06
MarTop 50 JSP Interview Questions and Answers
JSP interview questions and answers are an essential resource for candidates preparing for Java web development roles. JSP (JavaServer Pages) is a core technology in Java EE used to create dynamic, server-side web content by embedding Java code within HTML.
In this Java tutorial, JSP interview questions and answers ranging from basic concepts like lifecycle, directives, and scriptlets to advanced topics such as thread safety, MVC integration, and performance optimization are given. To learn Java programing from basics to advanced enroll in our Free Java Course to boost your career.
JSP Interview Questions and Answers for Freshers
1. What is JSP?
JSP (JavaServer Pages) is a server-side technology used to create dynamic web pages in Java. It allows developers to embed Java code directly into HTML pages, which the server processes to generate dynamic content before sending it to the client’s browser.
Key features of JSP are:
- Server-Side Technology: JSP runs on the server and produces HTML, XML, or other formats for the client.
- Dynamic Content: Unlike static HTML, JSP can generate content based on user input, database queries, or server-side logic.
- Built on Java: Fully integrates with the Java EE platform, leveraging Java APIs, servlets, and JavaBeans.
- Separation of Concerns: Allows presentation (HTML) and business logic (Java) to be separated, often using JSP with servlets or MVC frameworks.
- Lifecycle: JSP is compiled into a servlet by the server, then executed like any other Java servlet.
2. What is the use of Java Server Pages (JSP)?
Uses of Java Server Pages are:
- Dynamic Content Generation:JSP can generate content dynamically based on user requests, database data, or session information.
- Separation of Presentation and Business Logic:Works well with JavaBeans and Servlets to separate UI (HTML/CSS) from business logic.
- Web Application Development:Enables developers to build interactive and responsive web pages for Java web applications.
- Form Handling and Data Processing:Can process user input from forms, perform calculations, and display results dynamically.
- Integration with Java EE Components:Works with Servlets, JDBC, EJBs, and MVC frameworks for enterprise-level web applications.
3. Explain the JSP life cycle.
The JSP (JavaServer Pages) life cycle defines the steps a JSP page goes through from creation to destruction on the server.
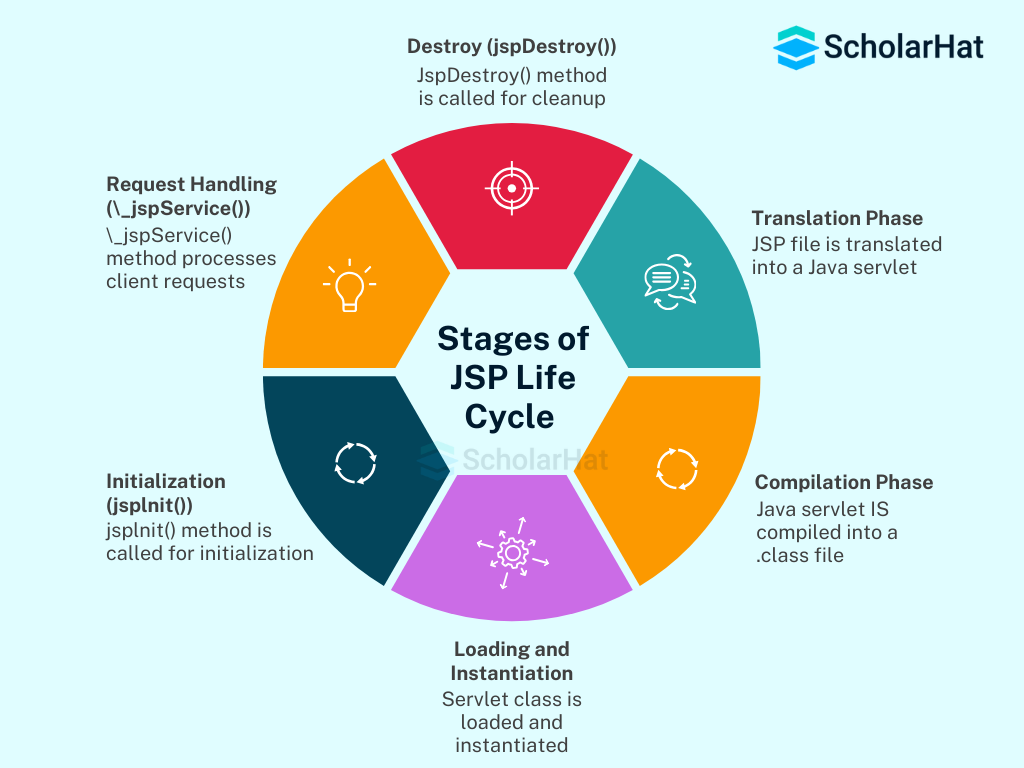
Stages of JSP Life Cycle
- The JSP file (.jsp) is translated into a Java servlet by the JSP engine.
