09
MarC# Attributes
C# Attributes are declarative tags to add metadata to your code. It plays a crucial role in enhancing code readability, providing metadata, and enabling runtime behaviors. You can use attributes in C# to tell the system how to handle parts of your code without changing the actual logic.
What are C# Attributes?
Attributes in C# are declarative tags that add metadata (information about the behavior or usage) to program elements like classes, methods, properties, assemblies, and more. They are like special notes you can attach to things like classes, methods, or properties. These attributes in C# give extra information that can change how the code behaves or help tools, and the compiler understand more about your code.
Purpose and Role of Attributes in C#
- Attributes in C# add extra information (metadata) to your code without changing how it works.
- Attributes are added to the code by using a declarative tag that is placed using square brackets ([ ]) on top of the required code element.
- They help describe parts of your code like classes or methods for better understanding.
- Attributes allow the compiler or programs to react differently based on this extra information.
- You can use attributes in C# to mark things like obsolete methods or control how data is handled.
- The main role of attributes in C# is to give useful details that help tools and programs work smarter with your code.
Properties of C# Attributes
Here are the properties of attributes in C#:
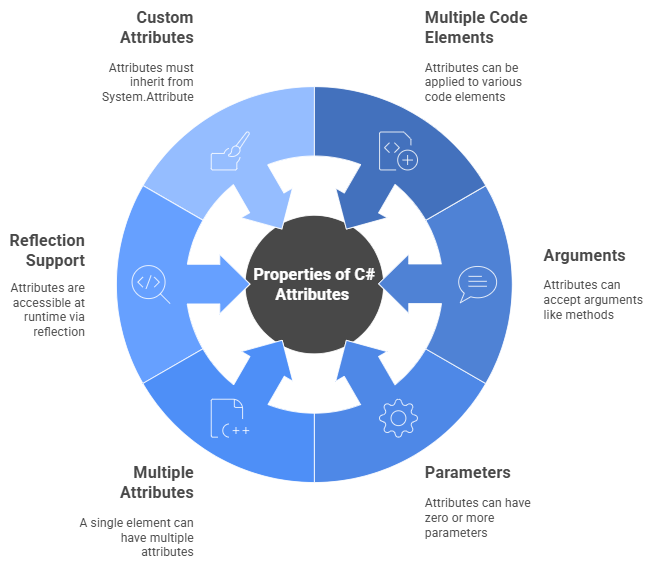
1. Multiple Code Elements Can Have Attributes
- That include classes, methods, properties, assemblies, etc.
2. Attributes Can Have Arguments
- Like methods, attributes can accept arguments.
- These arguments are passed to the attribute's constructor.
3. Attributes Can Have Zero or More Parameters
- No parameters (e.g., [Serializable]).
- One or more positional or named parameters.
4. Multiple Attributes
- A single code element can have multiple attributes.
5. Reflection Support
- Attributes Are Accessible at Runtime via Reflection.
- The .NET Reflection API can be used to retrieve attribute metadata at runtime.
- All attributes must inherit from the System.Attribute base class.
Attribute Targets in C#
Default vs. Explicit Targeting
Default Targeting: If you place an attribute just before a code element, C# applies it to that element.
csharp[Obsolete]
public void OldMethod() { }
csharp[return: Obsolete("Avoid using this return value")]
public int GetValue() => 42;
List of Attribute Target Values:
| Target Value | Applies To |
| assembly | The entire assembly |
| module | The current assembly module |
| field | A class or struct field |
| event | An event |
| method | A method or property accessors (get, set) |
| param | Method parameters or set accessor parameters |
| property | A property |
| return | A method’s or property accessor’s return value |
| type | A struct, class, interface, enum, or delegate |
Applying Attributes in C#
Attributes in C# can be applied to many code elements and can also accept parameters to provide more detailed descriptions. These attributes are not just decorations—they tell the compiler or runtime how to treat that code differently, depending on the purpose of the attribute.
Syntax of Applying an Attribute
Let's understand Attributes in C# syntax:
[AttributeName]
public class MyClass
{
// Your code here
}If the attribute takes parameters (like a warning message), you pass them inside the brackets:
[Obsolete("This method is outdated. Use NewMethod instead.")]
public void OldMethod()
{
// Code
}Examples of applying built-in Attributes
1. [Obsolete] attribute warns the developer not to use a method or class anymore.
