20
FebWhat is Inheritance in Java: Types of Inheritance in Java
Inheritance in Java is a fundamental OOP feature that enables one class (called the subclass) to acquire the properties and behaviors of another class (called the superclass). It allows for code reuse, improved organization, and the creation of a logical class hierarchy.
In this Java tutorial, we will learn the concepts of Java Inheritance, types of inheritance in Java, etc. Are you new to coding? Our Free Java Course is your ticket to a thriving tech career in Java.
What is Inheritance in Java?
Inheritance in Java is a powerful object-oriented programming feature that allows a new class to be created by reusing the fields and methods of an existing class. This promotes code reusability, reduces redundancy, and helps build a clear class hierarchy in Java applications.
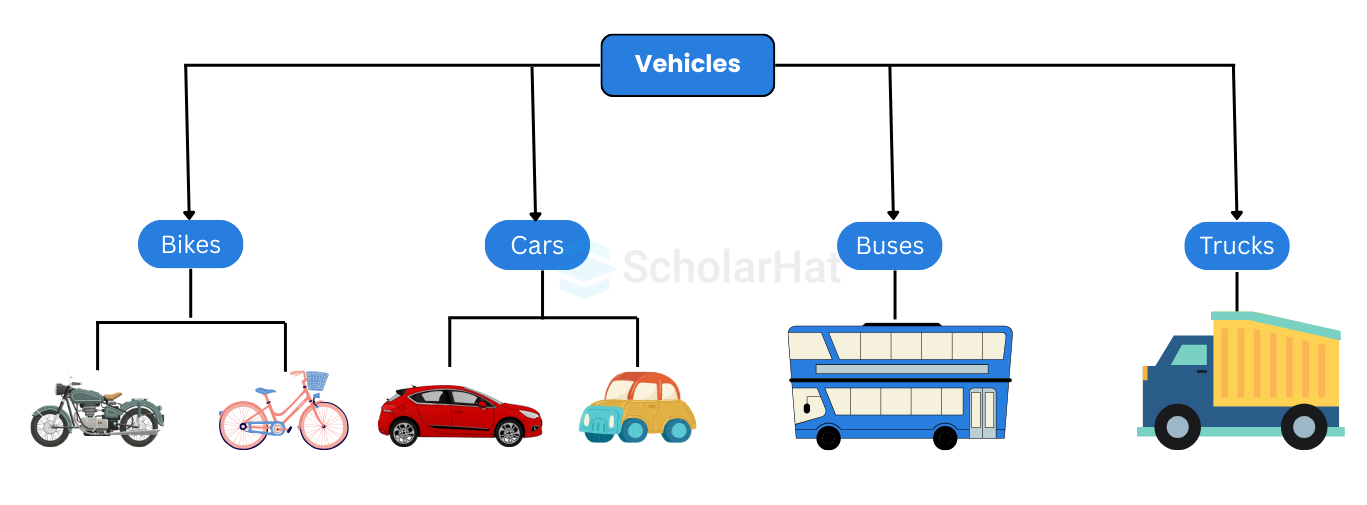
Java is-a relationship
In Java, inheritance is an is-a relationship. We can use inheritance only if there is an is-a relationship between two classes. For example,
In the above figure:
- A car is a Vehicle
- A bus is a Vehicle
- A truck is a Vehicle
- A bike is a Vehicle
Here, the Car class can inherit from the Vehicle class, the bus class can inherit from the Vehicle class, and so on.
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions
Important Terminologies Used in Java Inheritance
- Class: A class in Java is a blueprint or template used to create objects. It defines a set of properties (attributes) and behaviors (methods) that the created objects will share. While a class itself doesn't represent real-world entities directly, it provides the structure to model them in code.
- Superclass/Parent Class: The superclass (also called the base class or parent class) is the class from which other classes inherit. It contains common fields and methods that can be shared by multiple subclasses.