- All HTML is converted to out.println() statements, and Java code is included in the servlet class.
- The generated servlet .java file is compiled into a .class file (a servlet class).
- Compilation errors here prevent the JSP from running.
- The compiled servlet class is loaded into the server memory.
- A servlet instance is created.
- The server calls the jspInit() method once to initialize the JSP.
- Used for resource allocation like opening database connections or initializing variables.
- For every client request, the _jspService(HttpServletRequest, HttpServletResponse) method is called.
- Contains the logic to process requests and generate dynamic content.
- JSP developers cannot override _jspService() directly; it’s handled internally.
- When the JSP is taken out of service or server shuts down, jspDestroy() is called.
- Used to release resources like closing database connections.
4. What are implicit objects in JSP? Name at least five.
| Object | Purpose |
| request | Represents HttpServletRequest; used to get request parameters, headers, etc. |
| response | Represents HttpServletResponse; used to set response content type, headers, or redirect. |
| out | Represents JspWriter; used to write output to the client. |
| session | Represents HttpSession; used to store and retrieve session data. |
| application | Represents ServletContext; used to store application-wide data. |
5. What are JSP directives? Explain the types.
<%@ directive attribute="value" %>
Types of JSP Directives
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=UTF-8" %>
<%@ include file="header.jsp" %>
<%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core" %>
6. What is the difference between JSP and JavaScript?
| Aspect | JSP | JavaScript |
| Type | JSP is a server-side technology | JavaScript is a client-side scripting language |
| Execution | Runs on the web server. The server processes JSP code and sends HTML to the client. | Runs in the user’s browser. Executes scripts after the HTML is loaded. |
| Purpose | Generates dynamic web content using Java | Adds interactivity, handles events, manipulates DOM |
| Integration | Integrates with Java, servlets, JavaBeans | Works with HTML/CSS; can interact with server via AJAX |
| Output | Produces HTML, XML, or other content | Directly manipulates content in the browser |
| Dependency | Requires a web server with JSP/Servet support | Requires a browser to exceutes |
| Use Case | Processing form data, database access, and creating dynamic web pages | Validating forms, creating animations, handling user events, interactive UI |
7. What are JSP operators? List some common ones.
JSP operators are used within JSP scripting elements (like scriptlets or expressions) to perform operations on variables and values. Since JSP uses Java syntax, it supports all Java operators.They perform arithmetic, logical, relational, or bitwise operations in JSP code. They also helps to manipulate data, make decisions, and control flow within JSP pages.
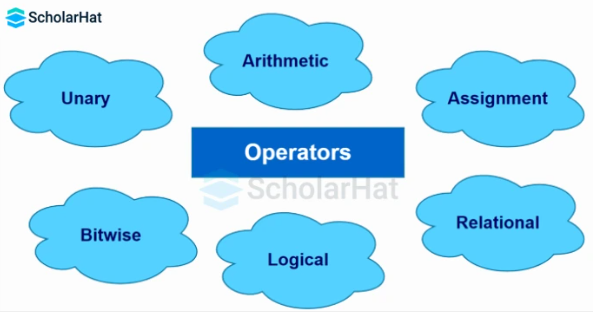
Common JSP Operators are:
- Arithmetic (+, -, *, /, %)
- Relational (==, !=, <, >, <=, >=)
- Logical (&&, ||, !)
- Assignment (=, +=, -=)
- Unary(+,-,++,--)
- Ternary (? :)
- Bitwise (&, |, ^, ~, <<, >>).
8. What is the role of the jspInit() method?
The jspInit() method is a lifecycle method in JSP that is called once when the JSP page is initialized. It is similar to the init() method in servlets
- It initializes resources required by the JSP page, such as database connections, file streams, or configuration parameters.
- It executes only once during the lifecycle, before the _jspService() method handles any requests.
- It helps set up the environment so that subsequent requests can be processed efficiently.
