06
MarEntity Framework Architecture: A Complete In-Depth Guide
Entity Framework (EF) is Microsoft’s premier Object Relational Mapper (ORM) for .NET developers. It bridges the gap between relational databases and object-oriented programming by allowing developers to interact with databases using .NET objects. Instead of writing raw SQL queries, EF provides a higher-level abstraction that simplifies data access, improves productivity, and reduces boilerplate code. At the heart of EF lies its architecture, which ensures seamless interaction between applications and databases.
What is Entity Framework?
With EF, developers can:
- Perform CRUD operations without writing raw SQL.
- Use LINQ to Entities for querying data.
- Work with different database providers (SQL Server, Oracle, MySQL, PostgreSQL, etc.).
- Maintain a strongly-typed model that improves readability and reduces runtime errors.
- But to understand how all of this is possible, let’s analyze EF’s architecture.
Overview of Entity Framework Architecture
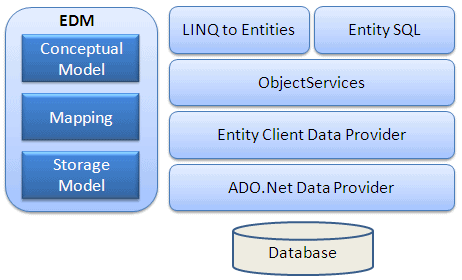
- Conceptual Model (CSDL)
- Mapping Layer (MSL)
- Storage Model (SSDL)
- Entity Data Model (EDM)
- Entity Client Data Provider
- Object Services Layer
- LINQ to Entities
- Entity SQL
- ADO.NET Data Provider
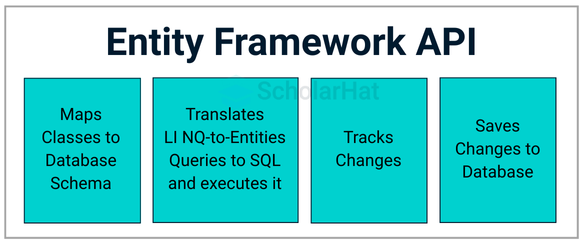
Core Components of Entity Framework Architecture
1. Conceptual Model (CSDL)
2. Storage Model (SSDL)
3. Mapping Layer (MSL)
4. Entity Data Model (EDM)
- CSDL (Conceptual Schema)
- SSDL (Storage Schema)
- MSL (Mapping Schema)
5. Entity Client Data Provider
- Parses queries.
- Converts them into a format that the EF runtime understands.
- Passes them to the lower data provider layer.
- Think of it as a translator for queries.
6. Object Services Layer
- Converts database rows into entity objects.
- Tracks changes made to objects.
- Performs identity resolution to avoid duplicate objects.
- This is the layer that developers interact with the most when working with entities.
7. LINQ to Entities
Example:
var students = context.Students.Where(s => s.Name == "John").ToList();8. Entity SQL (ESQL)
Example:
SELECT VALUE s FROM Students AS s WHERE s.Name = 'John'9. ADO.NET Data Provider
- It could be SQL Server, Oracle, or another database provider.
- Handles connections, commands, and transactions.
- This is the lowest-level layer that directly communicates with the database.
Working of Entity Framework Architecture
The Entity Framework (EF) architecture simplifies data interaction between a .NET application and a database using an Object-Relational Mapping (ORM) approach. lets see how it works
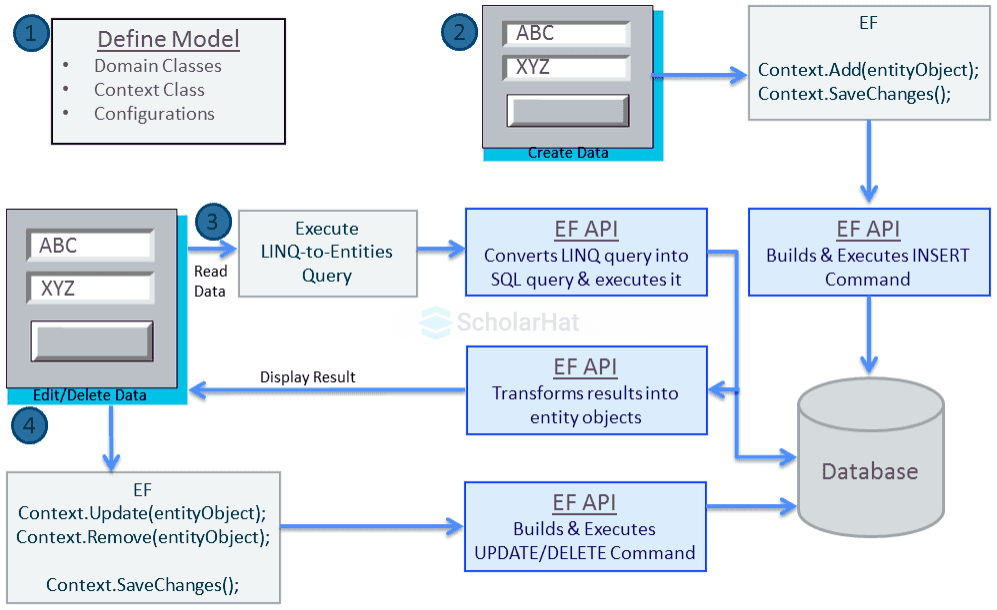
Step 1: Defining the Model
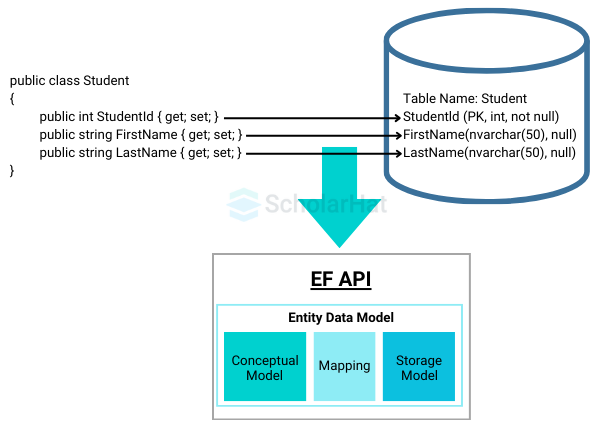
The process starts with defining the data model, which includes domain classes (e.g., the Student class with properties like StudentId, FirstName, and LastName) and a context class (e.g., DbContext). These represent the application’s conceptual structure.
