20
FebTernary Operator in Java with Examples: Ternary Operator vs. if...else Statement
Ternary Operator in Java
Ternary Operator in Java takes three operands, evaluates the condition, and returns the result. It is also known as the conditional operator. Don't get it? Imagine you are in a hurry and need to decide between two options. Wouldn’t it be nice to have a quick, one-liner way to make decisions in your code too? That’s where the ternary operator in Java comes to the rescue! It’s like a shorthand for an if-else statement, perfect for those situations where you want to keep your code neat and concise.
In this Java Tutorial, we'll explore the syntax along with the Java Ternary Operator with Examples and advantages of the Ternary Operator. We'll also understand the ternary operator vs. if...else statement in Java. The tech industry moves fast, 90% of unskilled coders get left behind. Start today, Enroll now in our Free Java Training Course to secure your future.
What is a Ternary Operator in Java?
In Java, the ternary operator, also known as the conditional operator, is a shorthand way of writing an if-else statement. It makes code more concise and readable by evaluating a Boolean expression and returning one of two values based on the evaluation result.
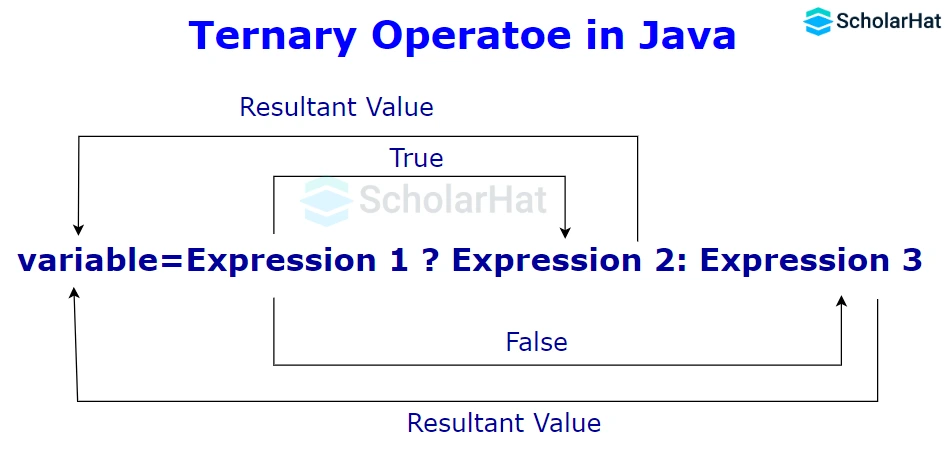
Syntax of Ternary Operator in Java
Variable = Condition ? Expression1 : Expression2
- Condition: It denotes the condition specified in an if statement.
- Expression 1: If the condition is met, this expression will be saved in the Variable.
- Expression 2: If the condition is false, this expression will be saved in the variable.
- It stores the result returned by either expression in a variable.
| Read More - Top 50 Java Interview Questions |
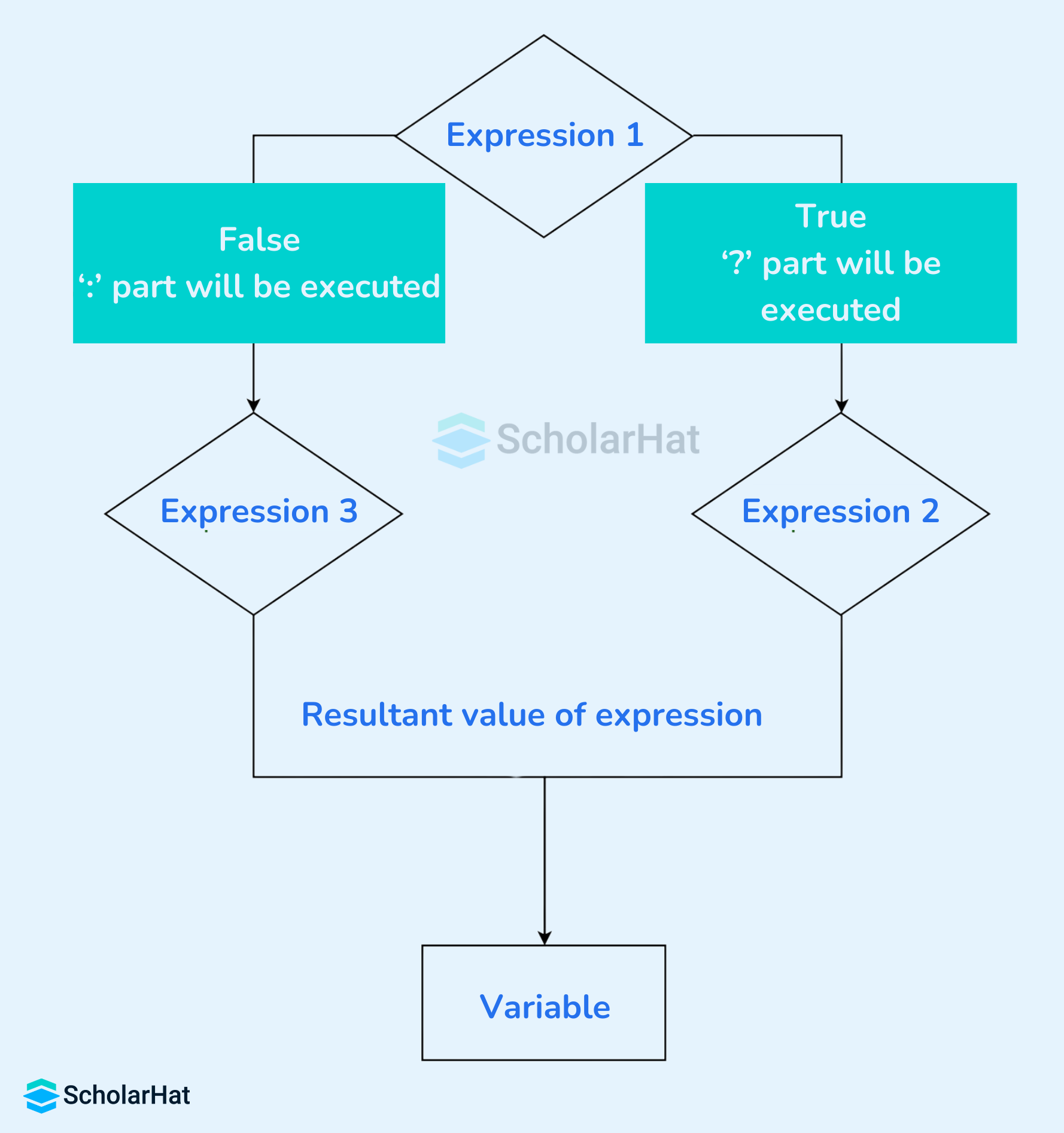
Flowchart of Ternary Operation
Examples Illustrating Ternary Operator in Java
Example 1: Finding the greatest of two numbers
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
int y = 20;
int result = (x > y) ? x : y;
System.out.println("The maximum of " + x + " and " + y + " is: " + result);
}
}
Explanation
In this specific example, the code determines the maximum value between x and y using the ternary operator and then prints the result to the console. The output on execution in the Java Compiler will be "The maximum of 10 and 20 is: 20," as the value of y (20) is greater than the value of x (10).
