13
FebUnderstanding Proxy Design Pattern
Proxy Design Pattern
Proxy Design Pattern is a key concept in software design. It enables you to control access to objects by introducing a proxy object, which acts as an intermediary. This leads to more efficient resource management and enhances security by controlling object interactions, making the system easier to comprehend and manage.
In this design patterns tutorial, we will discuss the Proxy Design Pattern, including "What is the Proxy Design Pattern?" and "When to use the Proxy Design Pattern?" We'll also explore examples of the Proxy Design Pattern in action. By 2026, 65% of enterprise tech stacks will rely on .NET Design Patterns. Stay ahead with our Free .NET Design Patterns Online Course!
What is the Proxy Design Pattern?
- The Proxy Design Pattern provides a surrogate or placeholder for another object to control access to it.
- This pattern is useful when you need to add an extra layer of security, lazy initialization, or reduce resource usage.
- The proxy acts as an intermediary, ensuring controlled access to the original object.
For example, A bank ATM acts as a proxy for interacting with your bank account. Instead of directly accessing the bank, the ATM handles transactions on your behalf.
Why do we need a Proxy Design Pattern?
1. Lazy Loading
- Proxies are primarily used for lazy loading.
- When building or initializing an object requires a significant amount of resources, the proxy postpones the creation of the actual object until it is required.
- This can contribute to better performance by eliminating wasteful resource allocation.
| Read More: Lazy Loading in Angular |
2. Access Control
- Proxies can apply access control policies.
- Proxy servers can restrict access to the real object based on particular conditions, offering security or authorization checks.
3. Protection Proxy
- Protection proxies give extra security checks to real objects, limiting access to them.
- They can verify that the client code has the proper rights before granting access to the actual object.
4. Caching
- Proxies can use caching methods to store results or resources.
- This is especially beneficial when performing repeated operations on a real object and storing prior results to save duplicate computations or data retrieving.
5. Logging and Monitoring
- Proxies provide an easy way to add logging or monitoring functionality.
- Proxies can record information, track usage, and measure performance by intercepting method calls to the real object without altering it.
Real-world Illustration of Proxy Design Pattern

- It is like having a security guard at the entrance of a high-profile building.
- Instead of everyone walking in directly, the guard checks their identity first.
- The security guard acts as a proxy, ensuring only authorized people enter.
- It helps keep the building secure by filtering out those who shouldn’t have access.
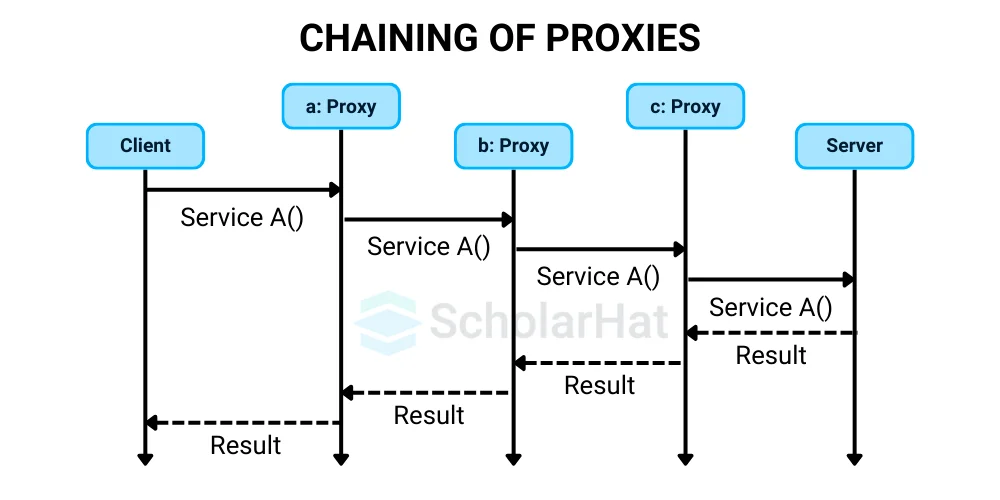
Chaining of Proxies
- In the Proxy Design Pattern, chaining proxies involves connecting them in a sequential order, with each proxy adding its own action or checks before passing the request on to the next proxy or the real object.
- It's like constructing a chain of guards, each with a specific task.
