20
FebJava Arrays: Single Dimensional and Multi-Dimensional Arrays
Java Arrays: An Overview
Arrays in Java are one of the most versatile and powerful data structures in Java. In this Java tutorial, we'll discuss in detail, Java Arrays, types of arrays in Java, implementation of arrays in Java, etc. Basic Java skills can boost your pay to ₹10 LPA. Don’t wait—Enroll now in our Free Java Certification Course to start earning big!
What is an Array?
An array is a data structure used to store the elements of a particular type. For example, an integer array will hold only the value of any integer, but a character array will hold only the characters. The structure of an array is linear and holds similar elements in "contiguous memory addresses". In Java, not only array but also exception handling is essential to manage and deal with unexpected errors that may occur during the execution of a program which helps the execution process.
Pros and Cons of Using Array
Advantages of using Java arrays
- Arrays help to increase code optimization.
- It helps in ordering and indexing data structures to store a particular type of element.
- It can also store variables and objects of class in Java.
- Every element of an array is held in a definite memory location.
Disadvantages of using Java arrays
- An array can only hold the same type of elements.
- Removing and adding elements is very tough.
Types of Array in Java
There are two types of arrays in Java:
- Single-dimensional array in Java
- Multi-dimensional array in Java
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions
1. Single-Dimensional Array in Java
- A 1D Array in Java is a linear array that allows the storage of multiple values of the same data type.
- It's a collection of data that stores elements of the same type in a sequentially allocated space in memory.
- Single-dimensional arrays can be utilized to store both simple and complex data types, anything from strings, integers, and booleans to custom-made classes depending on the user's requirements.
- In memory, a one or single-dimensional array holds the data in a linear list.
- The index of the memory runs from the array size of 0 to -1.
- Single-Dimensional Arrays are initialized just like regular variables, but instead of assigning a single value the programmers can pass several values separated by commas or define an array with static size.
- 1D Arrays are one of the handy tools contained within Java.
- They are useful for organizing data quickly and efficiently as well as giving us access to stored data using looping structures.
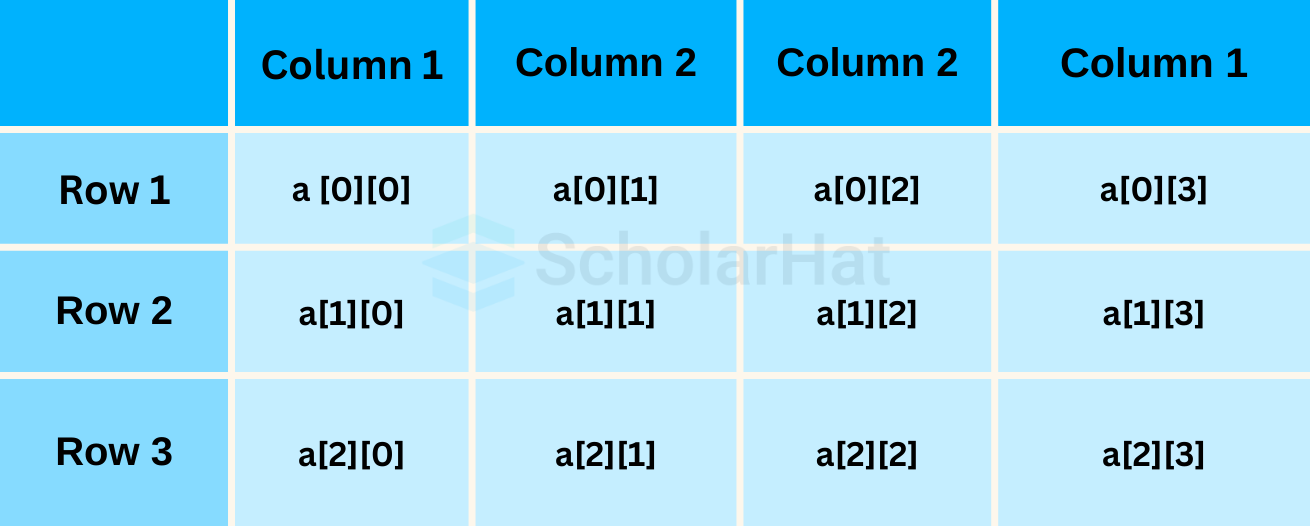
2. Multi-Dimensional Array in Java
- Multi-Dimensional Array in Java is an array of arrays, i.e. it is an array object that has multiple dimensions.
