06
MarTop Java Microservices Skills Every Java Developer Must Master
Java Microservices Developer Skills are essential for building modern, scalable, and resilient applications in today’s fast-paced software industry. As organizations move away from monolithic architectures, microservices have become the preferred approach for developing modular, independently deployable services.
What are Java Microservices?
Java Microservices is an architectural approach where a large Java application is broken into smaller, independent services to build loosely coupled, independently deployable, data layers applications. Each service runs in its own process, handles a specific business function, and communicates with others via lightweight APIs usually HTTP/REST or messaging queues. This design follows the microservices architecture, allowing services to be developed, deployed, and scaled independently.
How to Become Java Microservices Developers?
- Master Core Java concepts like OOP, collections, multithreading, and design patterns.
- Learn Spring Boot and Spring Cloud for building scalable microservices.
- Gain proficiency in SQL and NoSQL databases with ORM tools like Hibernate/JPA.
- Understand REST API design and asynchronous communication using Kafka or RabbitMQ.
- Acquire cloud and containerization skills with Docker, Kubernetes, and platforms like AWS/Azure/GCP.
- Implement security best practices using JWT, OAuth2, and Spring Security.
- Build real-world projects and maintain a portfolio on GitHub.
- Engage in continuous learning, follow industry trends, and pursue relevant certifications.
Core Technical Skills for Java Microservices Developers
To succeed as a Java Microservices Developer, you need a solid mix of programming expertise, frameworks, and supporting technologies. Below are the must-have technical skills:
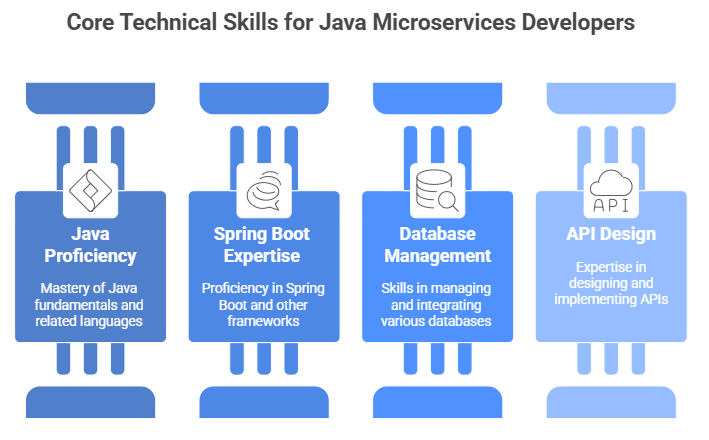
1. Proficiency in Java and Related Languages
A Java Microservices Developer must have a strong command of Core Java. It is the foundation of microservices development. Developer must understand:
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOPs) in Java
- Java Collections framework, generics, exception handling in java.
- Multithreading in Java and concurrency management
- JVM performance tuning
- Additionally, knowledge of related languages such as Kotlin or Scala can be an advantage when working in diverse teams.
2. Expertise in Spring Boot and Other Frameworks
Spring Boot is the most widely used framework for building Java microservices because of its simplicity and production-ready features. A developer should be skilled in:
- Creating lightweight REST APIs with Spring Boot
- Using Spring Cloud for service discovery, API Gateway, and centralized configuration
- Implementing Dependency Injection (IoC) and Aspect-Oriented Programming (AOP)
- Familiarity with other frameworks like Micronaut or Quarkus is also beneficial for performance-driven microservices.
3. Database Management and Integration
Every microservice often has its own database, making database skills essential. Java Microservices developers should know how to:
- Work with SQL databases like MySQL and PostgreSQL
- Manage NoSQL databases such as MongoDB, Cassandra, or Redis
- Use ORM tools like Hibernate/JPA for persistence
- Optimize queries and ensure data consistency in distributed systems
4. API Design and Communication
Since microservices communicate with each other, mastering API design is crucial. Key areas include:
- Designing RESTful APIs with consistent, scalable endpoints
- Handling data formats such as JSON and XML
- Implementing asynchronous messaging with Kafka or RabbitMQ
- Documenting APIs using Swagger/OpenAPI for better collaboration and maintainability
Advanced Technical Skills for Java Microservices Developer
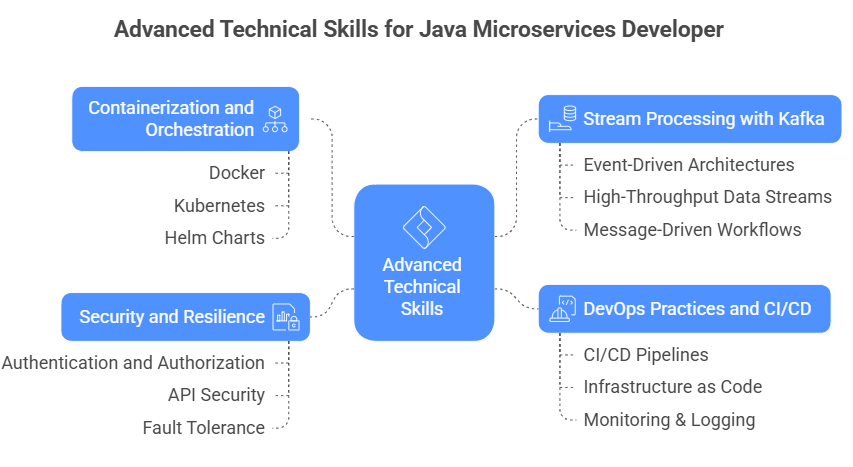
1. Containerization and Orchestration
Modern microservices are deployed as containers to ensure consistency across development, testing, and production environments.