[Obsolete("Use NewMethod instead.")]
public void OldMethod() { }2. [Serializable] marks a class so it can be saved to a file or sent over a network.
[Serializable]
public class Student { public string Name; }3. [DllImport] is used when calling a method from an external DLL (used in advanced interop scenarios).
[DllImport("user32.dll")]
public static extern int MessageBox(int hWnd, string text, string caption, int type);Types of C# Attributes
In C#, there are two major types of attributes, based on how they are defined and used.
- Predefined attributes
- Custom attributes
Predefined Attributes
Predefined attributes in csharp are those that are supported by the C# compiler for a particular use and are a component of the .NET Framework Class Library.
Key Characteristics:
- Already defined in the .NET base class library.
- Supported directly by the C# compiler or runtime.
- Often used for serialization, marshaling, compiler instructions, deprecation warnings, etc.
The following are basic classes for attributes.
| Attribute | Description |
| AttributeUsageAttribute | This property describes how to use an alternative attribute. |
| CLSCompliantAttribute | This property indicates whether or not a specific code element conforms to the Common Language Specification. |
| ContextStaticAttribute | This property indicates that different contexts shouldn't share a static field. |
| FlagsAttribute | The ability to utilize an enumeration as a collection of flags is indicated by the FlagsAttribute. Bitwise operators are the most typical applications for this. |
| LoaderOptimizationAttribute | In the main method, this property determines the optimization policy for the default loader. |
| NonSerializedAttribute | This property indicates that serializing the serializable class field is not recommended. |
| ObsoleteAttribute | This characteristic designates code components that are out-of-date or no longer in use. |
| SerializableAttribute | This property indicates that the serializable class's field is serializable. |
| ThreadStaticAttribute | This property shows that every thread has a different static field value. |
| DllImportAttribute | According to the unmanaged DLL, this characteristic shows that the method is a static entry point. |
Custom Attributes
The .Net Framework allows creation of custom attributes that can be used to store declarative information and can be retrieved at run-time.These are attributes that you define yourself, tailored to your application's specific metadata needs.
Key Characteristics:
- Defined by inheriting from the System.Attribute base class.
- Can include positional and named parameters.
- Useful for scenarios like: Custom validation, Code generation, Documentation tools, Unit testing frameworks. Custom logic via reflection
Creating and using custom attributes involve four steps −
- Declaring a custom attribute
- Constructing the custom attribute
- Apply the custom attribute on a target program element
- Accessing Attributes Through Reflection
Example:-
Step1:Create the Custom Attribute Class
csharp public class InfoAttribute : Attribute
{
public string Author { get; }
public string Version { get; set; }
public InfoAttribute(string author)
{
Author = author;
}
}Explanation:
- InfoAttribute inherits from System.Attribute.
- Author is a required (positional) parameter (via constructor).
- Version is a named (optional) property.
Step2: Apply the custom attribute
csharp[Info("Name", Version = "1.0")]
public class MyClass { }
Explanation:
- We apply InfoAttribute to MyClass.
- "Name" is passed as the required constructor parameter.
- Version = "1.0" sets the optional named property.
Step3: Access at runtime using reflection
csharpusing System;
using System.Reflection;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
Type type = typeof(MyClass);
// Get all attributes applied to MyClass
object[] attrs = type.GetCustomAttributes(typeof(InfoAttribute), false);
foreach (InfoAttribute attr in attrs)
{
Console.WriteLine($"Author: {attr.Author}");
Console.WriteLine($"Version: {attr.Version}");
}
}
}Explanation:
- Uses Reflection to get the attribute applied to MyClass.
- Casts it to InfoAttribute and reads its properties.
Conclusion
FAQs
- To influence runtime behavior using reflection.
- To improve code clarity and intent.
- To integrate with frameworks like ASP.NET or Entity Framework.
- To implement custom logic through custom attributes.
- [Obsolete] – Marks code as outdated.
- [Serializable] – Marks a class as serializable.
- [DllImport] – Used for interop with unmanaged code (P/Invoke).
- [NonSerialized] – Prevents a field from being serialized.
Take our Csharp skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