9. What are the types of elements in JSP?
JSP elements are the building blocks used to write Java code, embed dynamic content, and control the behavior of JSP pages. They can be broadly categorized as follows:
The main types of JSP elements are:
- Directives: They give instructions to the JSP container for page translation and compilation (page, include, taglib).
- Scripting Elements: They embed Java code in JSP: Declarations, Scriptlets, and Expressions.
- Actions: They are predefined XML-style tags to perform tasks like including files, forwarding requests, or using JavaBeans (jsp:include, jsp:forward, jsp:useBean).
- Implicit Objects: They are predefined objects available without declaration (request, response, session, out, application).
- Comments: They add notes ignored by the container and not sent to the client (<%-- comment --%>).
10. What is a JSP comment tag?
- Unlike HTML comments (<!-- comment -->), JSP comments are completely invisible to the client.
- They are useful for adding notes or explanations for developers within the JSP page.
- JSP comments cannot contain JSP elements or code that needs to be executed.
11. What is JSP for loop.
12. What is a JSP declaration?
A JSP declaration is used to declare variables and methods that are available throughout the JSP page. Declarations are inserted into the generated servlet class outside the _jspService() method, making them accessible across multiple requests if needed.
13. What is a JSP Scriptlet?
A JSP scriptlet allows you to embed Java code directly into a JSP page. The code inside a scriptlet is inserted into the _jspService() method of the generated servlet and executed every time the page is requested.
Key Points:
- Scriptlets execute for each request since they are part of _jspService().
- Variables declared inside a scriptlet are local to that request.
- Should be used carefully; modern JSP encourages JSTL and EL instead of heavy use of scriptlets.
14. What is the syntax of the JSP while loop?
A while loop in JSP is used to execute a block of Java code repeatedly as long as a specified condition is true. Since JSP supports Java syntax, you can use a standard Java while loop inside scriptlets to generate dynamic content.
Syntax:
<%
while (condition) {
// Java statements
out.println("Output text or dynamic content");
}
%>Explanation:
- <% %> is the scriptlet tag.
- out.println() is used to display content in the browser.
- The loop runs while the condition is true, allowing dynamic repeated output.
15. What are Java Servlets?
Java Servlet is a server-side Java program that handles client requests and generates dynamic web content, typically in response to HTTP requests. Servlets run inside a web container (like Apache Tomcat) and are part of the Java EE / Jakarta EE framework.
Key Features of Java Servlets:
- Server-side execution: All code runs on the server, not the client.
- Platform-independent: Java Servlets are portable across servers that support the Servlet API.
- Dynamic content: Can generate HTML, XML, JSON, or other responses based on request data.
- Session management: Supports cookies, URL rewriting, and HttpSession for maintaining client sessions.
- Integration: Can interact with databases, JSPs, and other server-side components.
Basic Servlet Structure
import java.io.*;
import javax.servlet.*;
import javax.servlet.http.*;
public class HelloServlet extends HttpServlet {
protected void doGet(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response)
throws ServletException, IOException {
response.setContentType("text/html");
PrintWriter out = response.getWriter();
out.println("Hello, World!");
}
}- HttpServlet is extended to create a servlet.
- doGet() handles HTTP GET requests; doPost() handles POST requests.
- HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse are used to access request data and send responses.
16. Difference between include directive and include action?
| Aspect | Include Directive | Include Action |
| Type of Include | Static include | Dynamic include |
| Execution Time | Performed at translation/compile time (before JSP is converted to servlet) | Performed at request/runtime (every time the page is requested) |
| Syntax | %@ include file="filename.jsp" | <jsp:include page="filename.jsp" /> |
| Content Inclusion | Entire content of the included file is merged into the JSP page before compilation | Includes output of the included JSP/servlet at runtime |
| Use Case | For reusable static content like headers, footers, or menus | For dynamic content that may change per request |
| Impact of Changes | Requires recompilation if included file changes | Changes reflect immediately without recompilation |
17. What is the purpose of the Page directive in JSP?
Page directive in JSP is used to define global settings and configuration information for a JSP page. It tells the JSP container how to process the page and controls aspects like importing classes, handling errors, session usage, etc.
Purpose of the Page Directive:
- To set up environment details for the JSP page.
- To control page-level behaviors like session, error handling, buffer, and content type.
- To import Java classes for use within the JSP.
