06
MarMicroservices Architecture : Examples and Implementation
Microservices example can be best understood by looking at real-world applications like Netflix, Amazon, or Uber, where complex systems are broken into small, independent services. Each microservice handles a specific business function such as user authentication, payments, or notifications and communicates with others through APIs.
In this microservices tutorial, you will explore the key components of microservices, real-world examples, and step-by-step implementation of microservices. Prepare for high-paying developer roles with salaries up to ₹12–20 LPA — all 100% free with our Free .NET Microservices Course.
What is Microservices Architecture?
Microservices architecture is a design pattern where an application is broken down into smaller, self-contained services. Each service is built around a specific business capability like authentication, payments, or order management and runs as its own process.
These services:
- Focuses on a single business capability (e.g., user authentication, order processing, payment handling).
- Runs in its own process and communicates with other services via lightweight protocols like HTTP/REST, gRPC, or messaging queues.
- Can be developed, deployed, and scaled independently without affecting other services.
Why Choose Microservices Architecture?
Microservices architecture breaks a big application into small, independent services that can run, scale, and deploy separately. Companies like Netflix, Uber, and Amazon use it because it solves many limitations of traditional monolithic systems. Microservices make systems scalable, reliable, and adaptable compared to monolithic architectures.
- Scalability: Scale only the services that need extra resources (e.g., Payment during sales).
- Flexibility: Microservices use different tech stacks for different services.
- Faster Development: Independent teams can build and deploy services separately.
- Resilience: Failure in one service doesn’t crash the entire system.
- Continuous Deployment: Easier updates without affecting other services.
- Better Maintainability: Small, focused codebases are simpler to manage.
Key Components of Microservices Architecture
1. Services
- Each service is a self-contained unit that performs a specific business function. Example: User Service, Order Service, Payment Service.
2. API Gateway
- Acts as a single entry point for clients to interact with the system.
- Routes requests to the appropriate service and handles cross-cutting concerns like authentication and rate limiting.
3. Service Discovery
- Helps microservices find each other dynamically.
- Useful in cloud and container environments where service instances may change frequently.
- Tools: Consul, Eureka, Kubernetes Service Discovery.
4. Load Balancing
- Distribute incoming requests across multiple instances of a service to ensure high availability and performance.
- Tools: NGINX, HAProxy, Kubernetes Ingress.
5. Data Management
- Each service manages its own database, ensuring loose coupling. Challenges: Data consistency, eventual consistency, and distributed transactions.
- Used for monitoring, logging, scaling, and maintaining microservices.
6. Communication Protocols
- Services communicate via lightweight protocols like HTTP/REST, gRPC, or messaging systems (e.g., Kafka, RabbitMQ).
7. Monitoring and Logging
- Centralized logging and monitoring are essential for troubleshooting and performance optimization.
- Tools: Prometheus, Grafana, ELK Stack (Elasticsearch, Logstash, Kibana).
8. Containerization and Orchestration
Services are often deployed as containers using Docker and orchestrated using Kubernetes.
Real-World Microservices Architecture Examples
1. Amazon
Amazon, one of the world’s largest e-commerce platforms, shifted from a monolithic architecture to microservices to manage its billions of daily transactions, global user base, and rapidly growing feature set. This shift allows Amazon to operate like a collection of independent services, each responsible for a specific function in the customer shopping journey.
How Amazon is Broken Down into Microservices
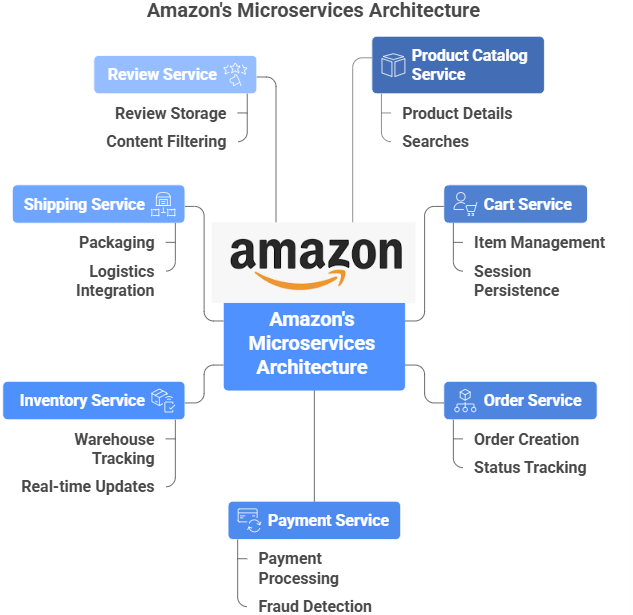
- It stores and displays product details, images, and specifications.
