13
MarUnderstanding Inheritance in Entity Framework
Inheritance in Entity Framework is a way to bring the power of object-oriented programming into your database world. In simple terms, it lets you map a class hierarchy (like base classes and derived classes) from C# into your relational database tables. Now, since relational databases don’t naturally understand inheritance the way object-oriented languages do, Entity Framework steps in with smart strategies to make it work.
Whether it’s Table-per-Hierarchy (TPH), Table-per-Type (TPT), or Table-per-Concrete Class (TPC), EF gives you flexibility to design your data model in a way that keeps both developers and the database happy. This not only makes your code cleaner and more reusable but also ensures that your database structure stays organized and efficient. In this Entity Framework tutorial we will understand what is inheritance.
What is Inheritance in Entity Framework?
Inheritance in Entity Framework is the process of mapping object-oriented class hierarchies (base and derived classes) to relational database tables using specific mapping strategies such as Table-per-Hierarchy (TPH), Table-per-Type (TPT), or Table-per-Concrete Class (TPC).
Types of inheritance in Entity Framework
Entity Framework supports three types of inheritances as given below-
Table-per-Hierarchy (TPH)
The TPH inheritance states that all entities, in a hierarchy of entities, are mapped to a single table in storage schema. It means, there is only one table in database and different Entity types in Entity model that inherits from a base Entity are mapped to that table.
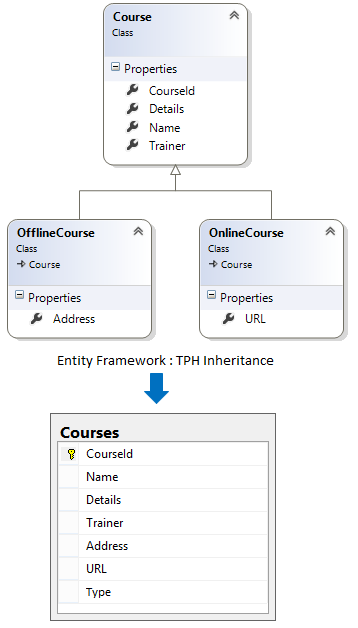
C# Implementation Code for TPH
public class Course
{
[Key]
public int CourseId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Details { get; set; }
public string Trainer { get; set; }
}
public class OnlineCourse : Course
{
public string URL { get; set; }
}
public class OfflineCourse : Course
{
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Entity Framework Code First Mapping for TPH
modelBuilder.Entity<Course>()
.Map<OnlineCourse >(m => m.Requires("Type").HasValue("OnlineCourse "))
.Map<OfflineCourse >(m => m.Requires("Type").HasValue("OfflineCourse "));
Note
By default, Entity Framework supports TPH inheritance, if you don't define any mapping details for your inheritance hierarchy.
Table-per-Concrete-Type (TPC)
The TPC inheritance states that each concrete class (a class which can be instantiated) in the hierarchy of entities is mapped to a separate table in storage schema. It means, there is separate table in database to maintain data for each derived entity type.
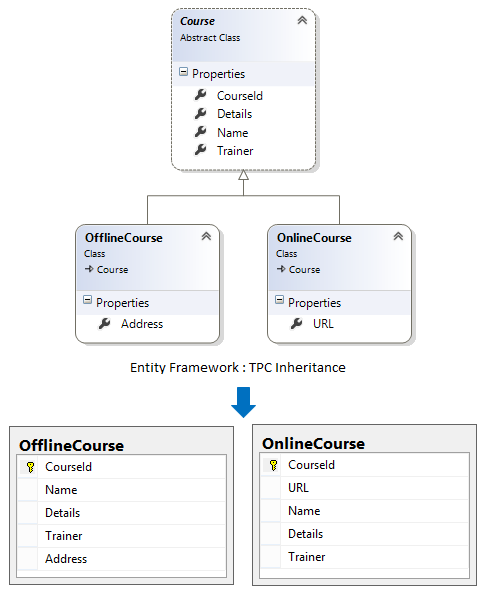
C# Implementation Code for TPC
public abstract class Course //abstract class
{
[Key]
public int CourseId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Details { get; set; }
public string Trainer { get; set; }
}
public class OnlineCourse : Course //concrete class
{
public string URL { get; set; }
}
public class OfflineCourse : Course //concrete class
{
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Entity Framework Code First Mapping for TPC
modelBuilder.Entity<OnlineCourse >().Map(m =>
{
m.MapInheritedProperties();
m.ToTable("OnlineCourse ");
});
modelBuilder.Entity<OfflineCourse >().Map(m =>
{
m.MapInheritedProperties();
m.ToTable("OfflineCourse ");
});
Note
The TPC inheritance is commonly used to inherit basic features.
Table-per-Type (TPT)
The TPT inheritance states that each entity in the hierarchy of entities is mapped to a separate table in storage schema. It means, there is separate table in database to maintain data for each Entity Type.
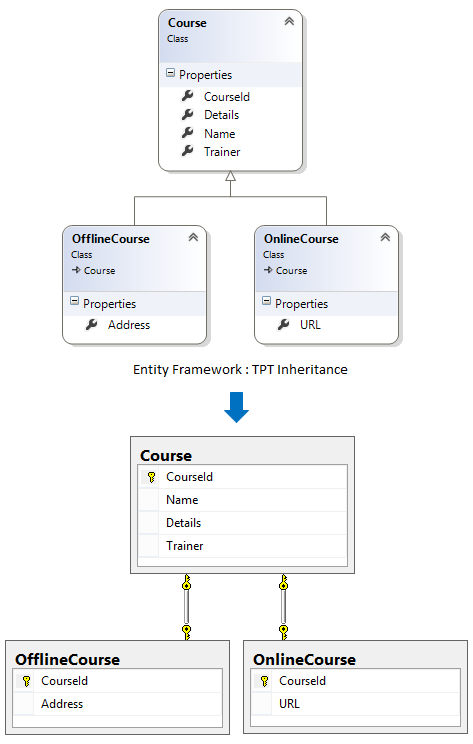
C# Implementation Code for TPT
public class Course
{
[Key]
public int CourseId { get; set; }
public string Name { get; set; }
public string Details { get; set; }
public string Trainer { get; set; }
}
public class OnlineCourse : Course
{
public string URL { get; set; }
}
public class OfflineCourse : Course
{
public string Address { get; set; }
}
Entity Framework Code First Mapping for TPT
modelBuilder.Entity<Course>().ToTable("Course");
modelBuilder.Entity<OnlineCourse >().ToTable("OnlineCourse ");
modelBuilder.Entity<OfflineCourse >().ToTable("OfflineCourse ");
Note
TPH inheritance patterns generally deliver better performance in the Entity Framework than TPT inheritance patterns, because TPT patterns can result in complex join queries.
Conclusion
Inheritance in Entity Framework provides a seamless way to align object-oriented programming concepts with relational databases. By supporting strategies like TPH, TPT, and TPC, it allows developers to choose the best approach for performance, maintainability, and scalability. This not only simplifies code reuse and data modeling but also ensures that applications remain both efficient and flexible when handling complex data structures. Also if you are planning to prepare for interview then go through these Top 50 Entity Framework Interview Questions & Answers.
I hope you will enjoy the tips while programming with Entity Framework. I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Your valuable feedback, question, or comments about this article are always welcome.
FAQs
Take our Entityframework skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.








