20
FebVariables in C++ Programming
Variables in C++: An Overview
Are you curious about usingvariables in C++? Using the right variables can not only make the code easier to read but also help optimize your program. If you're looking to deepen your understanding of variables and enhance your C++ programming skills, consider enrolling in C++ Online Course Free.In this article, we'll explore all the aspects of a variable. By utilizing the insights gained from C++ for beginners, you will be able to create powerful programs that efficiently utilize memory resources.
What are Variables in C++?
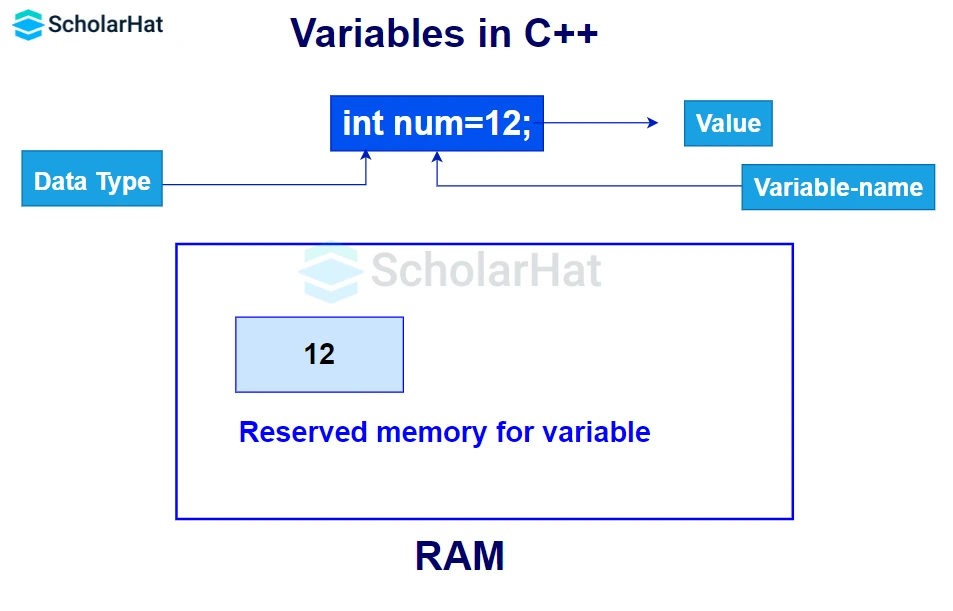
A variable is a named storage location of data in memory. Data types of variables can be int, float, boolean, char, and double.
Read More - C++ Interview Questions Interview Questions for Freshers
How to Declare a Variable?
Syntax
type variableName;
Example
float f;
Here we can see that a float type variable f is created. This means that a memory location of name f which can store floating value is being created in the memory.
You can assign the value to the variable f after a declaration like this:
f=15.7;
The variables of the same type can be declared in a single line like this:
Syntax
type var1, var2, ... varn;
Example
int a, b, c;
You can also declare a variable by assigning values to it in the following way:
int a=10,b=20;//declaring 2 variable of integer type
float f=20.8;
char c='A';Initialization of Variables in C++
This can be done in two ways:- Initialization at the time of declaration
int a=10; float f=20.8; char c='A'; - Initialization after the declaration
int a, b, c; a = 55; b = 10; c = a - b;
If we don't assign the value at the time of declaration, the garbage value is assigned by the compiler
What are the rules for naming a variable?
In C++ programming language, there are rules for defining variables, which are as follows:- Name can consist of
alphabets(both uppercase and lowercase),digits, andunderscore(_). - The first character must be either an
alphabetor anunderscore. - Variable names are case sensitive, i.e.,
numandNumare two different variable names. - No
white spacesand special characters like!,*, must be there in the variable names. - A
keywordcannot be your variable name. - The type of the declared variable cannot be changed after declaration.
Operations that can be performed on variables
- Assigning the value of one variable to another variable
Example in C++ Online Editor
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 15;
int b = 20;
a = b; // Assign the value of 'b' to 'a'
cout << a << endl;
return 0;
}
Here we first declared a and b with values. Then we assigned the value of b to a.
Output
20
- Declaring multiple variables and printing them
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int x = 5, y = 6, z = 50;
cout << x << "\t" << y << "\t" << z << endl;
return 0;
}
Here we have declared 3 int type variables in a single line separated by commas. In the cout function \t is used for giving spacing between 2 values in the same line.
