and build world-class projects!