- Subclass/Child Class: A subclass (also known as a derived class or child class) is a class that inherits from a superclass. It gains access to the fields and methods of the parent class and can also introduce its own additional features.
- Reusability: Inheritance promotes the concept of code reusability. If an existing class already has certain functionality, you can create a new class that reuses that functionality without rewriting code. This helps in maintaining a cleaner, more efficient, and scalable codebase.
How to Use Inheritance in Java?
Syntax
// Parent class (Superclass)
class ParentClass {
// Fields and methods
}// Child class (Subclass) that inherits from ParentClass
class ChildClass extends ParentClass {
// Additional fields and methods
}Example
// Parent class (Superclass)class Animal {
String name;
int age;
public Animal(String name, int age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void speak() {
System.out.println(name + " makes a sound.");
}
}// Child class (Subclass) that inherits from Animal
class Dog extends Animal {
String breed; public Dog(String name, int age, String breed) {
super(name, age); // Call the constructor of the parent class
this.breed = breed;
} // Override the speak() method
@Override
public void speak() {
System.out.println(name + " barks loudly!");
} public void fetch() {
System.out.println(name + " fetches a ball.");
}
}public class InheritanceExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Create instances of Animal and Dog
Animal genericAnimal = new Animal("Generic", 5);
Dog myDog = new Dog("Buddy", 3, "Golden Retriever"); // Call methods
genericAnimal.speak(); // Output: Generic makes a sound.
myDog.speak(); // Output: Buddy barks loudly!
myDog.fetch(); // Output: Buddy fetches a ball.
}
}
Explanation:
Java inheritance is shown in the Java Online Compiler. The Dog class is a subclass that derives from Animal, overrides the speak() function, and adds a fetch() method. The Animal class serves as the parent class and has attributes and a speak() method. Instances of both classes are created by the main method, demonstrating polymorphism as they call their respective speak() methods and generating output specific to their behaviors.
Output
Generic makes a sound.
Buddy barks loudly!
Buddy fetches a ball.Read More - Java Web Developer Salary
Access Modifiers in Java
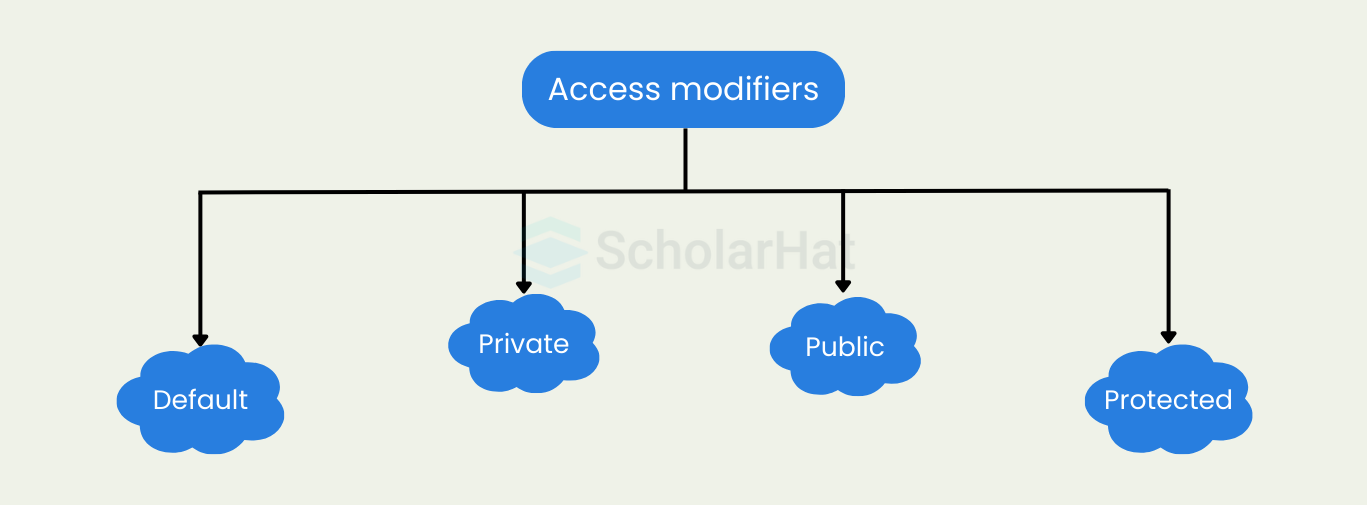
- Default Access Modifier: When no access modifier is specified, Java applies the default access level. Members with default access are accessible only within the same package. They are not visible to classes in other packages, even if they are subclasses.