Proxy Design Pattern Basic Structure and Implementation
The structure for the implementation of the Proxy Design Pattern is given below:
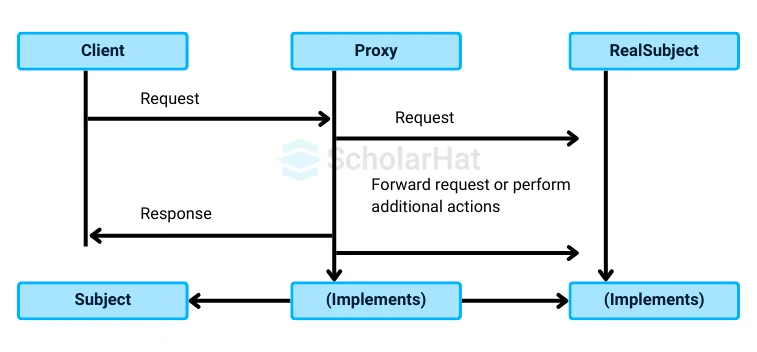
1. Subject
- This is an interface or abstract class that defines the common operations that both the real object (RealSubject) and the proxy must implement.
- It declares the methods that clients will use to interact with either the real object or the proxy.
- By defining this contract, clients can interact with either the RealSubject or Proxy without knowing which one they are interacting with.
2. RealSubject
- This class implements the Subject interface and represents the actual object that is being accessed.
- It contains the core functionality that the client wants to perform. For example, in the case of a file downloader, the RealSubject would contain the logic to download the file.
- It performs the operation requested by the client, but the client may not access this directly due to security, performance, or other constraints.
3. Proxy
- The Proxy class also implements the Subject interface but serves as an intermediary between the client and the RealSubject.
- It controls access to the RealSubject by handling requests before forwarding them to the real object or by taking additional actions like caching results, logging, or checking access permissions.
- This allows the Proxy to provide controlled or delayed access to the RealSubject, enhancing performance or enforcing security rules.
- It can also create or manage the lifecycle of the RealSubject as needed.
This design pattern helps in situations where access control, lazy initialization, or additional functionality (like caching or logging) is needed without altering the actual real object’s behavior.
Real Life Example
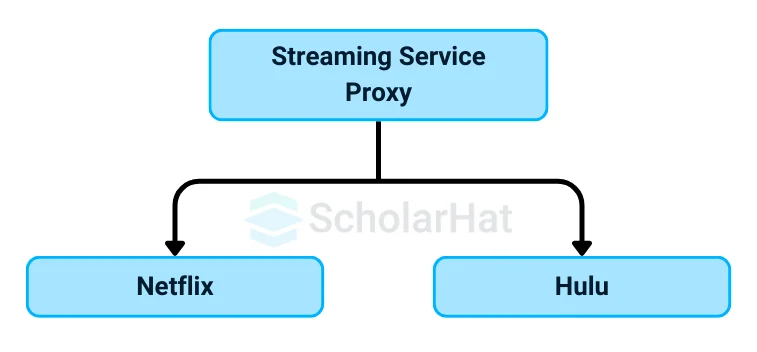
Subsystems (Online Streaming Service)
- In a digital world, you often use various streaming services like Netflix, Hulu, or Amazon Prime.
- Each service has its own content library and streaming technology.
Proxy (Streaming Service Proxy)
- It is the Streaming Service Proxy that acts as an intermediary.
- Instead of connecting directly to each streaming service, you use a single proxy to manage access to them.
Operation Flow
- Simplified Interaction: When you want to watch a show or movie, you interact with the streaming service proxy.
- Command Handling: The proxy (facade) handles requests, checks if you have the required subscription, and ensures that content is available before streaming.
- Subsystem Response: Each streaming service responds to the proxy’s requests by delivering the content. It is the proxy that ensures efficient streaming by managing access and loading content only when needed.
How the Proxy Helps
- Unified Interface: It is the Streaming Service Proxy that provides a single point of access. This means you don’t need to handle multiple streaming services separately.
- Reduced Complexity: By using the proxy, it is not necessary to interact with each streaming service’s complex interface. It simplifies content access through one management system.
- Improved Usability: The proxy makes it easier to access and manage multiple streaming services. It is the proxy that coordinates everything, enhancing your streaming experience.