- It handles searches and product categorization.
- It manages items added by the customer.
- It saves state across sessions (so you don’t lose your cart if you log out).
- It creates and manages customer orders.
- It tracks order status (confirmed, shipped, delivered).
- Payment Service processes payments via credit/debit cards, wallets, or Amazon Pay.
- It also handles refunds and fraud detection.
- It tracks product availability across warehouses.
- It updates stock in real-time when purchases are made.
- Shipping service manages packaging, delivery schedules, and tracking.
- It integrates with logistics partners.
- It stores and displays customer ratings and reviews.
- It also filters inappropriate content.
Workflow Example: Buying a Laptop
- Product Catalog Service → Displays available laptops to the user.
- Cart Service → Adds the selected laptop to the cart.
- Order Service → Creates an official order once the user proceeds to checkout.
- Payment Service → Processes the payment securely.
- Inventory Service → Updates stock levels in the warehouse.
- Shipping Service → Arranges delivery and provides tracking information.
- Review Service → Allows the customer to leave a review after purchase
Netflix
How Netflix is Broken Down into Microservices
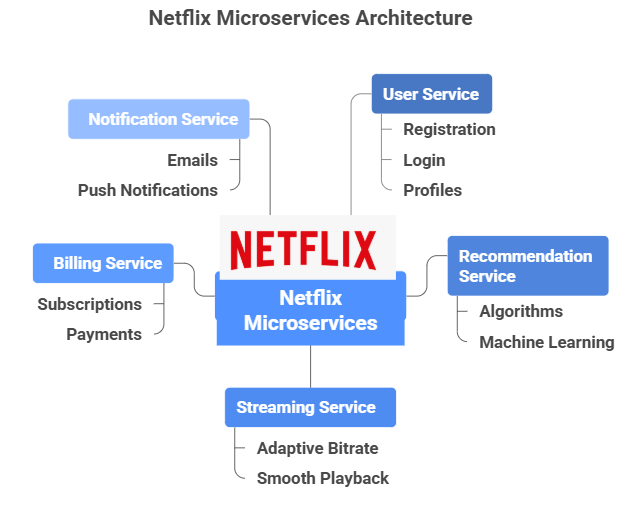
- Handles user registration, login, profiles, and account settings.
- Keeps track of viewing history and preferences.
- Uses algorithms and machine learning to suggest shows/movies based on previous watch behavior.
- Continuously improves with user feedback and new data.
- Responsible for delivering video/audio content with adaptive bitrate streaming.
- Ensures smooth playback regardless of network conditions.
- It manages subscriptions, payments, renewals, and refunds.
- It integrates with global payment gateways.
- Sends personalized notifications, reminders, and promotional alerts.
- Supports emails, push notifications, and in-app alerts.
Workflow Example: When a User Clicks “Play”
- User Service first authenticates the user to confirm account access.
- Billing Service checks whether the subscription is active and valid.
- Streaming Service delivers the requested video in real-time, adjusting quality based on the user’s internet speed.
- Recommendation Service logs the movie/series being watched and updates future recommendations.
- Notification Service may later remind the user: “A new episode of your show is available!”
Uber
Uber is a global ride-hailing platform that connects millions of passengers and drivers in real time. To handle massive scale, high availability, and rapid feature growth, Uber moved from a monolithic application to a microservices architecture. This allows Uber to independently manage services like ride booking, payments, and notifications.
How Uber is Broken Down into Microservices
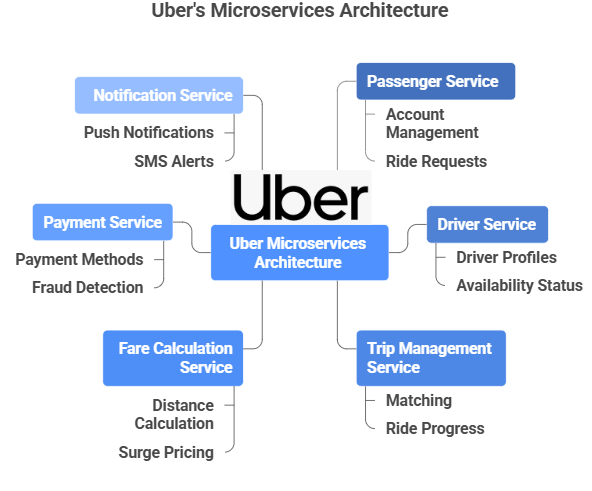
- It manages passenger accounts, logins, and ride requests.
