15
MarWhat is String in Java - Java String Methods & Type (Examples)
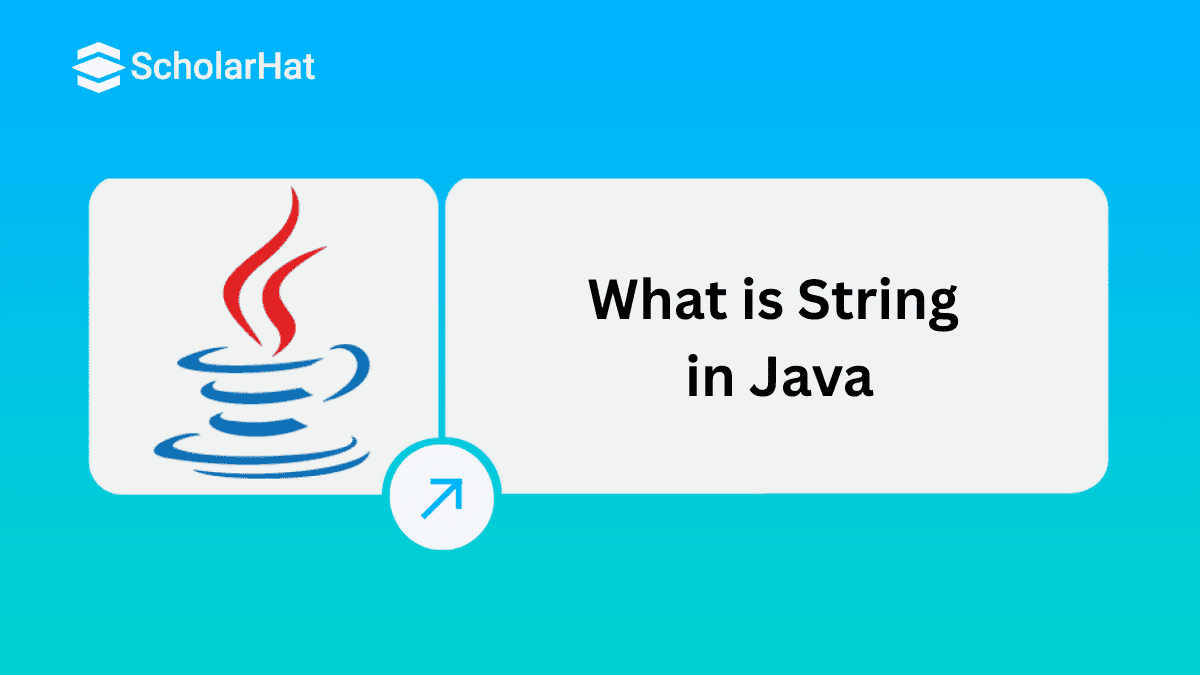
The String in Java is a fundamental and widely used class provided by the java.lang package to represent sequences of characters. In Java, strings are immutable, meaning once a string object is created, its value cannot be changed, which ensures security and efficient memory handling.
Internally, the String in Java is implemented as a character array (char[]) and uses a string pool to save memory by reusing existing string objects. Java also offers a rich set of built-in methods like .length(), .equals(), .substring(), and .replace() to make text manipulation simple and powerful.
In this Java tutorial, we will thoroughly understand the String in Java. Learn Java from scratch at zero cost. Join the Free Java Certification Course now.
What are Strings in Java?
In Java, a String is an object that represents a sequence of characters and is one of the most commonly used classes in the java.lang package. Strings are immutable, meaning once created, their values cannot be changed. Java provides powerful built-in methods for string manipulation, such as concatenation, comparison, substring extraction, and pattern matching. Because of their importance in text processing and data handling, Strings play a critical role in Java programming.
Example:
String name = "ScholarHat";
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions For Freshers
How to Create a String Object in Java?