18. Explain some advantages of using JSP
Some advantages of using JSP (Java Server Pages) are:
19. What do you mean by Expression Tag in JSP?
In JSP, an Expression Tag is used to evaluate and print Java expressions directly into the client’s browser, without using out.print().
- Syntax: <%= expression %> (without semicolon at the end).
- The expression is evaluated at runtime, converted to a string, and then displayed in the response.
20. What are the best practices for using JSP ?
- Follow MVC: Keep JSPs as view only; move business logic to servlets or backend classes.
- Avoid Scriptlets: Use EL (Expression Language) and JSTL for cleaner, maintainable code.
- Use Tag Libraries: Promote reusability and modularity; avoid repetitive code.
- Secure JSPs: Place JSPs under WEB-INF to prevent direct access.
- Optimize Performance: Precompile JSPs, use caching, connection pooling, and externalize static resources.
JSP Interview Questions for Intermediate
21. How does JSP handle session management?
JSP handles session management mainly through the HttpSession object, which is one of its implicit objects. It allows you to track user interactions across multiple requests.
Ways JSP handles session management:
- JSP automatically creates a session object for each user unless explicitly disabled.
- Example:
<%
String name = (String) session.getAttribute("username");
if(name == null){
session.setAttribute("username", "Yamini");
}
%>
2. Cookies
- JSP can use cookies to store small pieces of user data on the client’s browser
- Example:
Cookie ck = new Cookie("user", "Name");
response.addCookie(ck);
3. URL Rewriting
- If cookies are disabled, JSP appends a session ID to the URL for tracking.
- Example:
<a href="profile.jsp;jsessionid=<%= session.getId() %>">Profile</a>
4. Hidden Form Fields
- Pass session data between requests using hidden fields in forms.
22. What is JSTL? What are its core tags used for?
JSTL stands for JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library. It is a collection of predefined JSP tags that simplify the development of JSP pages by eliminating the need for writing Java code inside JSP. It provides standard functionalities like iteration, condition checking, database access, internationalization, and XML manipulation.
The core tags belong to the c library (http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core) and are mainly used for flow control, iteration, variable manipulation, and conditional processing.
| Tag | Purpose |
| c:out | Displays data on the JSP page (like expression tag <%= %>). |
| c:set | Sets a variable in a given scope (page, request, session, or application). |
| c:remove | Removes a variable from a specified scope. |
| c:if | Performs conditional execution |
| c:choose, c:when, c:otherwise | Works like a switch-case structure for multuple conditions. |
23. How does JSP support MVC architecture?
JSP supports MVC (Model–View–Controller) architecture by acting as the View component that displays data to users, while Servlets act as the Controller and JavaBeans (or other Java classes) act as the Model.
- Contains application logic and interacts with the database (e.g., JavaBeans, POJOs, or EJBs).
- Stores and manages the data to be shown.
- JSP is used for the UI (HTML, CSS, JS, JSTL, EL).
- Displays data sent by the controller in a user-friendly way.
- Receives requests from users.
- Invokes the Model to process data.
- Selects the JSP page (View) to render the response.
24. What's the difference between forward and redirect in JSP?
| Feature | Forward ( RequestDispatcher.forward() ) | Redirect ( response.sendRedirect() ) |
| Definition | Passes the request from one resources to another on the server side. | Sends a response to the client, asking the browser to make a new request to another resource. |
| Request Object | Same request is shared | A new request object is created |
| URL in Browser | URL does not change (browser still shows the first page). | URL changes to the redirected page. |
| Performance | Faster (single request, server-side transfer). | Slower (two requests: one to original page, one to new page). |
| Use Case | Used when transferring control within the server (e.g., to another JSP or Servlet). | Used when you need to navigate to an external resource or after a form submission to prevent duplicate submissions. |
25. How does JSP processing take place?
When a client requests a JSP page, the server first checks whether the page is already compiled. If not, the JSP is converted into a servlet class and then compiled into bytecode. The compiled servlet executes on the server, interacts with business logic or databases if needed, and dynamically generates the response (usually HTML, JSON, or XML). Finally, this output is sent back to the client’s browser.
26. What are the various action tags used in JSP?
JSP action tags are XML-style tags that instruct the JSP container to perform specific tasks like including files, forwarding requests, interacting with JavaBeans, or generating dynamic content.