- It also stores trip history and preferences.
- Driver Service handles driver registration, profiles, and availability status.
- It tracks driver ratings and compliance.
- The “core brain” of Uber’s system.
- Trip Management Service matches passengers with nearby drivers.
- It manages ride start, progress, and completion.
- It calculates trip costs using distance, time, traffic, and surge pricing.
- It supports dynamic adjustments during high-demand periods.
- It charges the user and transfers money to the driver after ride completion.
- It supports multiple payment methods and fraud detection.
- Notification Service sends real-time alerts about driver arrival, trip progress, and ride completion.
- It works via push notifications, SMS, and in-app alerts.
Workflow Example: Booking a Ride
- Passenger Service → User opens the app, logs in, and requests a ride.
- Trip Management Service → Searches available drivers by querying the Driver Service.
- Fare Calculation Service → Estimates the ride cost (including surge pricing if applicable).
- Payment Service → Pre-authorizes the fare amount on the passenger’s chosen payment method.
- Notification Service → Alerts both passenger and driver about the booking and pickup details.
- Trip Management Service → Continuously tracks ride progress and updates status until completion.
How to Implement Microservices Architecture?
1. Understand Business Domains (Domain-Driven Design)
- Break the application into business capabilities like User, Order, Payment, Inventory, etc.
- Each microservice should handle one business capability.
2. Define Service Boundaries
- Each service should be independent and handle one business responsibility.
- Avoid tightly coupling services.
3. Choose Technology Stack
- Select programming languages and frameworks suitable for each service.
- Backend → Java (Spring Boot), Node.js, Python (Flask/FastAPI)
- Frontend → React, Angular, Vue.js
- Databases → Polyglot persistence
4. Data Management (Database per Service)
- Each microservice should have its own database to ensure independence.
- Use different databases if needed (SQL, NoSQL, Graph).
5. Communication Between Services
- Services must communicate efficiently and reliably.
- Use lightweight communication protocols:
- Use synchronous (REST, gRPC) for request/response.
- Use asynchronous (Kafka, RabbitMQ) for event-driven architecture.
6. API Gateway
- Implement an API Gateway as a single entry point.
- Responsibilities: routing, load balancing, authentication, rate limiting.
- Tools: Kong, Nginx, AWS API Gateway, Zuul, Traefik.
7. Implement Service Discovery
- Use tools like Eureka, Consul, or Kubernetes DNS for dynamic service location.
- This allows scaling services without hardcoding IPs.
- Service Discovery helps them find each other automatically.
8. Security and Authentication
- Implement JWT/OAuth2.0 for authentication across services.
- Use API Gateway for centralized authentication and authorization.
9. Monitoring and Logging
- Use centralized logging (ELK Stack, Prometheus, Grafana).
- Distributed tracing with Jaeger/Zipkin to trace requests across services.
10. CI/CD Pipeline
- Automate build, test, and deployment with Jenkins, GitHub Actions, or GitLab CI.
- Use Docker to containerize services.
- Deploy with Kubernetes for scalability and orchestration.
11. Testing Strategy
- Unit Tests: Verify the correctness of individual service functions or components.
- Contract Tests: Ensure a service’s API meets the agreed request/response contract.
- Integration Tests: Check how multiple services interact and exchange data.
- End-to-End Tests: Validate the complete user journey across all services.
Conclusion
Microservices architecture has become the backbone of modern, large-scale applications because of its ability to break down complex systems into smaller, manageable services. Through real-world examples like Netflix, Amazon, and Uber, it is clear that microservices enable scalability, faster deployments, independent development, and fault isolation. Unlike monolithic systems, where a single failure can disrupt the entire application, microservices provide flexibility and resilience by allowing each service to function independently.
Build and deploy .NET microservices like a pro. Enroll in our .Net Microservices Training to enhance your skills and earn credentials that open doors to senior .NET positions.
FAQs
Take our Microservices skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.