06
FebTypes of variables in Java with examples: Local, Instance & Static
A variable in Java is like a container or box that stores some values, such as numbers, text, or any data. You give the box a name, and you can use and change the value stored inside it during a program.
In this Java tutorial, we'll get into the details of Java variables. Java Online Training is a convenient option for gaining expertise in Java and harnessing its power for various applications.
Start coding with confidence—join our Java Certification Course for Free and gain hands-on experience.
Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions For Freshers
What is a Variable in Java?
A variable in Java is a name for a memory location used to store data. It must be declared with a data type like int, String, or float. A variable in Java can hold only one type of data, and its value can be changed during the program. You should always initialize the variable before using it. Overall, variable in Java helps in storing, changing, and reusing data throughout the program.
Declaration of Variable in Java
A variable in Java is used to store different types of data like numbers, text, or true/false values. Based on the type of data, there are different ways to declare a variable in Java.
- String is used to store text, like "Hello World".
- int is used to store whole numbers without decimals, like 10 or 100.
- float is used to store numbers with decimal points, like 3.14 or 5.75.
- char is used to store single characters, like 'x' or 'y', and is always written in single quotes.
- boolean is used to store only two values: true or false.
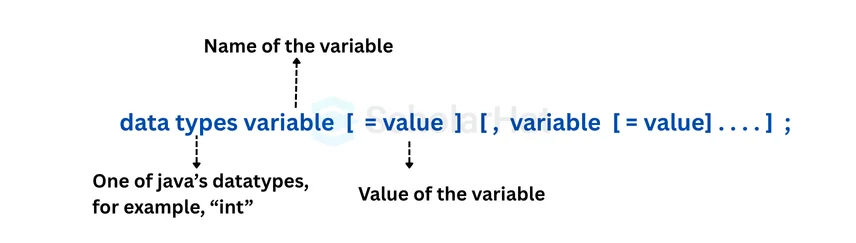
To declare a variable in Java, programmers must follow two main parts:
- Data type: This tells what kind of data the variable will store, such as int, float, or String.
- Variable name: This is the name you give to the variable, so you can use it later in your code.
In short, declaring a variable in Java helps you store data in a proper format and use it again when needed.
Rules for Declaring Variables in Java
When you declare a variable in Java, you need to follow some simple rules to avoid errors. Let’s look at them one by one.
- A variable in Java must start with a letter (like a or B), a dollar sign ($), or an underscore (_). You cannot start it with other special characters like @ or #. int $count = 5; or int _total = 10; are valid.
- A variable in Java cannot have more than 64 characters in its name.int studentMarksInMathAndScience = 90; is okay, but avoid names that are too long.
- You are not allowed to use blank spaces in the name of a variable in Java.int student age = 20; is wrong. You should write it as studentAge.
- You cannot use Java's reserved keywords (like class, public, static) as variable names. int class = 10; is not allowed because class is a keyword.
- The name of the variable must come before the assignment operator (=). int age = 25; is correct, but 25 = age; is incorrect.
Let's look at the variable declaration in our Java Playground.
Example
class Example
{
public static void main ( String[] args )
{
long payAmount = 184; //the declaration of the variable
System.out.println("The variable contains: " + payAmount );
}
}
Output
Long payAmount = 184;
Variable Initialization
To initialize a variable in Java, there are three main components:
- Data type: It defines the type of data that will be stored, such as int, float, String, etc.
- Variable name: This is the specific name given to the variable so you can use it in the program.
- Value: This is the actual data that you assign to the variable when initializing it.
Read More - Java Web Developer Salary
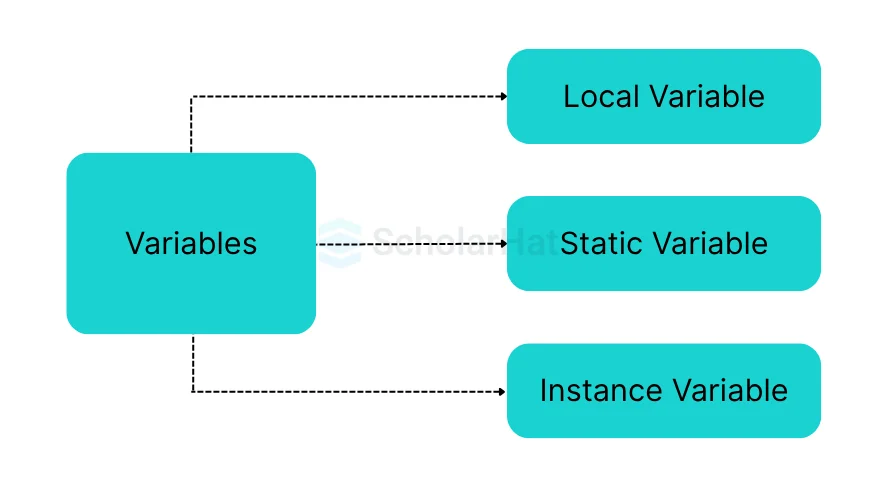
Types of Variables in Java
There are three main types of variables in Java: local variables, instance variables, and static variables, each used in different parts of a program
1. Local Variables in Java
A local variable in Java can be declared inside a method, a constructor, or a block, and can be used within the method, constructor, or block.