Output
The maximum of 10 and 20 is: 20Example 2: Checking odd/even numbers
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// Given expression: int x = 10; String message = (x % 2 == 0) ? "Even" : "Odd";
int x = 10;
int y = 11;
String message1 = (x % 2 == 0) ? "Even" : "Odd";
String message2 = (y % 2 == 0) ? "Even" : "Odd";
// Displaying the result
System.out.println("Number " + x + " is " + message1);
System.out.println("Number " + y + " is " + message2);
}
} Explanation
The TernaryOperatorExample class in Java demonstrates the usage of the ternary operator to determine whether a given number is even or odd. The main method initializes two integer variables, x, and y, with values 10 and 11, respectively. It then uses the ternary operator to assign a corresponding message based on whether the number is even or odd.
Output
Number 10 is Even
Number 11 is Odd| Read More - Java Developer Salary In India |
Ternary Operator Vs. if...else Statement in Java
The ternary operator may sometimes be used to replace multiple lines of code with a single line. It is often used to replace simple if-else statements. By reducing the length of your program, the ternary operator enhances code readability.
public class DivisibilityCheck {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 25
if (number % 5 == 0) {
// If divisible, print the following message
System.out.println("The number " + number + " is divisible by 5.");
} else {
// If not divisible, print the following message
System.out.println("The number " + number + " is not divisible by 5.");
}
}
}
The above code checks whether a number is divisible by 5 with the help of an if-else statement.
We can use the ternary operator to perform the same operation.
public class DivisibilityByFive {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 25;
// Using the ternary operator to check if the number is divisible by 5
String result = (number % 5 == 0) ? "Divisible by 5" : "Not divisible by 5";
System.out.println("Number " + number + " is " + result);
}
}
If we compare the above two codes, we can see that the code using the ternary operator looks more readable and short than the one using if-else. The ternary operator can be used to check any condition using a single if-else statement. However, you can choose what to select.
Use of Ternary Operator in Java
The ternary operator in Java is a concise and powerful tool used for conditional expressions. Its primary purpose is to simplify the syntax of certain if-else statements, making code more compact and often improving readability. Here are some common use cases for the ternary operator in Java:
1. Conditional Assignment
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int number = 15;
String result = (number > 0) ? "Positive Number" : "Negative Number";
System.out.println(result);
}
}Explanation
This example illustrates how the ternary operator provides a concise way to conditionally assign a value based on a boolean expression, making the code more readable and succinct for simple conditional assignments.
Output
Positive Number 2. Inline Printing
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int temperature = 25;
System.out.println("The weather is " + ((temperature > 20) ? "warm" : "cold"));
}
}Explanation
By using the ternary operator to determine and print a weather description based on the temperature. The main method initializes an integer variable temperature with a value of 25. The ternary operator is then employed within a System.out.println statement to decide whether the weather is "warm" or "cold" based on the condition (temperature > 20).
Output
The weather is warm3. Nested Ternary Operators
public class TernaryOperatorExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num1 = 5, num2 = 11, num3 = -15;
int lowest = (num1 <= num2) ? ((num1 <= num3) ? num1 : num3) : ((num2 <= num3) ? num2 : num3);
System.out.println("Minimum Number: " + lowest);
}
} Explanation
This example in our Java Online Editor demonstrates the use of nested ternary operators to efficiently find the minimum value among three numbers in a single line of code. While nested ternary operators can be powerful, it's important to use them with caution to maintain code readability.
Output
Minimum Number: -15Advantages of Java Ternary Operator
- Code Conciseness: Ternary operators reduce the amount of code required for simple conditional assignments.
- Improved Readability: In certain cases, the ternary operator can make the code more readable, especially when dealing with short conditional expressions.
- Inline Usage: Ternary operators can be used inline, making code more compact and reducing the need for additional lines.
| Read More |
Summary
The ternary operator in Java is a powerful tool for simplifying conditional expressions. While it offers conciseness and readability advantages, it should be utilized with caution to maintain code clarity.
Top developers are mastering full-stack Java to lead projects. Stay a basic coder, and you’ll lag behind—Enroll now in our Java Full Stack Course to become a versatile pro.
FAQs
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.