06
MarDifference Between MySQL and PostgreSQL: Which Database Should You Choose?
In the MySQL tutorial, you will able to know about the difference between MySQL and PostgreSQL, key similarities between MySQL and PostgreSQL, use cases of MySQL and PostgreSQL, how to choose between MySQL and PostgreSQL.
What is MySQL?
MySQL is an open-source RDBMS developed by MySQL AB and acquired by Oracle Corporation in 1995. MySQL organizes data into tables made up of rows and columns, with each row displaying a record and each column representing an attribute. Many kinds of data are supported, including dates, texts, floats, inte gers, and others. MySQL also includes features like replication, transactions, and indexing for dependable and efficient data administration.

- It can be operated on different platforms of operating systems like Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- It handles huge databases and can manage several users concurrently.
- MySQL follows the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) properties, which provide dependable transactions and data integrity.
- It supports different storage engines, including InnoDB (default) and MyISAM.
What is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an open-source relational database management system (RDBMS) originally developed at the University of California, Berkeley, and maintained by the PostgreSQL Global Development Group. It is known for its advanced features and strong standards compliance, PostgreSQL organizes data into tables consisting of rows and columns, where each row represents a record and each column denotes an attribute. It supports a wide range of data types, including custom user-defined types. PostgreSQL also provides powerful features like multi-version concurrency control (MVCC), replication, full-text search, and indexing for reliable and efficient data management.

- It runs seamlessly on multiple operating systems such as Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- It efficiently manages large and complex databases while handling multiple concurrent users.
- PostgreSQL fully follows ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) principles, ensuring data reliability and transaction integrity.
- It is extensible by design, allowing support for custom functions, operators, and procedural languages in addition to built-in features.
Key Differences Between MySQL and PostgreSQL
| Feature | MySQL | PostgreSQL |
| Origin & Developer | Developed by MySQL AB, acquired by Oracle Corporation in 1995. | Originated at the University of California, Berkeley; maintained by PostgreSQL Global Development Group. |
| Database Model | It is a Relational database management system (RDBMS). | It is a Object-relational database management system (ORDBMS). |
| Data Types | It supports standard types like INT, VARCHAR, TEXT, DATE, FLOAT. | It provides advanced types including JSON, XML, arrays, hstore, custom data types. |
| Standards Compliance | Partially compliant with ANSI SQL standards. | Highly compliant with ANSI SQL standards and advanced features. |
| Extensibility | Limited customization and fewer extensibility options. | Extensible by design, allows custom functions, operators, and procedural languages. |
| Performance | Optimized for simple read-heavy operations and web applications. | Excels at handling complex queries, large datasets, and analytical workloads. |
| Concurrency Control | Uses InnoDB engine (default) with ACID compliance and row-level locking | Implements Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC) for seamless concurrent transactions. |
| Replication & Clustering | It provides master-slave replication, Group Replication, and clustering options. | It supports streaming and logical replication, with strong clustering and high availability solutions. |
| Use Cases | Best for web apps, e-commerce, and small-to-medium scale projects. | Ideal for financial systems, data warehousing, geospatial applications, and enterprise solutions. |
| Community & Support | Backed by Oracle and a large developer community. | Backed by global open-source contributors with extensive documentation. |
Key Similarities Between MySQL and PostgreSQL
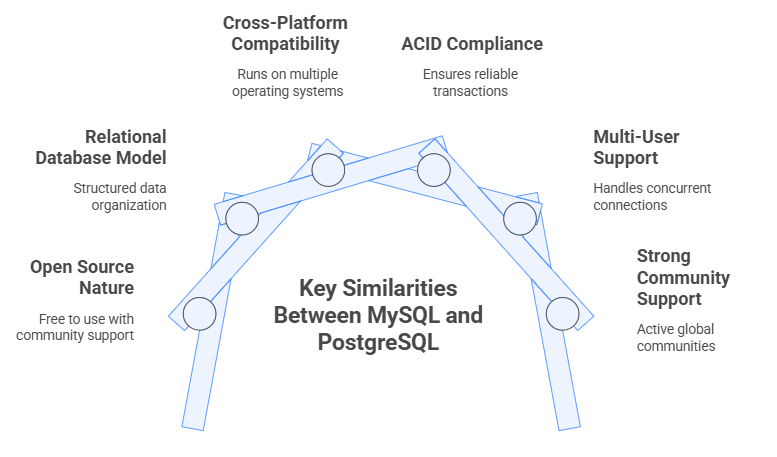
1. Open Source Nature
- Both MySQL and PostgreSQL are open-source relational database management systems.