Example
using System;
interface IStreamingService
{
void StreamContent(string content);
}
class Netflix : IStreamingService
{
private string content;
public Netflix(string content)
{
this.content = content;
LoadContent();
}
private void LoadContent()
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading content on Netflix: " + content);
}
public void StreamContent(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("Streaming on Netflix: " + content);
}
}
class Hulu : IStreamingService
{
private string content;
public Hulu(string content)
{
this.content = content;
LoadContent();
}
private void LoadContent()
{
Console.WriteLine("Loading content on Hulu: " + content);
}
public void StreamContent(string content)
{
Console.WriteLine("Streaming on Hulu: " + content);
}
}
class StreamingServiceProxy : IStreamingService
{
private IStreamingService realService;
private string content;
private string serviceName;
public StreamingServiceProxy(string serviceName, string content)
{
this.serviceName = serviceName;
this.content = content;
}
public void StreamContent(string content)
{
if (realService == null)
{
if (serviceName == "Netflix")
{
realService = new Netflix(content);
}
else if (serviceName == "Hulu")
{
realService = new Hulu(content);
}
}
realService.StreamContent(content);
}
}
class ProxyPatternDemo
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
IStreamingService netflixProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Netflix", "Inception");
IStreamingService huluProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Hulu", "The Handmaid's Tale");
// Content is loaded and streamed
netflixProxy.StreamContent("Inception");
// Content is streamed without reloading
netflixProxy.StreamContent("Inception");
// Content is loaded and streamed
huluProxy.StreamContent("The Handmaid's Tale");
}
}
interface StreamingService {
void streamContent(String content);
}
class Netflix implements StreamingService {
private String content;
public Netflix(String content) {
this.content = content;
loadContent();
}
private void loadContent() {
System.out.println("Loading content on Netflix: " + content);
}
@Override
public void streamContent(String content) {
System.out.println("Streaming on Netflix: " + content);
}
}
class Hulu implements StreamingService {
private String content;
public Hulu(String content) {
this.content = content;
loadContent();
}
private void loadContent() {
System.out.println("Loading content on Hulu: " + content);
}
@Override
public void streamContent(String content) {
System.out.println("Streaming on Hulu: " + content);
}
}
class StreamingServiceProxy implements StreamingService {
private StreamingService realService;
private String content;
private String serviceName;
public StreamingServiceProxy(String serviceName, String content) {
this.serviceName = serviceName;
this.content = content;
}
@Override
public void streamContent(String content) {
if (realService == null) {
if ("Netflix".equals(serviceName)) {
realService = new Netflix(content);
} else if ("Hulu".equals(serviceName)) {
realService = new Hulu(content);
}
}
realService.streamContent(content);
}
}
public class ProxyPatternDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
StreamingService netflixProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Netflix", "Inception");
StreamingService huluProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Hulu", "The Handmaid's Tale");
// Content is loaded and streamed
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception");
// Content is streamed without reloading
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception");
// Content is loaded and streamed
huluProxy.streamContent("The Handmaid's Tale");
}
}
from abc import ABC, abstractmethod
class StreamingService(ABC):
@abstractmethod
def stream_content(self, content: str):
pass
class Netflix(StreamingService):
def __init__(self, content: str):
self.content = content
self.load_content()
def load_content(self):
print(f"Loading content on Netflix: {self.content}")
def stream_content(self, content: str):
print(f"Streaming on Netflix: {content}")
class Hulu(StreamingService):
def __init__(self, content: str):
self.content = content
self.load_content()
def load_content(self):
print(f"Loading content on Hulu: {self.content}")
def stream_content(self, content: str):
print(f"Streaming on Hulu: {content}")
class StreamingServiceProxy(StreamingService):
def __init__(self, service_name: str, content: str):
self.service_name = service_name
self.content = content
self.real_service = None
def stream_content(self, content: str):
if self.real_service is None:
if self.service_name == "Netflix":
self.real_service = Netflix(content)
elif self.service_name == "Hulu":
self.real_service = Hulu(content)
self.real_service.stream_content(content)
# Client code
if __name__ == "__main__":
netflix_proxy = StreamingServiceProxy("Netflix", "Inception")
hulu_proxy = StreamingServiceProxy("Hulu", "The Handmaid's Tale")
# Content is loaded and streamed
netflix_proxy.stream_content("Inception")
# Content is streamed without reloading
netflix_proxy.stream_content("Inception")
# Content is loaded and streamed
hulu_proxy.stream_content("The Handmaid's Tale")
interface StreamingService {
streamContent(content: string): void;
}
class Netflix implements StreamingService {
private content: string;
constructor(content: string) {
this.content = content;
this.loadContent();
}
private loadContent() {
console.log(`Loading content on Netflix: ${this.content}`);
}
public streamContent(content: string) {
console.log(`Streaming on Netflix: ${content}`);
}
}
class Hulu implements StreamingService {
private content: string;
constructor(content: string) {
this.content = content;
this.loadContent();
}
private loadContent() {
console.log(`Loading content on Hulu: ${this.content}`);
}
public streamContent(content: string) {
console.log(`Streaming on Hulu: ${content}`);
}
}
class StreamingServiceProxy implements StreamingService {
private realService: StreamingService | null = null;
private content: string;
private serviceName: string;
constructor(serviceName: string, content: string) {
this.serviceName = serviceName;
this.content = content;