Common JSP Action Tags
| Tag | Purpose |
| jsp:include | Includes the output of another JSP or servlet at runtime |
| jsp:forward | Forwards the request to another resource (JSP/Servlet). |
| jsp:useBean | Instantiates or accesses a JavaBean and stores it in a given scope. |
| jsp:setProperty | Sets the property of a JavaBean. |
| jsp:getProperty | Retrieves the value of a JavaBean property and displays it. |
27. What is the anatomy of a JSP page?
A JSP page is a combination of HTML and special JSP elements that allow dynamic content generation. The main components are:
- Directives: Provide instructions to the JSP container about page behavior (e.g., %@ page %, %@ include %).
- Scriptlets: Embed Java code executed per request (<% ... %>).
- Declarations: Declare variables or methods for use across the JSP (<%! ... %>).
- Expressions: Evaluate and display Java expressions directly (<%= ... %>).
- Action Tags: XML-style tags for tasks like including pages or using JavaBeans (<jsp:include>, <jsp:useBean>).
- Implicit Objects: Predefined objects available without declaration (request, response, session, out).
- Comments: Notes ignored by the server: JSP (<%-- comment --%>) and HTML (<!-- comment -->).
- HTML / Static Content: Standard HTML, CSS, JavaScript defining page layout and style.
28. Which methods are used for reading form data in JSP?
In JSP, form data submitted via HTML forms can be accessed using the request implicit object, which represents the client’s request. The most common methods are:
<%
String username = request.getParameter("username");
%>
<%
String[] hobbies = request.getParameterValues("hobbies");
for(String hobby : hobbies){
out.println(hobby + "<br>");
}
%>
<%
java.util.Enumeration params = request.getParameterNames();
while(params.hasMoreElements()){
String name = (String) params.nextElement();
out.println(name + ": " + request.getParameter(name) + "<br>");
}
%>
29. What is J2EE?
J2EE is a platform for developing and deploying enterprise-level, multi-tier web applications in Java. It provides a standardized environment with a set of APIs, services, and protocols to build scalable, secure, and distributed applications.
30. What are JavaBeans in the context of JSP?
JavaBean is a reusable Java class that follows specific conventions and is used to encapsulate data. In JSP, JavaBeans are often used as model components to separate business logic from presentation logic, enabling clean MVC architecture.
- Must have a public default (no-argument) constructor.
- Properties should be private, accessed via public getter and setter methods.
- Must implement Serializable (optional, but recommended for session storage).
Example of a JavaBean:
public class User implements java.io.Serializable {
private String name;
private int age;
// Default constructor
public User() {}
// Getter and setter for name
public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
// Getter and setter for age
public int getAge() { return age; }
public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; }
}
Using JavaBeans in JSP:
<jsp:useBean id="user" class="com.example.User" scope="session" />
<jsp:setProperty name="user" property="name" value="Your Name" />
Hello, <jsp:getProperty name="user" property="name" />
- <jsp:useBean> creates or accesses a bean.
- <jsp:setProperty> sets property values.
- <jsp:getProperty> retrieves property values.
31. What is a JSP container?
JSP container (also called a JSP engine) is a part of a web server or servlet container that is responsible for executing JSP pages. It manages the translation of JSP into servlets, compilation, execution, and lifecycle of JSP pages.
Key Responsibilities of a JSP Container:
- Translation: Converts JSP pages into Java Servlets.
- Compilation: Compiles the generated Servlet into bytecode (.class file).
- Execution: Executes the servlet to generate dynamic content for the client.
- Lifecycle Management: Calls lifecycle methods like jspInit(), _jspService(), and jspDestroy().
- Session Management: Supports HTTP sessions using the HttpSession object.
- Error Handling: Manages JSP exceptions and forwards to error pages if configured.
32. What are context initialization parameters?
Context initialization parameters are global parameters defined for a web application in the web.xml file. They are accessible to all servlets and JSP pages in the application via the ServletContext object. Its purpose is to provide configuration data that can be used throughout the application. It is Commonly used for values like database URLs, API keys, or application-wide constants.
How to define in web.xml:
<context-param>
<param-name>databaseURL</param-name>
<param-value>jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/mydb</param-value>
</context-param>How to Access in JSP/Servlet:
<%
String dbURL = application.getInitParameter("databaseURL");
out.println("Database URL: " + dbURL);
%>
Explanation:
- Scope: Application-wide (accessible to all JSPs and servlets).