- Private Access Modifier: The private modifier restricts access only within the class where the member is declared. Methods or variables marked as private cannot be accessed or inherited by any other class, ensuring strong data hiding and encapsulation.
- Protected Access Modifier: The protected modifier allows access to class members within the same package and also in subclasses located in other packages. It strikes a balance between default and public, supporting inheritance while limiting exposure.
- Public Access Modifier: The public modifier makes a class, method, or variable accessible from anywhere in the application, across all packages. It is used when you want to expose functionality universally throughout your codebase.
To learn Access Modifiers in detail, refer to Access Modifiers in Java
Method Overriding in Java Inheritance
When you redefine any base class method with the same signature i.e. same return type, number, and type of parameters in the derived class, it is known as method overriding in Java. In this case, the method in the subclass overrides the method in the superclass.
Example of Method Overriding in Java
class DotNetTricks {
public void print() { // overridden function
System.out.println("Welcome to DotNetTricks");
}
}
class ScholarHat extends DotNetTricks {
@Override
public void print() { // overriding function
System.out.println("Welcome to ScholarHat");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScholarHat obj1 = new ScholarHat();
// Call the print() function of the ScholarHat class
obj1.print();
}
}
In the above code, the base class Scholarhat overrides the print() function of the parent class, DotNetTricks. When you create an object of ScholarHat and call its print() function, it executes the version of the function defined in the ScholarHat class.
Output
Welcome to ScholarHat
super Keyword in Java Inheritance
In the above topic we saw that when the same method is defined in both the base class and the derived class, the method in the subclass overrides the one in the superclass. In such cases, the super keyword in Java is used to call the method of the parent class from the method of the child class.
class DotNetTricks {
public void print() { // overridden function
System.out.println("Welcome to DotNetTricks");
}
}
class ScholarHat extends DotNetTricks {
@Override
public void print() { // overriding function
// call method of the superclass
super.print();
System.out.println("Welcome to ScholarHat");
}
}
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
ScholarHat obj1 = new ScholarHat();
// Call the print() function
obj1.print();
}
}
Here, the super keyword in the Java Online Editor is used to call the print() method present in the superclass.
Output
Welcome to DotNetTricks
Welcome to ScholarHat
Types of Inheritance in Java
There are five types of Inheritance in Java
- Single Inheritance
- Multilevel Inheritance
- Hierarchical Inheritance
- Multiple Inheritance
- Hybrid Inheritance
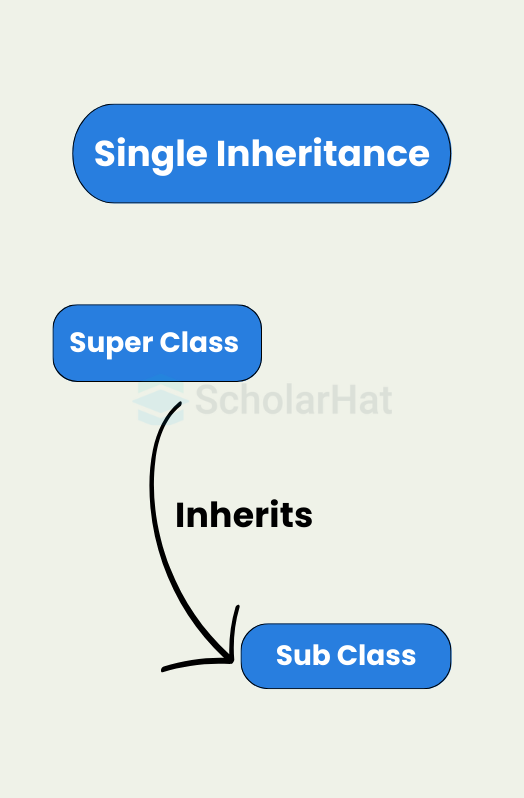
1. Single Inheritance in Java
This is a single-level Inheritance with one subclass with the properties of the superclass.