There are a few steps to create a String Object in Java, those are:

Java String Example
class String_Creation_Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String ob1 = new String(); //creates an empty string
//new keyword helps to create an object of class String
System.out.println("Empty String: " +ob1);
char arr[] = {'j','k','a','q','e' };
String ob2 = new String(arr); //String from an array
System.out.println("Contents of Array String: " +ob2);
String ob3 = new String(arr,1,2); //String from subsequence of an array
System.out.println("Contents of subsequence of Array String: " +ob3);
String ob4 = new String(ob3); //String from another string object
System.out.println("Contents of Array String ob4: " +ob4);
}
}
Output
Empty String:
Contents of Array String: jkaqe
Contents of subsequent of Array String: ka
Contents of Array String ob4: kaExplanation
- Creating an Empty String: String ob1 = new String(); creates an empty String object with no content, and it's printed as "Empty String: ".
- Creating a String from a Character Array: String ob2 = new String(arr); creates a String from the given character array and prints its content as "Contents of Array String: jkaqe".
- Creating a String from a Subsequence: String ob3 = new String(arr, 1, 2); creates a String using a part of the character array (from index 1 to 2) and prints it as "Contents of subsequence of Array String: ka".
2 Ways to Create a String in Java
String objects can be created in two ways:
- Using String Literal
- Using new keyword
1. Using String Literal
In computer science, a literal is a term used to represent a value. Double quotes can be used to produce and represent Java String literals. You can insert any text or character between double quotes.
Syntax
<string_type> <string_variable> = "<sequence_of_string>";
Example
Let's look at the illustration of creating a string using a string literal in our Java Online Editor.
public class Main {
public static void main(String args[]) {
// A string object
String demoString = "Scholarhat";
System.out.println(demoString);
}
}
Output
Scholarhat
Explanation
- The code defines a String variable demoString and assigns it the value "Scholarhat".
- The System.out.println(demoString); line prints the value of demoString to the console, which is Scholarhat.
2. Using new keyword
The Java new keyword can be used to construct string in java. A new object of the String class is produced in the heap memory, outside the string constant pool, when a string is created with the new command. These objects, as opposed to string literals, are given their place on the heap, regardless of whether or not another object with an identical value is already present there.
Syntax
String stringName = new String("string_value");
Example
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = new String("ScholarHat");
System.out.println(str);
}
}
Output
Scholarhat
Explanation
- The code creates a new String object str with the value "ScholarHat" using the new keyword.
- The System.out.println(str); statement prints the value of str to the console, which is ScholarHat.
Read More - Java Programmer Salary In India
Why strings in Java are important?
Strings are essential in Java because they are used to represent and manipulate textual data, which is a core requirement in almost every application. Here’s why strings are needed in Java:
1. Representing Textual Information
- Strings are used to store and display text such as names, messages, file paths, commands, and much more.
2. Input and Output Operations
- Most input from users or files is in the form of strings. Java uses strings extensively in I/O operations like Scanner, BufferedReader, and file handling.
3. Communication and Data Transfer
- Strings are used in networking, APIs, and web applications to send and receive data in formats like JSON, XML, or plain text.
4. GUI and Web Development
- In GUI or web applications, strings are used for displaying messages, labels, button names, form data, and error prompts.
5. Database Connectivity
- JDBC (Java Database Connectivity) uses strings for writing SQL queries, setting parameters, and retrieving data from the database.
6. Logging and Debugging
- String messages are used for logging system behavior, errors, and debugging information.
7. Easy Manipulation with Built-in Methods
- Java provides many built-in methods (substring(), replace(), toLowerCase(), concat(), etc.) to easily manipulate text data.
Interfaces and Classes in Strings in Java
In Java, the String class implements the CharSequence interface, which represents a readable sequence of characters. One of the notable implementations of this interface is CharBuffer, which allows efficient character manipulation using buffers. This is commonly utilized in Java's regular expression package (java.util.regex) for pattern matching and text processing. Strings in Java are immutable, meaning once a String object is created, its value cannot be changed. This immutability ensures security, thread safety, and efficient memory handling during string operations.
