15
Febwhile Loop in Java
while loop in Java is a control flow statement that repeatedly executes a block of code as long as a specified Boolean condition is true. It is typically used when the number of iterations is not known in advance and the loop's continuation depends on a condition evaluated before each iteration.
In this tutorial, we will learn What is while loop in Java, and while loop syntax in Java, and also look at some of the while loop programs in Java. Learn Java basics to earn ₹10 LPA fast. Don’t wait, Enroll now in our Free Java Course to kickstart your tech career!
Read More: Top 50 Java Interview Questions and Answers
Read More - Java Multithreading Interview Questions
What is a while loop in Java?
In Java, a while loop is an entry-controlled looping construct that repeatedly executes a block of code based on a Boolean condition. If the condition evaluates to true, the loop runs; otherwise, it stops.
Syntax of while loop in Java
while (condition) {
// code to be executed
}Parts of Java while Loop
1. Test Expression
In the Test Expression, the specified condition is checked. If the condition is evaluated to be 'True', the block of code inside the loop will be executed and it will move forward to the update expression. If the condition is false, the loop will terminate.
while (test_expression) {
// body of the loop
}Example:
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
// body of the loop
}2. Update Expression
The Update Expression does an increment or decrement to the loop variable every time the execution of loop body occurs. It is written after the body of the loop. When the execution occurs and the loop comes to this expression the variable is incremented or decremented as specified in the expression. In short, it updates the value of the variable.
while (test_expression) {
// body of the loop
update_expression;
}Example:
int i = 1;
while (i <= 5) {
System.out.println(i);
i++; // update expression
}
Read More: Java Developer Salary Guide in India – For Freshers & Experienced
Flowchart of Java while Loop
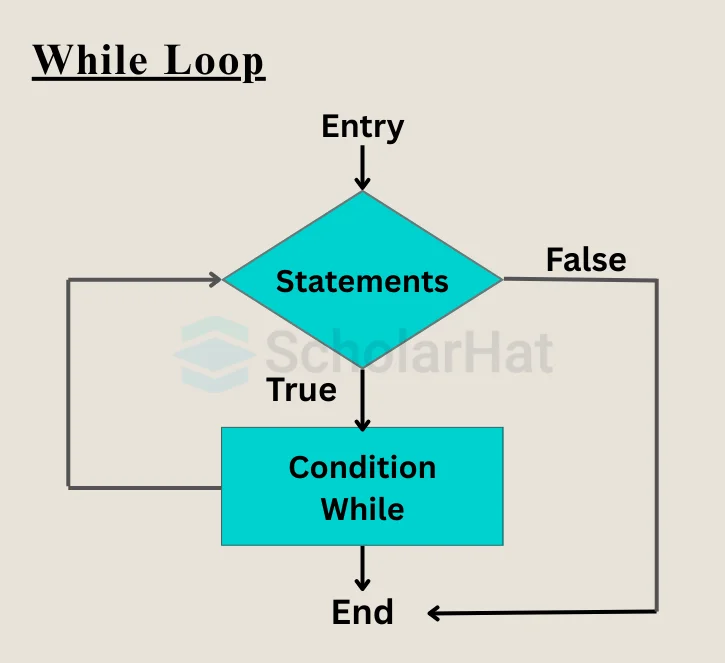
How Does a while loop execute?
Now let's try to understand how exactly a while loop is executed in a Java Program.
- Initialization-Before the loop starts, all variables that will be used inside the loop must be initialized. This setup happens outside the while loop. For example, initializing a counter variable is a common practice.
- Condition Checking-The loop then checks a condition. If the condition evaluates to true, the loop enters its body and begins executing the statements inside. If the condition is false, the loop is skipped entirely, and the program continues with the next statement after the loop.
- Loop Body Execution-If the condition is true, the code block (also called the loop body) is executed. This block contains the set of instructions that will run repeatedly.
- IterationAfter executing the loop body, one or more variables involved in the condition are typically updated. This update (such as increasing or decreasing a counter) affects whether the loop will continue running in the next cycle.
- Re-check Condition- Once the update is done, the program jumps back to the condition check. The condition is evaluated again to determine whether another iteration should occur. This cycle repeats as long as the condition remains true.
- Loop Termination-When the condition finally becomes false, the loop stops executing. The control then moves to the statement immediately following the loop.
Examples of Java while loop
1. Printing Numbers from 1 to 5
public class WhileLoopExample1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1; // Initialization
while (i <= 5) { // Test expression
System.out.println(i); // Body
i++; // Update expression
}
}
}Output
1
2
3
4
5
2. Calculating Factorial of a Number
public class WhileLoopExample2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int num = 5;
int factorial = 1;
int i = 1; // Initialization
while (i <= num) { // Test expression
factorial *= i; // Body
i++; // Update expression
}
System.out.println("Factorial of " + num + " is: " + factorial);
}
}Output
Factorial of 5 is: 120
3. Countdown from 5 to 1
public class WhileLoopExample4 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 5; // Initialization
while (i >= 1) { // Test expression
System.out.println(i); // Body
i--; // Update expression
}
System.out.println("Blast Off!");
}
}Output
5
4
3
2
1
Blast Off!
How to Break a While Loop in Java
In Java, the break statement is used to terminate the execution of a loop prematurely, even if the loop’s condition is still true. This is especially useful when a certain condition is met inside the loop and you want to exit the loop immediately.
while (condition) {
// statements
if (someCondition) {
break; // exits the while loop
}
// more statements
}
Example
public class BreakWhileExample {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
if (i == 5) {
System.out.println("Breaking the loop at i = " + i);
break;
}
System.out.println("i = " + i);
i++;
}
}
}
💡 Output:
i = 1
i = 2
i = 3
i = 4
Breaking the loop at i = 5
When to Use break in a While Loop:
- When a specific value or condition is encountered.
- To optimize performance by avoiding unnecessary iterations.
- In menu-driven programs or infinite loops (e.g., while(true)), to exit on a user action.
Java While Loop — Real-Time Example
Use Case: Counting Down a Timer (like a countdown clock)
Java Code:
public class CountdownTimer {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int seconds = 5;
while (seconds > 0) {
System.out.println("Countdown: " + seconds);
seconds--;
}
System.out.println("Time's up!");
}
}
Explanation:
- We start with seconds = 5
- The loop keeps running as long as seconds > 0.
- Each time, it prints the current value and decreases seconds by 1.
When seconds becomes 0, the loop stops and prints "Time's up!".
Output:
- Countdown: 5
- Countdown: 4
- Countdown: 3
- Countdown: 2
- Countdown: 1
- Time's up!
Common mistakes in while loop:
Missing Update Step: Forgetting to update the loop variable causes an infinite loop.
Using = Instead of ==: = assigns a value; == compares values. Using = in conditions leads to errors.
Condition Never Changes: If the condition is always true, the loop runs forever. Use break or update the condition inside the loop.
Summary
Through the above article, we learnt about while loop in Java, its structure, flowchart and also while loop example in Java Program. Do have a look on other loops in Java to have a proper understanding of them all.
95% of startups want full-stack Java pros. Don’t be left out—Enroll now in our Full Stack Java Training Course to become their top choice.
FAQs
count = 0
while count < 5:
print(count)
count += 1do {
// code block to be executed
} while (condition);- First, you need to initialize a variable outside of the loop.
- Use 'while' with a condition attached to it using the variable.
- Put an update expression after that so the loop eventually ends.
Take our Java skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.