Example
class Animal
{
void sleep(){System.out.println("sleeping...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void bark(){System.out.println("barking...");}
}
class TestInheritance
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Dog d=new Dog();
d.bark();
d.sleep();
}
}
The Dog class in this example inherits from the Animal class to demonstrate inheritance in Java. The TestInheritance class creates a Dog instance and calls the bark() and sleep() methods to show how a subclass inherits functionality from its superclass. The Dog class adds a bark() method.
Output
barking…
sleeping…
2. Multi-Level Inheritance in Java
If there are 3 classes named A, B, and C in the Java toolkit, then class B inherits the properties of class A, and class C inherits the properties of class B. This happens in multilevel inheritance in Java.
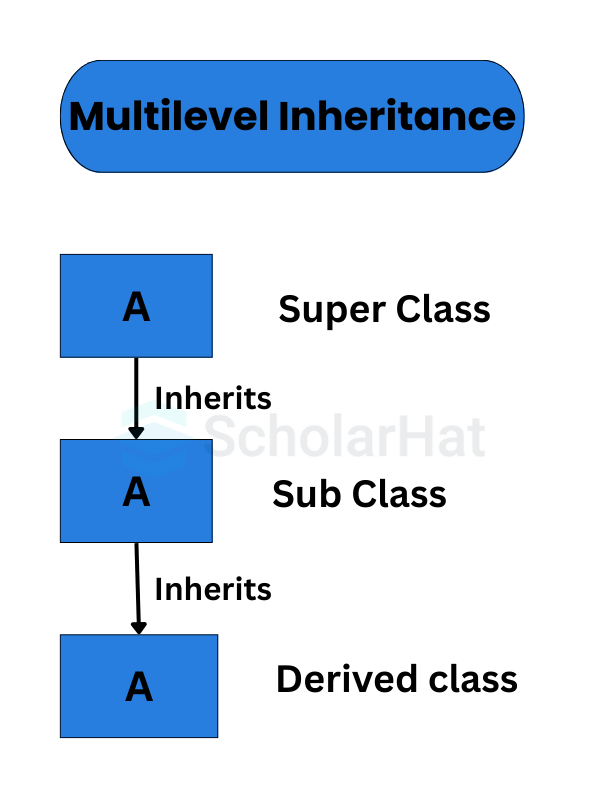
Multi-Level Inheritance in Java Example
class Animal
{
void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal{
void sleep(){System.out.println("sleeping...");}
}
class BabyDog extends Dog
{
void weep(){System.out.println("weeping...");}
}
class TestInheritance2
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
BabyDog d=new BabyDog();
d.weep();
d.sleep();
d.eat();
}
}
The 'BabyDog' class in this example illustrates multi-level inheritance in Java; it derives from the 'Dog' class, which in turn derives from the 'Animal' class. The 'BabyDog' object has access to and may call methods from all three types, showing how inheritance establishes a hierarchy of classes with similar functionality.
Output
weeping…
sleeping…
eating…
3. Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
It multiplied one parent class with their child classes. This type of Inheritance in Java helps to reduce the code length and also increases the "code modularity".