CharSequence Interface
In Java, the CharSequence Interface is used to represent the order of characters.
The CharSequence interface is implemented by the class known as CharBuffer. By using character buffers instead of CharSequences, this class enables their use. Java.util.regex's regular-expression package serves as an illustration of this usage. A string is a collection of characters. String objects in Java are immutable, which means they can never be modified after they have been created.
The following list includes classes that implement the CharSequence interface:
- String
- StringBuffer
- StringBuilder
1. String
A string is an immutable class i.e. it cannot be changed. We need to create a new object and functions like toupper, tolower, etc return a new object.
Example
String str= "Scholarhat";
or
String str= new String("Scholarhat")
2. StringBuffer
The majority of the functionality of strings is provided by the peer class of StringBuffer. StringBuffer represents expandable and writable character sequences, whereas the string represents fixed-length, immutable character sequences.
Example
StringBuffer demoString = new StringBuffer("Scholarhat");
3. StringBuilder
A mutable string of characters is represented by the Java class StringBuilder. The StringBuilder class offers a substitute for the String Class in Java since it constructs a mutable sequence of characters instead of an immutable one as the String Class does.
Example
StringBuilder demoString = new StringBuilder();
demoString.append("Scholarhat");
StringTokenizer
A string can be divided into tokens using Java's StringTokenizer class. A StringTokenizer object internally maintains a current position within the string to be tokenized. A token is returned by taking a substring of the string used to create the StringTokenizer object.
Example
Classes that Implement the CharSequence Interface in Java
Java provides several classes that implement the CharSequence interface, each with different characteristics and use cases. The main ones include:1. String
The String class in Java is immutable, meaning once a String object is created, its content cannot be changed. Operations like toUpperCase(), toLowerCase(), or replace() return a new String object instead of modifying the original one.Example:
String str = "Scholarhat";
// or
String str = new String("Scholarhat");
2. StringBuffer
StringBuffer is a peer class of String but represents a mutable and thread-safe sequence of characters. It allows modification of strings without creating new objects, making it suitable for use in multithreaded environments.Example:
StringBuffer demoString = new StringBuffer("Scholarhat");
3. StringBuilder
StringBuilder is similar to StringBuffer but is not thread-safe. It is used when string manipulation is needed in a single-threaded environment. Since it avoids synchronization overhead, it is faster than StringBuffer.Example:
StringBuilder demoString = new StringBuilder();
demoString.append("Scholarhat");
Java Strings: Mutable or Immutable
- Strings in Java are immutable, i.e. once they are formed, their values cannot be altered.
- To avoid conflicts that can result from numerous references to the same string object, immutability is required.
- Multiple references may point to a single string object in the String constant pool in Java.
- If one reference was permitted to change the string's value, it might impact other references and cause problems.
- To avoid these conflicts, Java ensures that string objects are immutable, meaning that their values cannot be changed.
Immutable String in Java
In Java, strings are immutable, which means that once a String object is created, its value cannot be modified. Any operation that appears to change a string—such as concatenation, replacement, or case conversion—actually creates a new String object in memory, leaving the original string unchanged. This immutability enhances performance, security, and thread safety in Java applications.
Characteristics:
- Strings cannot be changed once created:
When you create a string, its value stays the same. Any operation like concatenation or replacement creates a new string.
- Thread-safe:
Since strings are immutable, they can be safely shared between multiple threads without causing issues.
- Stored in the String Pool:
Java stores strings in a special memory area called the String Pool to save memory. If two strings have the same value, they share the same memory location.
- Changes create new objects:
When you modify a string, a new object is created in memory, and the original one remains unchanged.
- Safe in collections:
Because the string’s value doesn’t change, it works well in data structures like HashMap and HashSet that rely on consistent values.
- More predictable and less error-prone:
Since strings don’t change unexpectedly, your code is easier to understand and debug.
