09
MarWhat is Class in Java? - Objects and Classes in Java {Explained}
Java Class and Object
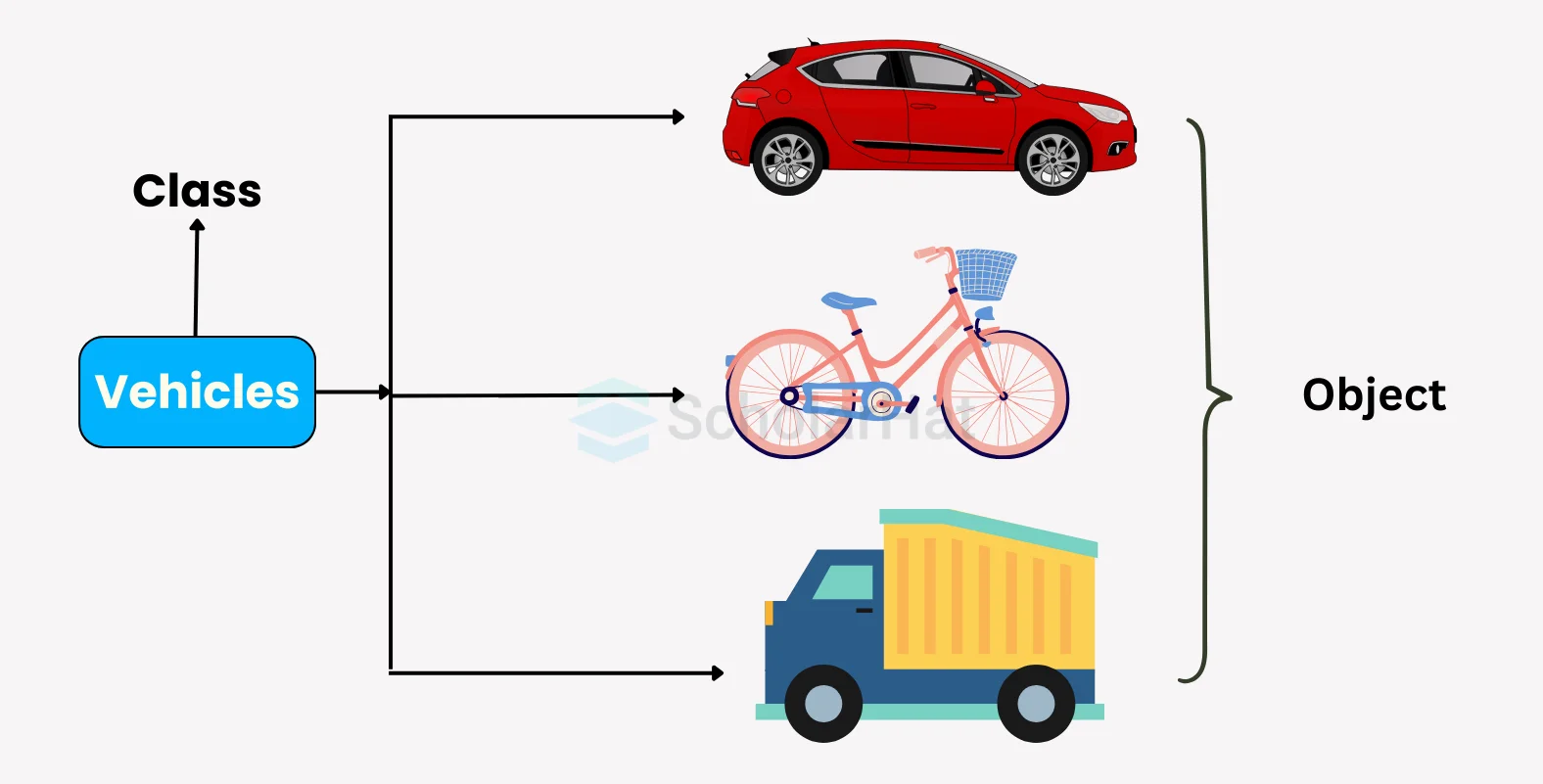
Fundamental ideas in Java programming are Classes and objects in Java, which resemble real-world things with states, behaviors, and characteristics. Classes, which include variables to hold object states and methods to specify their behavior, allow programmers to model their code after actual entities in the real world.
Java's natural object-oriented programming capabilities are built on this powerful combination, which makes writing easier. 70% of entry-level developers lack core Java skills. Build your foundation today with our no-cost course. Join Free Java Online Course today!
What is Java Classes?
An essential part of the Java language is the class, which contains objects with similar properties and specifies their data and behavior. It provides structure and efficiency for Java developers and serves as the blueprint for building objects.Abstraction in Java is an important aspect of object-oriented programming, where an object is an abstract concept in Java; it has no physical representation like variables or other types of data but instead acts as a template for entities being modeled within a program.