For example, the Student class mirrors the "Student" table, with StudentId as the primary key (int, not null) and FirstName/LastName as nvarchar(50, null) columns.
Step 2: Mapping Classes to Database Schema
The EF API maps these domain classes to the database schema. This involves linking the Student class to the "Student" table and its properties to the corresponding columns. This mapping is part of the EDM, consisting of the Conceptual Model (entities), Storage Model (database schema), and Mapping layer. See the diagram the blue arrow from the Student class to the "EF API" box with EDM components.)
Step 3: Creating and Managing Data
Developers create data objects (e.g., new Student instances like "ABC" or "XYZ") and add them to the context using Context.Add(entityObject) followed by Context.SaveChanges(). The EF API builds and executes INSERT commands, storing the data in the database via the EDM. See the diagram "Create Data" flow with Context.Add(entityObject) and Context.SaveChanges() leading to "Builds & Executes INSERT Command".)
Step 4: Executing Queries
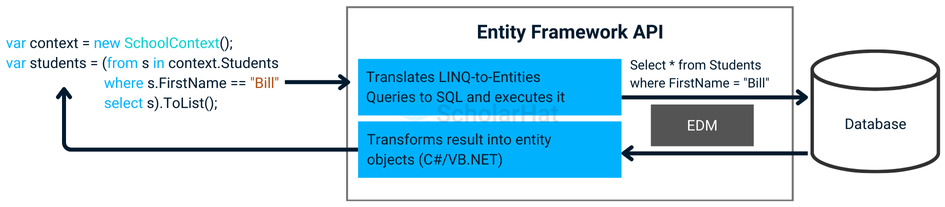
To read data, developers use LINQ-to-Entities queries
(e.g., var students = (from s in context.Students where s.FirstName == "Bill" select s).ToList();)
The EF API translates these into SQL
(e.g., SELECT * FROM Students WHERE FirstName = 'Bill')executes them, and transforms results into entity objects. LINQ query flow to "Translates LINQ-to-Entities Queries to SQL" and "Transforms results into entity objects".)
Step 5: Editing and Deleting Data
For updates or deletions, developers modify or remove entity objects
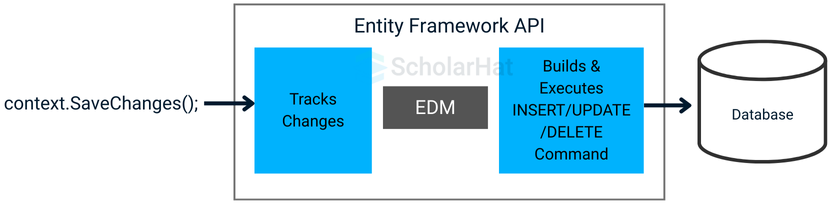
(e.g., Context.Update(entityObject) or Context.Remove(entityObject)) and call Context.SaveChanges(). Step 6: Tracking Changes
The EF API monitors changes to entity objects in memory. When SaveChanges() is called, it generates the appropriate SQL commands to update the database.
Step 7: Interaction with the Database
The EDM and EF API ensure all operations are executed via the database provider, handling low-level communication.
This architecture streamlines database operations, letting developers focus on logic while EF manages the data layer efficiently. Let me know if you need further clarification!
Advantages of Entity Framework Architecture
- Abstraction: Developers work with objects instead of writing raw SQL.
- Productivity: Eliminates repetitive CRUD operations.
- Maintainability: Strongly-typed queries reduce runtime errors.
- Portability: Works with multiple databases.
- Change Tracking: EF automatically tracks changes to entities.
- Scalability: Can be used in small to enterprise-level applications.
Different Approaches in Entity Framework
1. Database-First Approach
2. Model-First Approach
3. Code-First Approach
Conclusion
Entity Framework (EF) architecture provides a powerful and flexible framework for developers to work with data without worrying about the complexities of database interactions. In short, understanding EF architecture empowers developers to build robust, data-driven .NET applications efficiently while future-proofing their projects for evolving business needs. Want to master ASP.NET Core and Entity Framework but don’t know where to begin? Enroll in our ASP.NET Core Certification Training and build job-ready skills today!
FAQs
Take our Entityframework skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.