06
FebControl Statements in Java with Examples: If, If-Else and Switch Statement
Java Control Statements: An Overview
Conditional statements in Java are one of the significant parts of "Control Structure" in Java. Conditional statements are based on certain conditions and generate decisions accordingly. These statements are a bunch of codes that can be executed by "decision statements" which are crucial. In this Java tutorial, we'll learn them in detail. Core Java skills can unlock ₹8 LPA jobs. Don’t wait, Enroll now in our Free Java Course and start your success story!
What are Conditional Statements in Java?
Conditional statements are one of the significant parts of "Control Structure" in Java. Conditional statements are based on certain conditions and generate decisions accordingly. These statements are a bunch of codes that can be executed by "decisions statements". These conditions have some specific "boolean expressions." The boolean expression of these conditional statements generates "Boolean Value" which could be either true or false.
Read More - Advanced Java Interview Questions
Types of Control Statements in Java with Example
There are 4 types of conditional statements in Java discussed in this Beginner’s Guide to Java. They are if statements in Java, if else statements in Java, ladder statements or If Else If statements, and Switch statements. The types of conditional statements in Java will be discussed further.
1. If..statement in Java
- “If” is a statement execution that depends on certain conditions.
- These conditions only follow the "if" keyword.
- The "If" statement depends on the expression of a certain boolean and generates a Boolean Value.
- If the value is "True" then the execution will be done in the current block.
- But if the Value is "false", it will switch to the next statement.
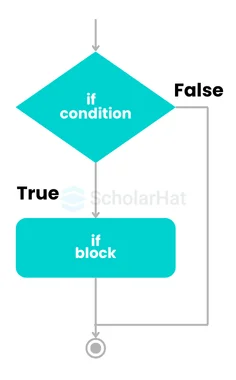
Syntax of If..statement in Java
If (condition)
{
//Statements to be executed
}Java if else example in Java Online Editor
class if_condition
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = 0.8;
if (a>0)
{
System.out.println(a + " is a Positive Number!");
}
}
}
This Java code assigns the value 0.8 to the variable "a," and a "if" condition determines whether "a" is greater than 0. If accurate, it confirms that 0.8 is a positive number by printing "0.8 is a Positive Number!" to the console.
Output
0.8 is a Positive Number!2. If..else statement in Java
- The if-else statement in Java is a particular control structure that depends on selecting the conditions of the chosen set of statements.
- The if-else program in Java depends on two types of conditions, which are "If" and "Else".
- If the expression generates the "true" value then it will execute the block "If" in the if-else program in the if else program in Java.
- But if the value is "False", it will execute the "Else" block which depends on the if-else condition.
Syntax of If..else statement in Java
if (condition)
{
//Statements to be executed if condition satisfies
}
else
{
//Statements to be executed if the condition is not satisfied
}
If-else example in Java
class if_else_condition
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double a = -0.8;
if (a>0)
{
System.out.println(a + " is a Positive Number!");
}
else
{
System.out.println(a + " is a Negative Number!");
}
}
}
This Java code gives the value -0.8 to the variable "a". It determines whether "a" is greater than 0 by using a "if-else" condition. If true, the console displays "0.8 is a Positive Number!"; if false, it displays "0.8 is a Negative Number!" to indicate that -0.8 is a negative number.
Output
-0.8 is a Negative Number!3. If else...if statement in Java
- This control structure statement depends on a series of tests to evaluate the solution
- It is generated by the multiple uses of the "If Else" statement.
- If the one condition meets the result then the first ladder will be executed.
- But if the condition does not meet the results then the default "Else" statement will be executed.
Read More - Java Programmer Salary In India
Syntax of If else...if statement in Java
if (condition)
{
//Statements set 1
}
else if (condition 2)
{
//Statements set 2
}
. . .
else
{
//Statements to be executed if no condition is satisfied.
}
Example
public class NestedIfElseCondition {
public static void main(String[] args) {
double totalMarks = 382;
double perc = (totalMarks / 500) * 100;
String grade; // Declaring grade variable outside if-else blocks
if (perc >= 80) {
grade = "A+";
} else if ((perc >= 70) && (perc < 80)) {
grade = "A";
} else if ((perc >= 60) && (perc < 70)) {
grade = "B+";
} else {
grade = "B";
}
System.out.println("The percentage of the student is: " + perc);
System.out.println("\nThe grade of the student is: " + grade);
}
}
With the help of this Java program, you can figure out a student's percentage, give them a grade based on predetermined ranges, and print out both the % and the grade. In this instance, the "nested_if_else_condition" class, which assesses student performance, would output the percentage and grade based on the 382 total marks.
Output
The percentage of the student is: 76.4
The grade of the student is: A+4. Switch Statement in Java
- This statement has multiple phases of execution. Not only that In Java, access modifiers play a crucial role in controlling the visibility of variables, methods, and classes.
- Switch statements generally evaluate the result which is assisted by some "primitive type" of data or "class type" of data.
- This statement has a test series of conditions that can do one or more cases at a time by switching expressions.
- If the case meets the result then the statement will be executed.
- But if it does not meet the result then the "default" cases will be executed.
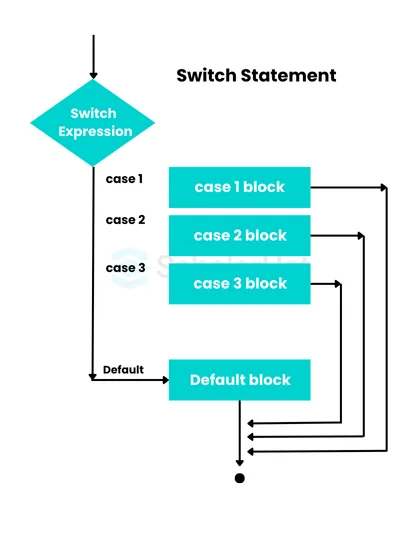
Syntax of Switch Statement in Java
switch (Expression)
{
case value 1: Statement 1;
case value 2: Statement 2;
case value 3: Statement 3;
.
.
.
case value n: Statement n;
default: default statement;
}Example
class Switch_Case {
public static void main(String[] args)
{
char a = 'C';
switch (a)
{
case 'A':
System.out.println("Letter A");
break;
case 'C':
System.out.println("Letter C");
break;
default:
System.out.println("Default case: NO Letter Matched!");
}
}
}
The switch-case statement is used in this Java code demonstration in the Java Compiler. Because it matches the 'C' case, it examines the value of the character variable "a" and prints "Letter C," but the default case is not used.
Output
Letter CIf..else vs. Switch statements
| Parameter | If...Else | Switch |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | The execution of both of the "If" blocks and "else", depends on the condition stored in the if statement. | The code blocks in the switch statement depend on the execution of multiple cases. |
| Usage | This statement is used for pointer, character, integer, a boolean type, and floating point type. | Switch statements are used for integer and character expressions |
| Testing | It tastes equality and logical expression. | It tests only equality |
| Expressions | It generates multiple statements for multiple decisions. | It generates a single expression for multiple decisions. |
| Editing | It is difficult to edit because of its nested type of program. | It is very easy to edit |
| Value | It is dependent on constraint. | It is dependent on users. |
Read More: Best Java Developer Roadmap 2024
Summary
This article gives a vast idea of conditional statements and their types. Features of every conditional operator in Java with examples and syntax are explained. This article also includes the different types of conditional statements in Java and the difference between the If-else condition and the switch condition. 98% of Java coders never become Solution Architects. Don’t stay stuck, Enroll now in our Java Solution Architect Course for a huge 70% pay boost! Also, Consider Java Full Stack Course to level up your career.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.