- Scope: A local variable is only accessible within the method, constructor, or block where it is declared. You cannot use it outside that block.
- Lifetime: The lifetime of a local variable is limited to the time the method or block is running. Once the block finishes, the variable is destroyed.
- Default Value: Local variables do not have a default value. You must initialize them before using, or it will cause a compile-time error.
Example
import java.io.*;
class DNT
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int var = 89; // Declared a Local Variable
// This variable is local to this main method only
System.out.println("Local Variable: " + var);
}}This demonstration in our Java Compiler illustrates the concept of local variables with a scope that is only the main method by declaring and initializing a local variable "var" with the value 89.
Output
Local Variable: 89
2. Instance Variables in Java
An instance variable in Java is a non-static variable declared inside a class but outside any method, and it is associated with an object. An instance variable is created when an object class is generated.
- Scope: An instance variable is accessible in all non-static methods of the class. It belongs to a specific object, so each object has its own copy.
- Lifetime: The lifetime of an instance variable lasts as long as the object exists. When the object is destroyed, the variable is also destroyed.
- Default Value: Instance variables do have default values. For example, int is 0, boolean is false, and object types are null if not initialized.
Example
import java.io.*;
class DNT
{
public String student; // Declared Instance Variable
public DNT()
{ // Default Constructor
this.student= "Urmi Bose"; // initializing Instance Variable
}
//Main Method
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Object Creation
DNT name = new DNT();
System.out.println("Student name is: " + name.student);
}
}In this Java example, the class "DNT" contains a declaration for an instance variable named "student" that is initialized in the default constructor to demonstrate the use of instance variables. An object of the class is then constructed to allow access to and printing of the student's name.
Output
Student name is : Urmi Bose
3. Static Variables in Java
A static variable in Java belongs to the class itself, not to any specific object. This means all class objects share the same static variable.
- Shared Value: A static variable is shared among all class objects. If one object changes its value, it affects all others.
- Declared with the static keyword: You must use the static keyword while declaring it. Example: static int count;
- Scope: It can be accessed by all methods in the class, including static methods.
- Lifetime: The static variable exists as long as the program runs, and it is created when the class is loaded.
- Default Value: Static variables have default values, such as 0 for int, false for boolean, and null for objects.
- Accessing: You can access it using the class name like ClassName.variableName.
Example
import java.io.*;
class DNT
{
public static String student= "Urmi Bose"; //Declared static variable
public static void main (String[] args) {
//student variable can be accessed without object creation
System.out.println("Student Name is : "+DNT.student);
}
}This Java example prints the value "Urmi Bose" from a static variable named "student" that is declared inside the class "DNT," enabling access by class name simply without creating an object.
Output
Student Name is: Urmi BoseDifference between Instance and Static Variable in Java
Understanding the differences between instance variables and static variables in Java is crucial. So, let's look at the differences in the following table.
| Features | Instance Variable in Java | Static Variable in Java |
| Belongs To | Belongs to one object | Belongs to the class, not any one object |
| Keyword Used | No special keyword needed | Uses the static keyword |
| Memory | Each object gets its own copy | One copy is shared by all objects |
| How to Use | Use it with the object name | Use it with the class name |
| When Created | Created when you make a new object | Created when the class is loaded into memory |
| Lifetime | Lives as long as the object is in use | Lives as long as the program is running |
| Default Value | Gets the default value, like 0, false, or null | Also gets a default value like 0, false, or null |
| Used for | When you need different values for each object | When you want a common value for all objects |
This makes it easy to remember that an instance variable is personal to each object, and a static variable in Java is shared by everyone.
Conlusion
In conclusion, understanding variable in Java is very important because it helps you store and manage data in your program. By knowing the types, rules, and uses of variable in Java, you can write cleaner and more effective code. Whether it's a local, instance, or static variable, each one plays a key role in building a strong Java application.
Don’t just code—lead projects. Enroll in Advanced Java Full-Stack Training and become industry-ready. Also consider, Java Solution Architect Training to move into Java Architect roles.
If you are preparing for the Java Interview, this Java Interview Questions and Answers Book can really help you. It has simple questions and answers that are easy to understand. Download and read it for free today!
Test your skills with the following MCQs
Boost your confidence and sharpen your skills — take this quick quiz and see how much you really know!
Q 1: Which keyword is used to create a class in Java?
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.