}
public streamContent(content: string) {
if (this.realService === null) {
if (this.serviceName === "Netflix") {
this.realService = new Netflix(content);
} else if (this.serviceName === "Hulu") {
this.realService = new Hulu(content);
}
}
this.realService.streamContent(content);
}
}
// Client code
const netflixProxy: StreamingService = new StreamingServiceProxy("Netflix", "Inception");
const huluProxy: StreamingService = new StreamingServiceProxy("Hulu", "The Handmaid's Tale");
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception"); // Content is loaded and streamed
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception"); // Content is streamed without reloading
huluProxy.streamContent("The Handmaid's Tale"); // Content is loaded and streamed
class Netflix {
constructor(content) {
this.content = content;
this.loadContent();
}
loadContent() {
console.log(`Loading content on Netflix: ${this.content}`);
}
streamContent(content) {
console.log(`Streaming on Netflix: ${content}`);
}
}
class Hulu {
constructor(content) {
this.content = content;
this.loadContent();
}
loadContent() {
console.log(`Loading content on Hulu: ${this.content}`);
}
streamContent(content) {
console.log(`Streaming on Hulu: ${content}`);
}
}
class StreamingServiceProxy {
constructor(serviceName, content) {
this.serviceName = serviceName;
this.content = content;
this.realService = null;
}
streamContent(content) {
if (this.realService === null) {
if (this.serviceName === "Netflix") {
this.realService = new Netflix(content);
} else if (this.serviceName === "Hulu") {
this.realService = new Hulu(content);
}
}
this.realService.streamContent(content);
}
}
// Client code
const netflixProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Netflix", "Inception");
const huluProxy = new StreamingServiceProxy("Hulu", "The Handmaid's Tale");
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception"); // Content is loaded and streamed
netflixProxy.streamContent("Inception"); // Content is streamed without reloading
huluProxy.streamContent("The Handmaid's Tale"); // Content is loaded and streamed
Explanation
- This program illustrates the Proxy Design Pattern for streaming services.
- The StreamingService interface defines the method streamContent.
- Netflix and Hulu are concrete implementations that load and stream content.
- StreamingServiceProxy manages the instantiation of these services and ensures content is only loaded and streamed when needed.
- This approach delays the creation of the real service objects until their methods are actually invoked, optimizing resource use and simplifying access control.
Applications of Proxy Design Pattern
Use the Proxy pattern when you need a substitute or placeholder to control access to an object.
1. Access Control
- It is ideal for managing access to an object, especially when direct access needs to be restricted.
- For example, it is used to limit access to a resource-intensive object or provide additional functionality before accessing the real object.
2. Lazy Initialization
- It is useful for delaying the creation of a resource until it is actually needed.
- This helps manage performance and resource usage, especially with large or expensive objects.
3. Logging and Monitoring
- It is beneficial for adding extra functionality like logging or monitoring access to an object.
- This helps track how an object is used and can assist with debugging.
4. Remote Access
- It is used to represent objects that are on a different machine or process.
- The proxy handles the communication between the client and the real object, simplifying network or inter-process communication.
Benefits of Proxy Design Pattern
- It controls access to the real object by managing security or access control layers.
- It improves performance by loading resource-intensive objects only when they are needed, which reduces unnecessary memory or CPU usage.
- It adds extra functionality like logging, caching, or monitoring without changing the original object.
- It simplifies communication with remote objects, making complex interactions easier to handle.
When to use the Proxy Design Pattern
- It is used when direct access to an object is costly or needs control.
- It is ideal when you need to add a security layer or control access to certain objects.
- When the real object is resource-intensive, a proxy can delay or limit its creation until necessary.
- It is useful when interacting with remote objects to handle communication complexities and improve performance.
When not to use the Proxy Design Pattern
- It is unnecessary to use the Proxy pattern when direct access to the object is simple and efficient.
- In small applications, where performance and access control aren't concerns, adding a proxy can create unwanted complexity.
- It might violate the Single Responsibility Principle if the proxy is doing more than controlling access.
- If the proxy adds more overhead than benefits, it is likely over-engineering and should be avoided for straightforward scenarios.
Relationship with Other Patterns
- Decorator Pattern: The Proxy pattern is similar to the Decorator pattern in that both control access to objects, but the Proxy focuses on managing access while the Decorator adds additional functionality.
- Adapter Pattern: It is different from the Adapter pattern, as the Proxy controls object access, whereas the Adapter changes interfaces to ensure compatibility.
- Singleton Pattern: The Proxy pattern can be combined with the Singleton pattern to ensure a single proxy controls access to a particular resource or object.
- Facade Pattern: While the Facade provides a simplified interface to a system, the Proxy manages the lifecycle and access control of individual objects.
Summary
FAQs
- Virtual Proxy: Manages resource-intensive objects, producing them only as needed.
- Protection Proxy: Limits access to sensitive items by implementing security measures.
- Remote Proxy: Manages communication between items on various machines or networks.
- Caching Proxy: Stores results to reduce redundant operations and improve performance.
Take our Designpatterns skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.