Java classes provide the framework for building models incorporating essential concepts like inheritance in Java, polymorphism in Java, abstraction, & encapsulation. They act as the design manual for the construction of objects, making Java development essential.
How to Create a Class in Java?
Properties of Java Classes
1. Class is Not a Real-World Entity:- A class is an abstract concept and acts as a blueprint for creating objects. It represents the definition but not the physical existence of an entity.
- Example: A "Car" class defines properties like color, model, and speed but does not represent any specific car until instantiated.
2. Class Does Not Occupy Memory:
- Unlike objects, classes themselves do not occupy memory until an object is created from the class.
- Example: Declaring a class does not allocate space in memory until you create an object using the
newkeyword.
3. Class is a Grouping Mechanism:
- A class is a logical container that groups variables (data members) and methods (functions).
- These elements collectively define the behavior and state of objects created by the class.
- Data Members: Variables that hold data specific to the objects of the class.
class Car {
String color;
int speed;
}void drive() {
System.out.println("The car is driving.");
}Car(String color, int speed) {
this.color = color;
this.speed = speed;
}class Outer {
class Inner {
void display() {
System.out.println("This is a nested class.");
}
}
}interface Vehicle {
void start();
}Syntax of class in Java
access_modifier class<class_name>
{
data member;
method;
constructor;
nested class;
interface;
}
Example 1: Example of the class program in Java
class Student {
int id; // data member (also instance variable)
String name; // data member (also instance variable)
public static void main(String args[])
{
Student s1 = new Student(); // creating an object of
// Student
System.out.println(s1.id);
System.out.println(s1.name);
}
}
Output
0
null
A Student is defined by this Java class and has two instance variables (name and id). In the main method, a Student (s1) instance is created, and its uninitialized variables—which most likely have default values of 0 for id and null for name—are printed.
Example 2: Simple Class with Methods and Constructor
This example demonstrates a basic class with a constructor and methods to initialize and display object properties.
// Class definition
class Car {
// Data members (variables)
String color;
String model;
int year;
// Constructor to initialize the Car object
Car(String color, String model, int year) {
this.color = color;
this.model = model;
this.year = year;
}
// Method to display car details
void displayDetails() {
System.out.println("Car Model: " + model);
System.out.println("Car Color: " + color);
System.out.println("Car Year: " + year);
}
// Method to start the car
void startCar() {
System.out.println(model + " is starting...");
}
}
// Main class to test the Car class
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating objects of the Car class
Car car1 = new Car("Red", "Toyota", 2022);
Car car2 = new Car("Blue", "Honda", 2020);
// Calling methods
car1.displayDetails();
car1.startCar();
car2.displayDetails();
car2.startCar();
}
}
Example 3: Class with Nested Class
This example demonstrates how a nested class can be defined inside another class and how it can access the outer class's data members.
// Outer class
class OuterClass {
// Data member of outer class
String outerMessage = "This is the outer class.";
// Nested class inside the outer class
class InnerClass {
// Method in the inner class
void displayMessage() {
System.out.println(outerMessage); // Accessing outer class data member
System.out.println("This is the inner class.");
}
}
}
// Main class to test nested class functionality
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Creating an object of the OuterClass
OuterClass outerObject = new OuterClass();
// Creating an object of the InnerClass through the outer class object
OuterClass.InnerClass innerObject = outerObject.new InnerClass();
// Calling the method in the inner class
innerObject.displayMessage();
}
}
How to Create an Object in Java?
There are many different ways to create objects in Java, those are:
1. Define a Class
Before you can create an object in Java, you first need to define a class. A class is a blueprint or template from which objects are created. It contains data members (variables) and methods (functions) that describe the properties and behavior of the objects.
// Class definition
class Car {
// Data members (attributes)
String model;
String color;
int year;
// Constructor to initialize the object
Car(String model, String color, int year) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.year = year;
}
// Method to display car details
void displayDetails() {
System.out.println("Car Model: " + model);
System.out.println("Car Color: " + color);
System.out.println("Car Year: " + year);
}
} 2. Create an Instance of the Class
To create an object from the class, you need to declare a reference to the class and use the new keyword to allocate memory for the object. The new keyword is used to create an instance of the class, i.e., an object.
Car myCar = new Car("Toyota", "Red", 2022); In this line, Car is the class, myCar is the object reference (instance), and new Car(...) creates the actual object, initializing it with the provided values "Toyota", "Red", and 2022.