- Multi-dimensional arrays are useful when dealing with a large amount of data since they give the ability to store and access data from a single variable but with multiple levels of hierarchy.
- This multi-dimensional array can be expanded to a certain number of dimensions such as two dimensions, three dimensions, etc.
- Multi-dimensional arrays in Java can hold any type of item, i.e. two-dimensional arrays can hold int values or objects such as strings and objects.
- Multi-dimensional arrays also have several methods available to help search and arrange the data within the array, making them very flexible and efficient when dealing with complex tasks.
How to Declare and Initialize an Array in Java?
The syntax for one-dimensional array in Java
arrayName = new DataTye[length 1][length 2]....[length N];(OR)DataType[1st Dimension][2nd Dimension]....[Nth Dimension] arrayName = new DataTye[length 1][length 2]....[length N];Example
//declaration
int iArray1[] = new int[4];
//initialization
iArray1[0] = 32;
iArray1[1] = 13;
iArray1[2] = 56;
iArray1[3] = 78;In this example, a size-4 integer array named "iArray1" is declared and initialized with predetermined values, with each element's index denoting a different integer value.
The syntax for multi-dimensional array in Java
Datatype [][]Array_Name = new Datatype[row_size][col_size(optional)]; (OR)
Datatype Array_Name[] = [{Value separated by comma},{Value separated by comma},....}];
Example
//declaration
int matrix[] = new int[2][2];
//initialization
matrix[0][0] = 1;
matrix[0][1] = 2;
matrix[1][0] = 3;
matrix[1][1] = 4;This example declares and initializes a 2x2 integer matrix (a 2-dimensional array), where each member at a given row and column index corresponds to a different integer value.
Read More - Java Web Developer Salary
Accessing Elements of Array in Java
There are three types of Accessing Element:
- Direct access to an element
- Accessing elements using a loop
- Accessing elements using for-each loop
Read More: Loops in Java
Direct access to an element
This access method gives the user the authority to access the exact element directly of an array by using an index number.
Syntax
Array_Name[index]Example
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int[] a = {25, 50, 75, 100};
System.out.println(a[0]);
System.out.println(a[1]);
System.out.println(a[2]);
System.out.println(a[3]);
}
}
Output
25
50
75
100
The value stored at index 1 of the array is retrieved in this example by directly accessing the second member of the array 'iArray' using the index number.
Accessing elements using for loop
In this access method, any particular array can be accessed by using iteration statements such as,for loop. We will see this demonstration in our Java Online Editor.
Example
class MainDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] numbers = {1, 4, 5, 8, 7};
// using for loop go through the array
for(int i = 0; i < numbers.length; i++) {
System.out.println(age[i]);
}
}
}Output
1
4
5
8
7
This Java program creates the integer array "numbers" with predetermined values and then uses a "for" loop to traverse through the array, printing each element one at a time. However, there is a mistake in the code; to print the contents of the 'numbers' array, the correct syntax is 'System.out.println(age[i]);' rather than 'System.out.println(numbers[i]);'.
Accessing elements using for-each loop
In this method, the for-each loop can also be used for accessing the elements of the array
Example
class MainDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// create an array
int[] numbers = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8};
// using for-each loop to go through each element
for(int i : numbers) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}This Java program populates the integer array "numbers" with particular values, then iterates through each element of the array using a for-each loop, writing each element on a separate line.
Output
1
2
4
6
8
Assigning an Array Reference to Another Array
An array can be used as a reference type of variable and can be used to assign an already existing array.
Example
class MainDemo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// create an array
int[] arr = {1, 2, 4, 6, 8};
int[] arr1;
arr1 = arr; //assigning arr array reference to arr1
System.out.println(arr1[3]);
}
}This Java code creates the integer array 'arr' with the specified values. For 'arr' and 'arr1' to point to the same array in memory, another integer array 'arr' is declared and given the reference of 'arr'. As a result, 'arr1[3]' outputs the value 6, which is located at index 3 of the shared array.
Output
6Read More:
Summary
This article provides an insightful overview of the definition, pros, and cons of arrays, making it a valuable resource for individuals. Moreover, it thoroughly covers the concepts of single-dimensional and multi-dimensional arrays in Java, further enhancing your understanding of array manipulation.
Full-stack Java developer earn ₹25–40 LPA, way above coders. Soar high—Enroll now in our Java Full Stack Developer Course!
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.