- Use Docker to package applications into lightweight containers
- Manage deployments using Kubernetes for orchestration, scaling, and self-healing
- Apply Helm charts and YAML configuration for managing complex deployments
- Embrace cloud-native principles for building resilient microservices
2. Stream Processing with Kafka
Real-time data processing is critical for many applications. Apache Kafka is the industry-standard platform for handling real-time data streams. Skills in Apache Kafka Microservices include:
- Building event-driven architectures for microservices communication.
- Handling high-throughput data streams.
- Designing producers, consumers, and topics for message-driven workflows.
- Ensuring fault tolerance and message durability.
3. DevOps Practices and CI/CD
DevOps bridges the gap between development and operations, enabling faster and more reliable deployments. Java microservices developers should be comfortable with:
- CI/CD Pipelines: Knowledge of Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI/CD to automate build, test, and deployment workflows.
- Infrastructure as Code (IaC): Tools like Terraform and Ansible for automated environment setup.
- Monitoring & Logging: Experience with Prometheus, Grafana, and ELK Stack for tracking performance and resolving issues quickly.
4. Security and Resilience
- Implementing JWT and OAuth2 for authentication and authorization
- Securing APIs with HTTPS/TLS encryption
- Using Spring Security for role-based access control
- Designing fault-tolerant microservices with retry patterns, circuit breakers (Hystrix/Resilience4j), and graceful degradation
Soft Skills Required for Java Microservices Developers
While technical expertise is crucial, soft skills are equally important for a Java Microservices Developer to succeed in collaborative, fast-paced environments. Key soft skills include:
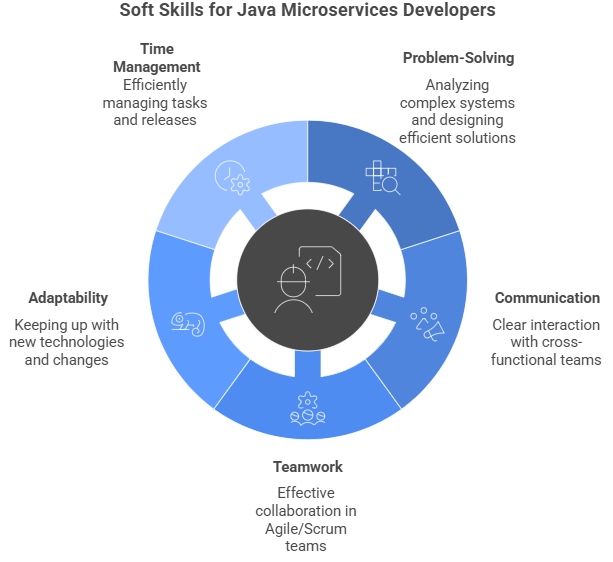
1. Problem-Solving and Analytical Thinking
- Ability to analyze complex systems and break them into modular services.
- Debugging and troubleshooting issues in distributed architectures.
- Designing efficient solutions for scalability and performance challenges.
2. Communication Skills
- Clear communication with cross-functional teams including QA, DevOps, and product managers.
- Writing well-documented code and APIs for easier team collaboration.
- Explaining technical concepts to non-technical stakeholders.
3. Teamwork and Collaboration
- Working effectively in Agile/Scrum teams.
- Participating in code reviews and collaborative design discussions.
- Mentoring junior developers and sharing knowledge.
4. Adaptability and Continuous Learning
- Keeping up with new tools, frameworks, and best practices in the microservices ecosystem.
- Quickly adapting to changes in requirements or architecture.
- Embracing cloud-native technologies, DevOps, and automation trends.
5. Time Management and Organization
- Managing multiple microservices tasks and releases efficiently.
- Prioritizing critical issues in production systems.
- Maintaining a balance between speed of delivery and code.
Salary and Job roles for Java microservices developers
The salary of Java Microservices Developers depends on experience, location, skills, and the company. Approximate ranges are:
| Experience | Salary (per year) |
| Entry-Level | ₹4–6 LPA (~$5k–$8k per year) |
| Mid-Level | ₹8–15 LPA (~$10k–$18k per year) |
| Senior-Level | ₹18–30 LPA (~$22k–$38k per year) |
Java Microservices Developers have diverse career opportunities across industries like finance, e-commerce, healthcare, and IT. Some common roles include:
- Java Microservices Developer – Design, develop, and maintain microservices-based applications.
- Backend Developer – Focus on server-side logic, APIs, and database management for distributed systems.
- Full-Stack Developer – Work on both frontend and backend, integrating microservices with user interfaces.
- Cloud/DevOps Engineer – Deploy and manage microservices in cloud environments using Docker, Kubernetes, and CI/CD pipelines.
- Solutions Architect – Design scalable, fault-tolerant microservices architectures for enterprise applications.
- Software Engineer in Distributed Systems – Handle performance, scalability, and reliability of large-scale microservices.
- API Developer– Build and manage APIs, ensuring smooth communication between microservices.
- Technical Lead– Lead development teams, review microservices design, and ensure best practices.
Conclusion
Java Microservices development has become a cornerstone of modern software architecture, enabling organizations to build scalable, resilient, and maintainable applications. To excel in this field, developers must combine core Java expertise, Spring Boot proficiency, database and API skills, cloud and DevOps knowledge, and strong security practices with essential soft skills like problem-solving, collaboration, and adaptability.
Looking to learn Java programming and build real coding skills that matter? You’re at the right place! Enroll in Full-Stack Java Developer Training and Java Microservices Certification Training to advance your career.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