- Set in: web.xml under <context-param>.
- Read using: ServletContext.getInitParameter() or application.getInitParameter() in JS
33. What are literals in JSP?
In JSP, literals are constant values that appear directly in the JSP page. They can be of types like numbers, strings, or boolean values and are used directly in expressions, scriptlets, or HTML content.
34. What is the purpose of the PageContext implicit object?
The pageContext is an implicit object in JSP that provides a single API to access all the namespaces, servlets, JSP implicit objects, and various page attributes. It essentially acts as a central hub for page-level information.
Purpose of PageContext:
- Access Implicit Objects: You can access objects like request, response, session, application, out, etc., through pageContext.
- Manage Page Attributes: Store, retrieve, or remove attributes specific to the page scope.
- Forward or Include Pages: Provides methods to forward requests or include other JSP/Servlets dynamically.
- Exception Handling: Accesses exceptions in error pages.
- Convenience Object: Reduces the need to call multiple objects separately; centralizes page-level operations.
35. How do you disable scripting in JSP?
Scripting in JSP refers to using Java code directly in the JSP page via scriptlets, expressions, or declarations. Disabling scripting ensures clean separation of presentation and business logic and encourages the use of JSTL, EL, and custom tags.
Disable Scripting in JSP by:
- Historically, JSP allowed disabling some scripting elements using page directives, but the modern approach is different.
- Do not use scriptlets, expressions, or declarations in JSP pages.
- Use JSTL (JSP Standard Tag Library) and Expression Language (EL) to handle dynamic content and logic.
- Example: Instead of <%= user.getName() %>, use EL: ${user.name}
3. Enforcing Scripting-Free JSP in web.xml (JSP 2.0+)
- You can restrict scripting elements in JSP files by configuring TLD (Tag Library Descriptor) and using JSTL/EL tags exclusively.
- Tools and IDEs like Eclipse or NetBeans can also flag scripting usage as errors in JSPs.
36. What are the different types of JSTL tags?
JSTL (JavaServer Pages Standard Tag Library) provides a standard set of tags to simplify JSP development. These tags are grouped into five main categories:
| Tag Type | Purpose |
| Core Tags(c) | Used for flow control, iteration, conditional processing, setting or getting variables, and URL management. Examples: c:if, c:forEach, c:set, c:choose. |
| Formatting Tags(fmt) | Used for formatting dates, numbers, and messages, and for localization. Examples: fmt:formatNumber, fmt:message, fmt:bundle. |
| SQL Tags (sql) | Used for database access like executing queries, updates, and managing transactions. Examples: sql:query, sql:update, sql:param |
| XML Tags(x) | Used for parsing and transforming XML documents. Examples: x:parse, x:out, x:transform. |
| Functions(fn) | Provides common functions for strings and collections, such as length, substring, contains, and join. Examples: fn:length(), fn:contains(). |
37. What is the difference between JSP and Servlets?
| Aspect | JSP (JavaServer Pages) | Servlets |
| Definition | A JSP is a server-side page that allows embedding Java code in HTML to generate dynamic content. | A Servlet is a Java class that handles requests and generates responses dynamically, usually writing HTML via out.println(). |
| Purpose | Mainly used for presentation layer(view). | Mainly used for bussiness logic and control flow(controller). |
| Syntax | HTML based with embedded Java code | Pure Java code |
| Ease of Writing | Easier for designers and front-end developers due to HTML integration. | Requires good Java programming skills; more verbose for UI content. |
| Use Case | Rendering dynamic HTML pages, showing UI content | Handling requests, business logic, controlling flow, and managing sessions |
38. What is the difference between a JSP page and a static HTML page?
A JSP page can generate dynamic content by embedding Java code or tags, processed on the server to produce customized output, while a static HTML page contains fixed content that doesn’t change based on user input or server logic. JSP pages are compiled into servlets, unlike HTML, which is served directly.
39. What are the attributes of the page directive in JSP?
The page directive in JSP is used to define global settings that affect the entire JSP page when it is translated into a servlet. It provides important attributes that control importing classes, session handling, error handling, threading, encoding, and output behavior.
- import → Imports Java classes/packages into JSP.
- contentType → Sets response MIME type and character encoding.
- pageEncoding → Defines encoding of the JSP source file.
- session → Enables/disables access to the session object.
- errorPage → Specifies the JSP page to handle exceptions.