Advantages:
Memory Optimization: Optimizes memory usage through the String Constant Pool by reusing existing string objects with the same value.
Thread-Safety: Strings can be safely shared between multiple threads without synchronization, improving performance in multithreaded applications.
Reliable Hashing: Since the value never changes, the hash code of a string remains constant. This is crucial when using strings as keys in collections like HashMap.
Fewer Bugs: Immutability prevents accidental changes to string values, reducing the risk of unexpected behavior in code.
Safe for Class Loading & Reflection: Strings are often used to refer to class names and methods. Their immutability ensures those names stay consistent.
Improves Caching: Frequently used strings can be cached safely because their content won’t change.
Example:
public class ImmutableStringExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str = "Hello";
str.concat(" World");
System.out.println(str); // Output: Hello
String newStr = str.concat(" World");
System.out.println(newStr); // Output: Hello World
}
} Output
Hello
Hello WorldExplanation
The concat method does not change the original string str but creates a new string newStr.
Memory Allotment of String
In Java, memory for strings is managed through two main areas:
Heap Memory: Stores string objects created using the new keyword. Each object gets its own memory allocation, even if it contains the same text.
String Constant Pool: A special memory area inside the heap used to store string literals. Java automatically reuses strings in this pool to optimize memory usage.
Characteristics:
Strings created using the new keyword are stored in the heap memory, creating a new object each time
The String Pool avoids storing duplicate values by pointing multiple references to the same string object.
Java uses String interning to enable memory-efficient reuse of string literals. The String Pool is maintained by the JVM, and it grows only when a new literal is encountered. Only one copy of each unique literal string is stored in the pool, ensuring memory savings.
Advantages:
Memory Efficiency: Stores only one copy of each string literal in the constant pool.
Improved Performance: Enhances speed in applications with frequent string use.
Fast Comparisons: Enables faster reference-based comparison using ==.
Reduces Garbage Collection Overhead: Fewer duplicate objects lead to less memory cleanup.
Thread-Safety of Pool Strings: Immutable and safely shared across threads.
Enhances Application Scalability: Ideal for large apps with repetitive string usage.
Optimized by the JVM: JVM efficiently manages the String Pool for better runtime performance.
public class StringMemoryExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "Hello"; // Stored in String Pool
String s2 = "Hello"; // References the same object in String Pool
String s3 = new String("Hello"); // Stored in Heap Memory
String s4 = s3.intern(); // References String Pool object
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
System.out.println(s1 == s4); // true
}
} Output
true
false
trueExplanation
- s1 and s2 point to the same object in the String Pool.
- s3 is a new object in the heap.
- s4 uses intern() to refer to the String Pool object.
Methods of Java Strings