3. Access the Object
Once an object is created, you can access its properties (data members) and behaviors (methods) using the object reference. You can call methods or modify the values of data members through the object.
myCar.displayDetails(); The method displayDetails() is called on the object myCar. This will print out the values of the car's model, color, and year.
Complete Example
Here is a complete Java program demonstrating the above steps:
// Define the Car class
class Car {
String model;
String color;
int year;
// Constructor to initialize the Car object
Car(String model, String color, int year) {
this.model = model;
this.color = color;
this.year = year;
}
// Method to display car details
void displayDetails() {
System.out.println("Car Model: " + model);
System.out.println("Car Color: " + color);
System.out.println("Car Year: " + year);
}
}
// Main class to create and access the object
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create an instance (object) of the Car class
Car myCar = new Car("Toyota", "Red", 2022);
// Accessing the object's method
myCar.displayDetails();
}
} Different ways to create objects in Java
1. Using the new keyword:
Example:
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();With this line of code, an object of the class "ClassName" is created and assigned to the variable "objectName."
2. Using Class.forName() method:
Example:
Class className = Class.forName("ClassName");
ClassName objectName = (ClassName) className.newInstance();In this code, the class "ClassName" is dynamically loaded by "Class.forName("ClassName")" and then created by "className.newInstance()" and assigned to the variable "objectName" after being cast to the proper type.
3. Using clone() method:
Example:
ClassName object1 = new ClassName();
ClassName object2 = object1.clone();According to this example, "object1" generates an instance of "ClassName," whereas "object2 = object1.clone()" makes a new instance of "object2" that is a copy or clone of "object1." You can duplicate objects with the same characteristics and behaviors thanks to this.
4. Using object deserialization:
Example:
ObjectInputStream objectInputStream = new ObjectInputStream(inputStream);
ClassName objectName = (ClassName) objectInputStream.readObject();In this example, the "ObjectInputStream" is initially set up to read serialized data from the "inputStream" and to deserialize that data into an instance of the "ClassName" class, which is then assigned to the variable "objectName."
5. Using Factory Method:
Example:
public static ClassName createObject() {
return new ClassName();
}
ClassName objectName = ClassName.createObject();In the "ClassName" class, the static function "createObject" in this example defines a brand-new instance of "ClassName." The "createObject" function is then used, which is a standard pattern for generating objects with specified initialization logic, to create an instance of "ClassName" called "objectName".
6. Using Dependency Injection:
Example:
public class MyClass {
private Dependency dependency;
public MyClass(Dependency dependency) {
this.dependency = dependency;
}
}
MyClass objectName = new MyClass(new Dependency());In this case, a constructor that initializes a private instance variable named "Dependency" and a class named "MyClass" is defined. Then, it establishes a dependency between the two classes by creating an instance of "objectName" of "MyClass" with a fresh instance of "Dependency" as a constructor argument.
Anonymous Object in Java
Java Objects
Java objects, which represent actual real-world objects, are instances of classes. They include data (attributes) and behaviors (methods) associated with a particular class.
Declaring Objects (Also called instantiating a class)
In Java, declaring an object entails making instances of a class. This includes naming a variable, the class type, and the class constructor before using the "new" keyword.
Example
ClassName objectName = new ClassName();
Initializing a Java object
When a Java object is initialized, its initial state is established by giving its attributes (data members) values. Usually, constructors or setter methods are used for this.
Example
public class Student { private String name;
private int age; // Constructor to initialize the object
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
}// Initializing a Student object
Student student = new Student("Mahesh", 20);The "Student" class is defined by this code and has a private name and age attributes as well as a constructor to initialize them. It then establishes the starting state of a "student" object with the name "Mahesh" and the age of 20.
Difference between Class and Object in Java
| Parameter | Class | Object |
| Definition | A class is a blueprint or a template that defines the properties and behavior of objects. | An object is an instance of a class that has actual values for those properties. |
| Usage | A class is used to create objects, which are instances of that class. | An object is an instance of a class that has been created using the constructor of that class. |
| Properties | A class defines the properties that objects of that class will have. These properties are defined using variables. | An object has values for those properties. |
| Methods | A class also defines the behavior that objects of that class will have. This behavior is defined using methods. | An object can call these methods to perform specific tasks. |
| Memory allocation | A class is not allocated memory in the Java Virtual Machine (JVM). | An object is allocated memory when it is created using the "new" keyword. |
Summary
Objects and Classes in Java are powerful concepts that can help create efficient code. It is important to become familiar and comfortable with the nuances of this fundamental object-oriented programming language features to be able to utilize its full potential. You can take your OOP knowledge to the next level with our Java Solution Architect Certification.
Full-stack Java developers earn ₹15–25 LPA, while coders stall at ₹8 LPA. Don’t settle—join our course today! Enroll in Java Full Stack Course.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.