- isErrorPage → Declares if the page can handle exceptions (exception object).
- isThreadSafe → Controls whether the JSP can handle multiple requests concurrently.
- isELIgnored → Enables/disables Expression Language (EL) evaluation.
- buffer → Defines size of the response output buffer.
- autoFlush → Controls whether buffer flushes automatically when full.
- language → Specifies scripting language (only "java" supported).
- extends → Makes the JSP-generated servlet extend a custom superclass.
40. What is the difference between a declaration tag and a scriptlet tag in JSP?
| Feature | Declaration Tag | Scriptlet Tag |
| Purpose | Used to declare variables and methods that will become part of the JSP-generated servlet class. | Used to write executable Java code that runs for each client request. |
| Placement in Servlet | Placed outside the _jspService() method (at the class level). | Placed inside the _jspService() method (method level). |
| Execution | Runs once when the servlet class is loaded. | Runs every time the JSP page is requested. |
| Scope | Class-level (shared across all requests and threads). | Request-level (executed separately for each request). |
| Method Declaration | You can declare methods using declaration tags. | You cannot declare methods inside scriptlet tags. |
| Variable Declaration | Declares instance/class variables (persist across requests). | Declares local variables (valid only within the request execution) |
| Typical Use | Defining helper methods, counters, constants. | Writing request-processing logic, conditional statements, loops, printing values. |
Advanced JSP Interview Questions and Answers
41. How do you manage error handling in JSP applications?
- Page-level error handling using errorPage and isErrorPage attributes
- Application-level error handling using web.xml (deployment descriptor)
1. Page-level Error Handling: JSP provides the page directive attributes errorPage and isErrorPage to manage exceptions.
Example: main.jsp
<%@ page errorPage="errorHandler.jsp" %>
<%
int num = 10 / 0; // This will cause ArithmeticException
%>
errorHandler.jsp
<%@ page isErrorPage="true" %>
<html>
<body>
<h2>Oops! An error occurred.</h2>
<p>Error details: <%= exception.getMessage() %></p>
</body>
</html>
Explanation:
- errorPage="errorHandler.jsp" tells JSP where to forward if an exception occurs.
- isErrorPage="true" gives access to the implicit exception object.
2. Application-level Error Handling (web.xml): You can configure global error handling in the deployment descriptor (web.xml).
Example
<error-page>
<error-code>404</error-code>
<location>/error404.jsp</location>
</error-page>
<error-page>
<exception-type>java.lang.Throwable</exception-type>
<location>/generalError.jsp</location>
</error-page>
Here:
- If a 404 error occurs → forward to error404.jsp.
- If any exception occurs → forward to generalError.jsp.
42. How can you avoid direct access to a JSP from the client browser?
To avoid direct access to JSP follow these :
- Files inside WEB-INF cannot be accessed directly via browser.
- Access only via servlet forwarding.
- All client requests go through controllers.
- JSPs are displayed only via RequestDispatcher.forward().
- Restrict access to JSP URLs using <security-constraint>.
- Only authorized users can access JSPs.
- Filter direct requests to JSPs.
- Redirect unauthorized access to login or error page.
- JSPs should only act as view components, never as direct entry points.
43. How do you optimize performance in large JSP applications?
Top 5 Ways to Optimize JSP Performance
- Follow MVC & Keep JSPs as Views:Avoid business logic and database code in JSP; handle it in servlets or Java classes.
- Precompile JSPs:Compile JSPs to servlets before deployment to reduce runtime compilation overhead.
- Use EL and JSTL Instead of Scriptlets:Minimizes Java code in JSP, making pages faster and easier to maintain.
- Implement Caching:Cache frequently used data in session, application scope, or external caches to reduce repeated computations or database hits.
- Optimize Database and Resource Usage:Use connection pooling, fetch only required data, minimize includes, compress resources, and enable browser caching.
44. What is the role of the tag library descriptor (TLD) in JSP?
TLD (Tag Library Descriptor) is an XML file that describes a custom tag library for JSP.It provides information to the JSP container about custom tags, their attributes, and the classes that implement them.
Role of a Tag Library Descriptor (TLD) in JSP:
- Defines Custom Tags:Specifies the names of custom tags and the Java classes that implement them.
- Specifies Tag Attributes:Defines attributes for each tag and their data types.
- Enables Reusability:Allows the same custom tags to be used across multiple JSP pages.