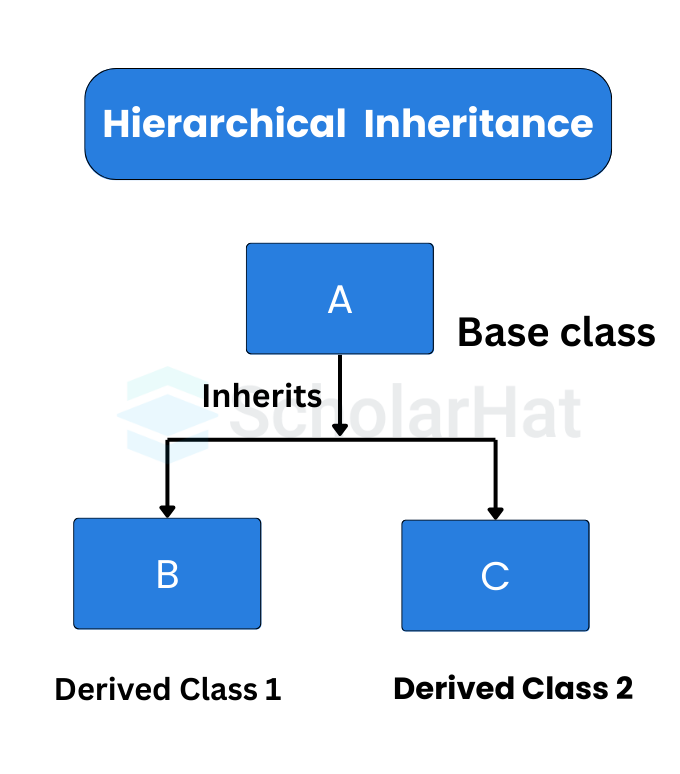
Example
class Animal
{
void eat(){System.out.println("eating...");}
}
class Dog extends Animal
{
void sleep(){System.out.println("sleeping...");}
}
class Cat extends Animal
{
void meow(){System.out.println("meowing...");}
}
class TestInheritance3
{
public static void main(String args[])
{
Cat c=new Cat();
c.meow();
c.eat();
//c.bark();//C.T.Error
}
}
This Java sample in the Java Compiler explains basic inheritance. As a result of the 'Cat' class' inheritance from the 'Animal' class, instances of the 'Cat' class can access and use the parent class' methods. A compile-time error (C.T.Error) is generated when attempting to call a method from a class that is unrelated to the one being called, such as "bark()," which is not a member of "Animal" or "Cat."
Output
meowing…
eating…Read More: Hierarchical Inheritance in Java
4. Multiple Inheritance (Through Interfaces) in Java
A class can inherit behaviors and method signatures from various interfaces using multiple inheritances through interfaces, which encourages code reuse and flexibility. Interfaces ensure that classes follow predetermined behaviors by defining method contracts without implementing them.
Example
// Define two interfacesinterface Animal {
void eat();
void sleep();
}interface Bird {
void fly();
}// Create a class that implements both interfaces
class Sparrow implements Animal, Bird {
@Override
public void eat() {
System.out.println("Sparrow is eating.");
} @Override
public void sleep() {
System.out.println("Sparrow is sleeping.");
} @Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Sparrow is flying.");
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Sparrow sparrow = new Sparrow();
sparrow.eat(); // Calls the eat() method from the Animal interface
sparrow.sleep(); // Calls the sleep() method from the Animal interface
sparrow.fly(); // Calls the fly() method from the Bird interface
}
}
The "Animal" and "Bird" interfaces are defined in this code, along with the class "Sparrow," which implements both interfaces. The 'eat()','sleep()', and 'fly()' methods are implemented by the 'Sparrow' class. It generates a "Sparrow" object and invokes its methods in the "main" method to show multiple inheritance through interfaces.
Output
Sparrow is eating.
Sparrow is sleeping.
Sparrow is flying.Read More: Multiple Inheritance in Java
5. Hybrid Inheritance in Java
When a class derives from numerous classes by combining various inheritance types, this is referred to as hybrid inheritance in Java. Java enables both single and multiple inheritance through classes and interfaces. When a class uses hybrid inheritance, it can derive from a variety of classes, some of which are descended from through interface inheritance and others through class inheritance.