- This means they are free to use, have strong community support, and receive regular updates and improvements from developers worldwide.
2. Relational Database Model
- Both databases organize data in a structured format using tables, rows, and columns.
- Each row represents a record, and each column represents an attribute, adhering to the standard relational database principles.
3. Cross-Platform Compatibility
- MySQL and PostgreSQL can run on multiple operating systems including Windows, Linux, and macOS, making them highly versatile for different development environments.
4. ACID Compliance
- Both databases follow the ACID (Atomicity, Consistency, Isolation, Durability) principles, ensuring that all transactions are reliable, consistent, and maintain data integrity even in concurrent operations
5. Multi-User Support
- They are capable of handling multiple users and concurrent connections efficiently, which is essential for web applications, enterprise systems, and other multi-user environments.
6. Strong Community Support
- Both MySQL and PostgreSQL have active global communities, extensive documentation, and commercial support options, making it easier for developers and businesses to get help and resources.
Use Cases of MySQL and PostgreSQL
Use Cases of MySQL
- Web Applications: MySQL is ideal for dynamic websites and content management systems (CMS) like WordPress, Joomla, and Drupal.
- E-commerce Platforms: It powers online stores and shopping platforms that require fast read-heavy operations.
- Blogging and Media Websites: Its performance and ease of setup make it suitable for blogs, news portals, and media sites.
- Small-to-Medium Applications: MySQL works efficiently for startups and businesses that need lightweight and easy-to-manage databases.
- Data Warehousing for Basic Analytics: Suitable for simple analytics and reporting when complex queries are not required.
Use Cases of PostgreSQL
- Enterprise Applications: Preferred for large-scale enterprise systems that require high reliability, complex transactions, and advanced SQL compliance.
- Financial and Banking Systems: Its ACID compliance and transactional integrity make it suitable for finance-related applications.
- Geospatial Applications: PostgreSQL with the PostGIS extension is widely used for GIS (Geographic Information System) projects and mapping services.
- Data Analytics and Warehousing: Handles complex queries and large datasets efficiently, making it perfect for business intelligence and analytics.
- Custom Applications with Complex Data: Supports JSON, arrays, and user-defined types, allowing developers to build applications requiring flexible data structures.
How to Choose Between MySQL and PostgreSQL?
Choosing between MySQL and PostgreSQL depends on your project requirements, data complexity, and performance needs. Both databases are reliable and widely used, but each has unique strengths that make it better suited for specific scenarios. Here’s a detailed guide to help you decide:
1. Consider Your Application Type
- MySQL is ideal for web applications, e-commerce platforms, and content management systems where read-heavy operations dominate. Its simplicity and speed make it perfect for straightforward database requirements.
- PostgreSQL excels in complex applications that require advanced querying, analytics, or handling large datasets. It is preferred for financial systems, geospatial applications, and enterprise solutions.
2. Evaluate Data Complexity
- If your data is mostly structured and fits well into simple tables, MySQL is sufficient.
- For applications requiring complex data types like JSON, arrays, or custom types, PostgreSQL’s extensibility and rich data type support are more suitable.
3. Performance & Concurrency Needs
- MySQL is generally faster for simple read-heavy operations and small-to-medium workloads.
- PostgreSQL handles concurrent transactions efficiently with Multi-Version Concurrency Control (MVCC), making it better for write-heavy or analytical workloads.
4. Extensibility & Customization
- PostgreSQL offers high extensibility, allowing custom functions, operators, and procedural languages. This makes it ideal for projects that require complex business logic inside the database.
- MySQL has limited extensibility, which is acceptable for simpler applications.
5. Standards Compliance & Reliability
- PostgreSQL is highly ANSI SQL-compliant and is considered more reliable for mission-critical applications where strict compliance and data integrity are priorities.
- MySQL is partially compliant but still suitable for most web-based applications.
Conclusion
Both MySQL and PostgreSQL are powerful, open-source relational database systems, but they serve different purposes and excel in different scenarios. MySQL is ideal for web applications, e-commerce platforms, and projects that require fast read-heavy operations with straightforward data structures. PostgreSQL, on the other hand, is designed for complex, data-intensive applications that demand advanced querying, analytics, and extensibility.
By 2026, 70% of developer jobs will demand full-stack .NET skills. Stay ahead—enroll in our .NET full stack developer course and dominate the tech market!
FAQs
Take our Mysql skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.