| Name | Description |
| length() | Returns the length (number of characters) of the string. |
| charAt(int index) | Returns the character at the specified index within the string (indexing starts at 0). |
| substring(int beginIndex) | Returns a new string that is a substring of the original string starting from the specified beginIndex. |
| substring(int beginIndex, int endIndex) | Returns a substring of the original string starting from beginIndex and ending just before endIndex. |
| concat(String str) | Concatenates the specified string str to the end of the current string. |
| equals(Object obj) | Check if the current string is equal to the specified object. Returns true if equal, false otherwise. |
| equalsIgnoreCase(String anotherString) | Compares the current string to another string, ignoring case differences. |
| indexOf(String str) | Returns the index of the first occurrence of the specified substring str within the string, or -1 if not found. |
| replace(char oldChar, char newChar) | Replace all occurrences of oldChar with newChar in the string. |
| split(String regex) | Splits the string into an array of substrings based on the regular expression regex. |
String Manipulation
String manipulation mainly works for changing the case, fetching a character from a string, and trimming the content. There are other various important methods in string manipulation such as:
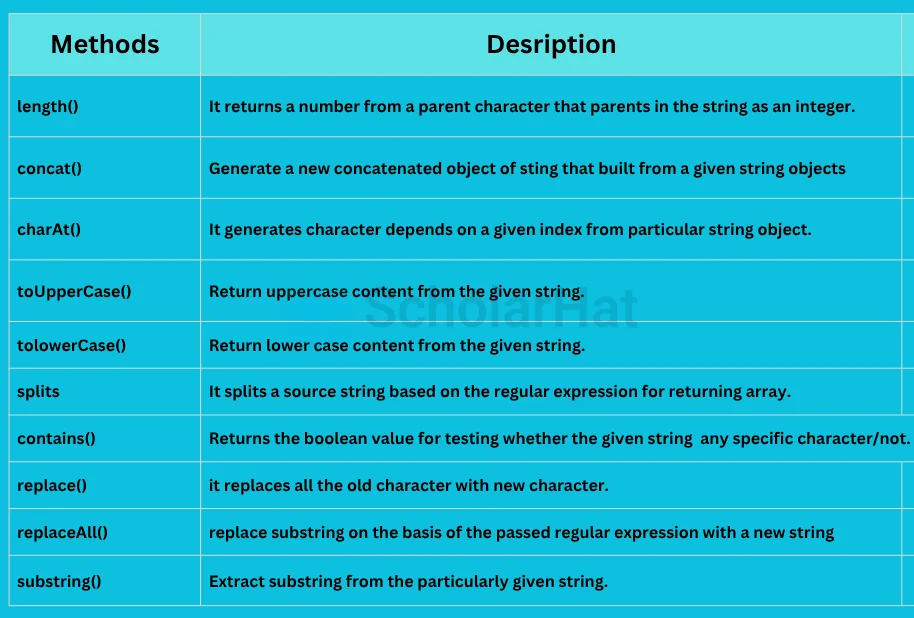
String Manipulation Example in Java in our Java Compiler
class String_Manipulation_Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String ob1 = "Scholar-Hat"; //creates a string object
//string length
System.out.println("Length of the String: " +ob1);
char arr[] = {'j','k','a','q','e' };
String ob2 = new String(arr); //String from an array
//string concatenation
System.out.println("Concatenate String and String Array: " +ob1.concat(ob2));
//to upper case
System.out.println("Contents of String in uppercase: " +ob1.toUpperCase());
//to lower case
System.out.println("Contents of String in lowercase: " +ob1.toLowerCase());
//split function
for(String res: ob1.split("-",2))
System.out.println("Splitting the String: " +res);
//contains function
System.out.println("Contains() function in String: " +(ob1.contains("Scholar")));
//Replace function
System.out.println("Replace function in String: " +(ob1.replace('o','a')));
//ReplaceAll function
System.out.println("ReplaceAll function in String: " +(ob1.replaceAll("lar","o")));
//substring function
System.out.println("Substring in String: " +(ob1.substring(3,6)));
//trim function
String str = " Scholar-Hat! ";
System.out.println("Without Trim function in String: " +str);
System.out.println("Trim function in String: " +(str.trim()));
}
}
When you execute the above program in the Java Playground to see the output.
Output
Length of the String: Scholar-Hat
Concatenate String and String Array: Scholar-Hatjkaqe
Contents of the String in uppercase: SCHOLAR-HAT
Contents of the String in lowercase: scholar-hat
Splitting the String: Scholar
Splitting the String: Hat
Contains() function in String: true
Replace function in String: Schalar-Hat
ReplaceAll function in String: Schoo-Hat
Substring in String: ola
Without Trim function in String: Scholar Hat!
Trim function in String: Scholar Hat!
