06
FebLogical operators in Java
Logical operators are special symbols or words used in programming to connect two or more conditions or expressions. They help evaluate whether the combined condition is true or false, allowing the program to make decisions and execute specific actions based on the result.
80% of employers prioritize Java developers with Core Java Skills. Start strong—Enroll now in our Free Java Training to build your foundation.
What are the Logical Operators in Java?
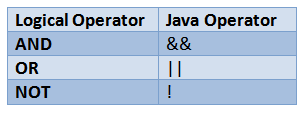
Logical operators in Java are special symbols used to perform operations on Boolean values or expressions. They enable developers to combine multiple conditions or manipulate Boolean logic, resulting in a single true or false outcome. These operators are commonly used in control flow statements such as if, while, and for. Java provides three primary logical operators:
- AND (&&) – Returns true only if both conditions are true.
- OR (||) – Returns true if at least one of the conditions is true.
- NOT (!) – Reverses the boolean value of the condition.
Syntax:
result = operand1 logical_operator operand2;Here, operand1 and operand2 are numeric values or variables, and logical_operator is the logical operator that defines the operation to be performed.
Read More - Java 50 Interview Questions,|Advanced Java Multithreading Interview Questions
Types of Logical Operators
1. && (Logical AND)
result = operand1 && operand2;Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class LogicalOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter value of x: ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter value of y: ");
int y = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter value of z: ");
int z = sc.nextInt();
if ((x < y) && (x < z)) {
System.out.println("Minimum: " + x);
}
else if ((y < x) && (y < z)) {
System.out.println("Minimum: " + y);
}
else {
System.out.println("Minimum: " + z);
}
sc.close();
}
}
Explanation
Output
Enter value of x: 10
Enter value of y: 50
Enter value of z: 40
Minimum: 10
2. || (Logical OR)
Syntax
boolean result = operand1 || operand2;Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class LogicalOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter value of x: ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter value of y: ");
int y = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter value of z: ");
int z = sc.nextInt();
// || operator
System.out.println((x < y) || (z > x));
System.out.println((x > y) || (z < x));
System.out.println((x < y) || (z < x));
sc.close();
}
} Explanation
Output
Enter value of x: 10
Enter value of y: 20
Enter value of z: 30
true
false
true
3. ! (Logical NOT)
Syntax
boolean result = !operand;Example
import java.util.Scanner;
class LogicalOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter value of x: ");
int x = sc.nextInt();
System.out.print("Enter value of y: ");
int y = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println(!(x == y));
System.out.println(!(x > y));
sc.close();
}
}
Explanation
Output
Enter value of x: 26
Enter value of y: 12
true
false Read More - Java Certification Salary
Examples of Logical Operators in Java
class LogicalOperator {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// && operator
System.out.println((4 > 3) && (7 > 6)); // true
System.out.println((4 > 3) && (7 < 6)); // false
// || operator
System.out.println((4 < 3) || (7 > 6)); // true
System.out.println((4 > 3) || (7 < 6)); // true
System.out.println((4 < 3) || (7 < 6)); // false
// ! operator
System.out.println(!(4 == 3)); // true
System.out.println(!(4 > 3)); // false
}
}
Explanation
The above code in the Java Playground illustrates how logical operators combine and manipulate Boolean values to produce different results based on the specified conditions. It is a practical example that showcases the behavior of logical operators in Java.
Output
true
false
true
true
false
true
false Logical Operators Table
| Operand 1 | Operand 2 | && (Logical AND) | || (Logical OR) | ! (Logical NOT) |
| true | true | true | true | false |
| true | false | false | true | false |
| false | true | false | true | false |
| false | false | false | false | true |
Common Mistakes to Avoid with Logical Operators in Java
1. Mixing Up && and &, or || and |
- && and || are logical operators (used with boolean conditions).
- & and | are bitwise operators (used with binary numbers).
- Mistaking one for the other can lead to unexpected results or performance issues.
2. Forgetting Short-Circuit Behavior
- Logical && and || use short-circuiting, meaning they stop checking as soon as the result is clear.
- This is helpful, but if the second condition has side effects (like a method call), it may not run as expected.
3. Writing Overly Complex Conditions
- Combining too many conditions in one line can make the logic hard to read and debug.
- Break them into smaller parts if possible for clarity.
4. Misunderstanding! (NOT Operator)
- Beginners often misuse !, especially when checking for false values.
- For example, writing if (!isActive == true) instead of simply if (!isActive).
5. Assuming All Conditions Will Be Checked
- With short-circuit operators, the second condition won’t run if the result is already known.
- This can cause problems if the skipped condition includes important operations.
6. Using Logical Operators with Non-Boolean Values
- Logical operators should only be used with true or false.
- Using them with non-boolean types (like numbers or strings) will cause compilation errors.
7. Not Grouping Conditions Properly with Parentheses
- If you don’t use parentheses, Java might not evaluate the conditions in the order you expect.
- Use () to control the order of evaluation clearly.
Advantages of Logical Operators in Java
1. Join Two or More Conditions
- You can check many conditions at once using logical operators, instead of writing separate checks.
2. Make Code Short and Clear
- They help you write less code that is easier to read and understand.
3. Save Time During Execution
- Java stops checking conditions when it already knows the answer, which saves time.
4. Avoid Repeating Code
- You don’t need to write long or repeated statements—just use logical operators to simplify things.
5. Used in If Statements and Loops
- They are very useful in decision-making parts of the code, like if, while, and for.
6. Skip Unnecessary Checks
- If the result is already clear, Java skips checking the rest—this prevents extra work and errors.
7. Useful in Real-Life Programs
- They are used in login systems, form checks, filters, and other everyday features.
8. Make Programs Work Better
- Logical operators help your code run smoothly and do the right thing at the right time.
Disadvantages of Logical Operators in Java
1. Can Make Code Confusing
- If too many conditions are combined, it can be hard to read and understand the logic.
2. Difficult to Debug
- When something goes wrong in a complex condition, it can be tricky to find out what part is causing the issue.
3. Overuse Can Reduce Clarity
- Using many logical operators in one line may make the code look messy and complicated.
4. Short-Circuiting May Cause Mistakes
- Java stops checking further conditions if the result is already known, which might skip important parts if not used carefully.
5. Not Suitable for All Situations
- In some cases, writing separate if statements is better for clarity and easier debugging.
6. Requires Understanding of Boolean Logic
- Beginners might find it hard to understand how true and false work when many conditions are joined together.
Explore More Operators in Java
- Relational operators in Java
- Arithmetic operators in Java
- Assignment operator in Java
- Unary operator in Java
- Bitwise operator in Java
- Ternary operator in Java
Summary
Logical operators are essential in decision-making, conditional statements, and loops, enabling developers to implement complex logic in their programs efficiently. Mastering them is crucial for Java beginners and forms the foundation for advanced topics like multithreading, exception handling, and Java microservices. 88% of Java pros without microservices will struggle. Stay competitive—Enroll now in our Java Microservices Training Course to excel.
Top developers are mastering full-stack Java to lead projects. Stay a basic coder, and you’ll lag behind—Enroll now in our Java Full Stack Developer Training to become a versatile pro.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.