Output
5 6 50
- Addition of two variables
Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a = 5;
int b = 10;
int sum = a + b;
cout << sum;
return 0;
}
Here we are adding two integer-type variables and getting the result stored in the sum variable.
Output
15
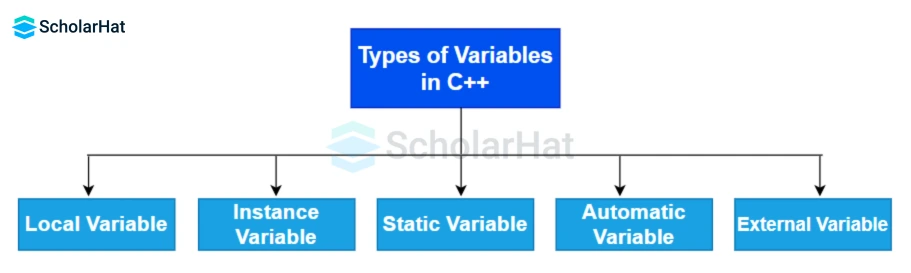
Types of Variables in C++
- Local Variable
- Instance Variable
- Static Variable
- Automatic Variable
- External Variable
- Local Variable in C++
Local variables are declared and initialized at the start of a function or block and allocated memory inside that execution scope. The statements only inside that function can access that local variable. Such variables get destroyed when the control exits from the function.Example in C++ Compiler
#include <iostream>
void local();
int main() {
int a = 22, b = 44;
local();
std::cout << "Values in the main() function a = " << a << " and b = " << b << std::endl;
return 0;
}
void local() {
int a = 50, b = 80;
std::cout << "Values in the local() function a = " << a << " and b = " << b << std::endl;
}
In the above code, there are two functions, main() and local(). The variables a and b are local variables declared inside each function with different values. The value of a and b is restricted to the function in which it is declared.
Output
Values in the local() function a = 50 and b = 80
Values in the main() function a = 22 and b = 44
- Instance Variable in C++
Instance variables are non-static variables declared in a class outside constructors, methods, and other blocks. Their memory is allocated when the object of that class in which they are declared is created and destroyed when the object is destroyed. Their initialization is not compulsory while declaring, by default, they will have garbage values. Every object of the class gets a separate copy of its instance variables. The scope of the instance variable is controlled by the access specifiers.Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
// instance variables
int roll_no;
string name;
float marks;
};
int main() {
Student obj; //object of Student class
return 0;
} You will understand instance variables in a better way while learning Object Oriented Programming (OOPs) Concepts in C++
- Static Variable in C++
These are similar to instance variables but common to every object of the class. There is only a single copy of static variables per class and static variables are declared with a static keyword. Their memory gets allocated at the start of the program and gets destroyed at the termination of the program. Their initialization is compulsory and it is done outside the class. by default int variable will have a 0 value, boolean will have a false value.Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
class Student {
public:
// static variable
static float passing_marks;
};
float Student::passing_marks = 21;
int main() {
Student obj; //object of Student class
return 0;
}
- Automatic Variable in C++
All the local variables are automatic variables by default. They are also known as auto variables.You will get to know the automatic variable in detail in the section, Storage Classes in C++.
Example in C++ Editor
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int x = 10; // local variable (also automatic)
auto y = 20; // automatic variable
return 0;
}
- External Variable in C++
External or global variables are declared using the extern keyword. You can declare an external variable any number of times but, the value can be assigned only once. Their default value is 0 or null.External variables specify an external linkage and so such variables are not allocated any memory. The initialization must be done globally and not within any function or block. If an external variable is not initialized anywhere in the program, the compiler will show an error.
Read more: Storage Classes in C++: Types of Storage Classes with Examples
Example
#include <iostream>
extern int a; // Declaration of the global variable 'a'
int main() {
std::cout << a << std::endl; // Display the value of the global variable 'a'
return 0;
}
int a; // Definition of the global variable 'a'
Summary
Becoming familiar with variables in C++ is essential for creating successful programming solutions. Understanding how to declare and use a variable correctly will help developers structure their code correctly. Experimenting with different techniques and researching the different types of variables can also give valuable insight into how each type of variable behaves. Take the time to practice and understand variables in C++, and consider pursuing a C++ Certification to demonstrate your skills to potential employers.React.js experts are landing ₹20–30 LPA roles while others struggle. Upgrade your skills with our React JS Online Training and secure your future.