Example
// Base class
class Animal {
void eat() {
System.out.println("Animal is eating.");
}
}// Interface for flying behavior
interface Flying {
void fly();
}// Interface for swimming behavior
interface Swimming {
void swim();
}// Derived class inheriting from Animal and implementing Flying interface
class Bird extends Animal implements Flying {
@Override
public void fly() {
System.out.println("Bird is flying.");
}
}// Derived class inheriting from Animal and implementing Swimming interface
class Fish extends Animal implements Swimming {
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("Fish is swimming.");
}
}// Derived class inheriting from Bird and Fish
class FlyingFish extends Bird implements Swimming {
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("FlyingFish is swimming.");
}
}public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Bird bird = new Bird();
bird.eat();
bird.fly(); Fish fish = new Fish();
fish.eat();
fish.swim(); FlyingFish flyingFish = new FlyingFish();
flyingFish.eat();
flyingFish.fly();
flyingFish.swim();
}
}
The code in the Java Playground shows how to create a class hierarchy using interfaces and class inheritance. It has two interfaces, 'Flying' and 'Swimming', which represent behaviors, as well as an 'Animal' base class with a 'feed' method. The derived classes "Bird" and "Fish" implement the "Flying" and "Swimming" interfaces, respectively, and both classes inherit from "Animal." The 'FlyingFish' class also implements 'Swimming' and further inherits from 'Bird'. To show method overriding and interface implementation, instances of these classes are created in the 'Main' class and their methods are called.
Output
Animal is eating.
Bird is flying.
Animal is eating.
Fish is swimming.
Animal is eating.
Bird is flying.
FlyingFish is swimming.Why Do We Need Java Inheritance?
- Code Reusability – Common fields and methods defined in the parent class can be reused in child classes, reducing redundancy.
- Method Overriding – Subclasses can modify methods from the superclass to implement runtime polymorphism and custom behaviors.
- Abstraction – Super classes can define generic structures, while subclasses handle the specific details, promoting clean design.
- Improved Maintainability – Centralizing shared logic in a superclass makes the code easier to manage and update.
- Logical Hierarchy – Helps establish a clear class hierarchy that reflects real-world relationships (e.g., Animal → Dog, Cat).
- Extensibility – New features or behaviors can be added in subclasses without changing existing code in the superclass.
- Consistent Behavior – Ensures that shared functionalities behave the same across all subclasses, improving reliability.
Java Access Modifiers and Inheritance Rules
| Access modifiers | Same class | Same package subclass | Different package subclass | Different package non-subclass | Inherited? |
| public | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| protected | Yes | Yes | Yes | No | Yes |
| default | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes |
| private | Yes | No | No | No | No |
Advantages of Inheritance in Java
- Code Reusability – Allows reuse of existing class code in new classes.
- Method Overriding – Enables runtime polymorphism for flexible behavior.
- Organized Code Structure – Helps maintain a clear class hierarchy.
- Extensibility – Makes it easy to add new features without modifying existing code.
- Reduces Redundancy – Common code is written once in the parent class.
- Easier Testing & Debugging – Shared code can be tested once and reused
Disadvantages of Inheritance in Java
- Tight Coupling – Child classes are dependent on parent classes, reducing flexibility.
- Increased Complexity – Deep inheritance hierarchies can make code harder to understand and maintain.
- Fragile Base Class Problem – Changes in the parent class can unintentionally affect all child classes.
- Limited Scope for Reuse – Inheritance only allows reuse from a single parent (Java doesn't support multiple inheritance with classes).
- Overriding Risks – Improper method overriding can lead to unexpected behavior.
Summary
In Java, inheritance is when one class can inherit the attributes and methods of another. While each type of inheritance has its unique benefits, they all ultimately allow for code reusability making programs more efficient. Leverage OOP principles like inheritance to design scalable systems with our Java Architect Certification
Only 10% of Java developers are full-stack ready. Don’t lag behind—join our course to lead! Enroll in Java Full Stack Course.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.