06
FebIEnumerable VS IQueryable
The difference between IEnumerable and IQueryable: An Overview
In this LINQ Tutorial, you will learn the difference between IEnumerable and IQueryable with some actual Programming Examples.In LINQ to query data from databases and collections, we use IEnumerable and IQueryable for data manipulation.
Basically, IQueryable inherits IEnumerable, Hence IQueryable has all the features of IEnumerable and except this, it has its own features. Both have their own methodology to query data and data manipulation. Let’s see both the features and learn how to use both the features to boost your LINQ Query performance.
What is IEnumerable?
IEnumerable exists in System.Collections Namespace.
IEnumerable can move forward only over a collection, it can’t move backward and between the items.
IEnumerable is best for querying data from in-memory collections like List, Array, etc.
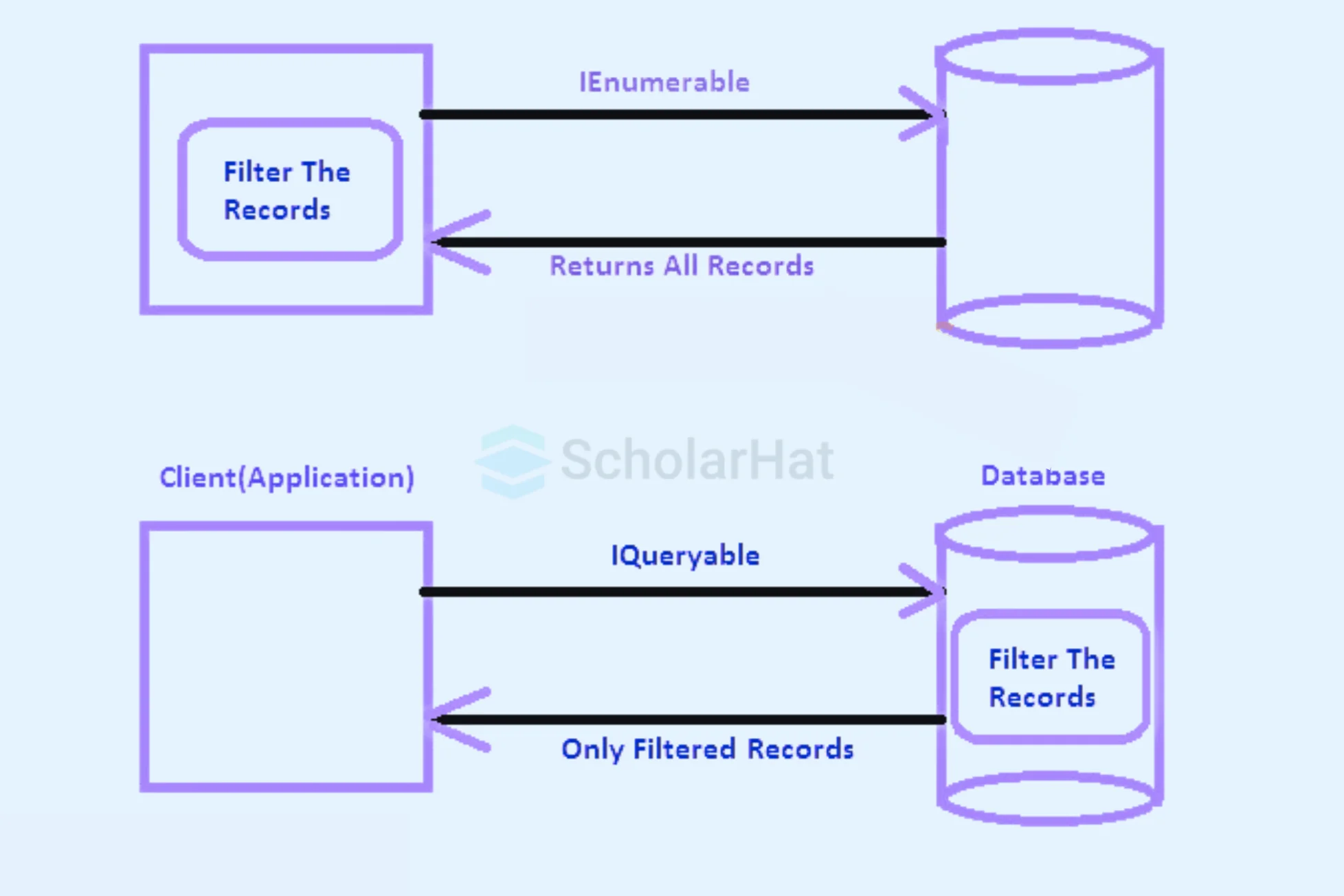
While querying data from a database, IEnumerable executes a select query on the server side, loads data in memory on the client side, and then filters data.
IEnumerable is suitable for LINQ to Object and LINQ to XML queries.
IEnumerable supports deferred execution.
IEnumerable doesn’t support custom queries.
IEnumerable doesn’t support lazy loading. Hence not suitable for paging-like scenarios.
Extension methods supported by IEnumerable take functional objects.
IEnumerable Example:
MyDataContext dc = new MyDataContext ();
IEnumerable<Employee> list = dc.Employees.Where(p => p.Name.StartsWith("S"));
list = list.Take<Employee>(10);Generated SQL statements of the above query will be :
SELECT [t0].[EmpID], [t0].[EmpName], [t0].[Salary] FROM [Employee] AS [t0]
WHERE [t0].[EmpName] LIKE @p0Explanation:
In the above IEnumerable Example We took the Employee list where we have to find the employee name starting with s, But you noticed that in this query "top 10" is missing since IEnumerable filters record on the client side. Now Let's see in IQueryable.
What is IQueryable?
IQueryable exists in the System. Linq Namespace.
IQueryable can move forward only over a collection, it can’t move backward and between the items.
IQueryable is best for querying data from out-memory (like remote database, service) collections.
While querying data from a database, IQueryable executes the select query on the server side with all filters.
IQueryable is suitable for LINQ to SQL queries.
IQueryable supports deferred execution.
IQueryable supports custom queries using CreateQuery and Execute methods.
IQueryable supports lazy loading. Hence it is suitable for paging-like scenarios.
Extension methods supported by IQueryable take expression objects, which means an expression tree.
IQueryable Example:
MyDataContext dc = new MyDataContext ();
IQueryable<Employee> list = dc.Employees.Where(p => p.Name.StartsWith("S"));
list = list.Take<Employee>(10); Generated SQL statements of the above query will be :
SELECT TOP 10 [t0].[EmpID], [t0].[EmpName], [t0].[Salary] FROM [Employee] AS [t0]
WHERE [t0].[EmpName] LIKE @p0Explanation:
In IQueryable Notice that in this query "top 10" exists since IQueryable executes a query in an SQL server with all filters.
Summary:
In this article, I explained the difference between IEnumerable and IQueryable. I hope after reading this article you will be able to boost your LINQ query performance. I would like to have feedback from my blog readers. Please post your feedback, questions, or comments about this article. Enjoy Coding..!