- Guides JSP Container:Informs the JSP container how to translate and process custom tags into servlet code.
- Supports Namespaces & Versioning:Provides a unique URI and prefix for the tag library to avoid conflicts.
45. Can you override JSP life cycle methods?
JSP page is compiled into a servlet by the JSP container. This means that JSP lifecycle methods are part of the generated servlet, and you can override them if needed.
Overriding JSP Lifecycle Methods
- Called once when the JSP servlet is initialized.
- Can be overridden using <%! %> for initialization tasks (e.g., database setup).
- Handles each client request.
- Cannot be overridden directly; generated automatically from JSP content.
- Called once when the JSP servlet is being destroyed.
- Can be overridden using <%! %> to release resources or cleanup.
<%!
public void jspInit() { /* initialization */ }
public void jspDestroy() { /* cleanup */ }
%>
- jspInit() → initialize resources
- _jspService() → automatically handles requests
- jspDestroy() → release resources
46. How does thread safety work in JSP?
- When a JSP is requested for the first time, the JSP container compiles it into a servlet.
- Lifecycle methods (jspInit(), _jspService(), jspDestroy()) are created.
- The container calls jspInit() once to initialize the JSP servlet.
- This happens before any request is processed.
- For each client request, the container creates a new thread that calls the _jspService(request, response) method of the servlet instance.
- This is where the main JSP code executes (HTML + scriptlets + EL).
- Local variables inside _jspService() are thread-safe because each thread has its own stack.
- Instance variables (declared with <%! %>) are shared across threads, so concurrent modifications can cause race conditions.
- If shared resources must be accessed, developers can use synchronized blocks or move logic to servlets/helper classes.
- Using <%@ page isThreadSafe="false" %> forces single-thread access but reduces scalability.
6. Servlet Destruction
- When the server shuts down or the JSP is reloaded, jspDestroy() is called to release resources.
47. How does JSP differ from templating engines like Thymeleaf or FreeMarker?
- JSP allows embedding Java code directly in HTML, whereas templating engines like Thymeleaf or FreeMarker focus on presentation with placeholders and expressions only.
- JSP mixes view and logic if not carefully designed, while template engines enforce a cleaner separation of concerns. JSP is compiled into servlets, while templates are interpreted at runtime, making engines like Thymeleaf and FreeMarker more maintainable and modern for MVC applications.
48. How does the JSP container translate and compile a JSP file internally?
- HTML → out.write()
- <% %> → Java code in _jspService()
- <%! %> → Class-level variables/methods
49. What is JSP's role in modern Java web development?
JSP’s role today is mainly as a view technology for legacy Java web apps, while modern applications prefer template engines or front-end frameworks for better design and maintainability.
- View Layer in MVC: JSP can still serve as the presentation layer in legacy MVC frameworks like Spring MVC or Struts.
- Legacy Support: It is primarily used for maintaining existing enterprise applications that were built using JSP.
- Limited New Development Use: For new projects, modern template engines (Thymeleaf, FreeMarker) or front-end frameworks (React, Angular, Vue) are preferred for better separation of concerns, maintainability, and scalability.
- Integration Role: JSP can interact with servlets and backend services but is often replaced by RESTful APIs + modern front-end in new applications.
50. How do you avoid common pitfalls like SQL injectionin JSP ?
- Use Prepared Statements: Always use PreparedStatement instead of concatenating user input into SQL queries.
- Validate User Input: Check for correct type, length, format, and allowed characters on both client and server sides.
- Move DB Logic Out of JSP: Keep JSP for view only; use servlets or DAO classes for database operations.
- Use Stored Procedures: Prefer calling stored procedures instead of dynamic SQL when possible.
- Escape Special Characters: Ensure special characters are properly handled, though PreparedStatement usually handles this automatically.
Conclusion:
Preparing for JSP interviews requires a solid understanding of both core concepts and practical best practices. Developers should focus on JSP lifecycle, directives, tag libraries, thread safety, and MVC integration, as well as common pitfalls like SQL injection and resource management.
Only 2% of Java developers reach top-tier Full Stack roles. Join our Full-Stack Java Course and be among the skilled 2% earning ₹10-25 LPA in leading tech companies!
FAQs
- JSP is easier for view/HTML rendering; Servlets are better for business logic.
- JSP is compiled into Servlets internally by the server
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