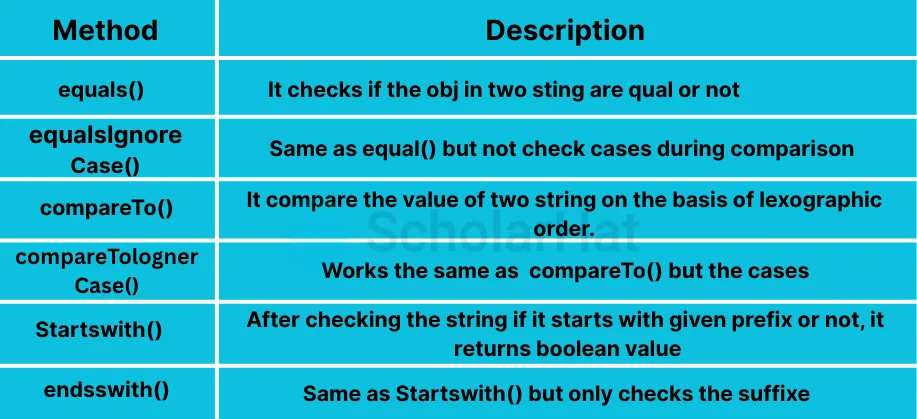
String Comparison
Some important methods are used to make the string comparison, such as:
String ComparisonExample
class String_Comparison_Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String ob1 = "Scholar-Hat"; //creates a string object
String ob2 = "scholar-hat";
//equals function
System.out.println("Using equals function: " +(ob1.equals(ob2)));
System.out.println("Using equalsIgnoreCase function: " +(ob1.equalsIgnoreCase(ob2)));
//compareTo function
System.out.println("Using compareTo function: " +(ob1.compareTo(ob2)));
System.out.println("Using compareToIgnoreCase function: " +(ob1.compareToIgnoreCase(ob2)));
//startsWith function
System.out.println("Using startsWith function: " +(ob1.startsWith("Sc")));
//endsWith function
System.out.println("Using endsWith function: " +(ob1.endsWith("at")));
}
}
Output
Using equals functions: false
Using equalsIgnoreCase functions: true
Using compareTo functions: 4
Using compareToIgnoreCase functions: 0
Using startsWith functions: true
Using endsWith functions: true
Searching in a String
There are some specific methods to search characters in a String Object, those are:

Searching in a StringExample
class String_Searching_Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
String ob1 = "Scholar-Hat"; //creates a string object
System.out.println("Using indexOf function: " +ob1.indexOf('a'));
System.out.println("Using lastIndexOf function: " +ob1.lastIndexOf('a'));
}
}
Output
Using indexOf function: 5
Using lastIndexOf function: 9Explanation
- String Initialization: String ob1 = "Scholar-Hat"; creates a string "Scholar-Hat".
- indexOf Method: ob1.indexOf('a') finds the first occurrence of 'a' (index 3) and prints it.
- lastIndexOf Method: ob1.lastIndexOf('a') finds the last occurrence of 'a' (index 9) and prints it.
| Read More: Top 30+ String in Java Interview Questions with Answers 2025 |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the String in Java is a powerful and essential part of the language used to handle and manipulate text data. Whether you are building simple applications or complex systems, understanding how to use the String in Java effectively is key to writing clean and efficient code.
Only 15% of Java Developers know Microservices well, stand out with Java Microservices Certification Training. Also, consider enrolling in Java Full Stack Course for full-stack expertise.
Practice with the Following MCQs
Q 1: Which method is used to compare two strings in Java?
Explanation: The equals() method is used to compare two strings in Java to check for their equality.
Q 2: Which of the following is the correct way to create a string in Java?
Explanation: Both ways are correct for creating a string in Java. The first method uses string literals, while the second uses the String constructor.
Q 3: What is the result of the following code snippet in Java?
Explanation: The substring() method extracts a part of the string. It returns the substring from index 0 to 5, i.e., "Hello".
Q 4: Which method is used to convert all characters of a string to lowercase?
Explanation: The toLowerCase() method in Java is used to convert all the characters in the string to lowercase.
Q 5: What does the length() method of a string return in Java?
Explanation: The length() method returns the total number of characters in the string, including spaces.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.