13
FebLearn PostgreSQL: Features, Setup, and Step-by-Step Learning Guide
PostgreSQL (pronounced Post-Gres-Q-L) is a powerful, open-source object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) known for its reliability, scalability, and advanced data-handling capabilities. PostgreSQL is widely used in web development, data analytics, and cloud-based systems due to its strong community support and continuous innovation.
In this PostgreSQL tutorial, you’ll learn what is postgreSQL, features of postgresql, history, why learn postgreSQL, prerequisites for Learning PostgreSQL, Installation and Setup, How to Start Learning PostgreSQL from Basics.
What is PostgreSQL?
PostgreSQL is an open-source, object-relational database management system (ORDBMS) designed to handle complex data workloads with reliability and extensibility. Unlike traditional relational databases, PostgreSQL supports advanced data types, user-defined functions, and procedural languages, making it highly flexible for modern application requirements. It adheres closely to SQL standards while providing unique features like JSON storage, geospatial capabilities, and full-text search.
Key Features of PostgreSQL:
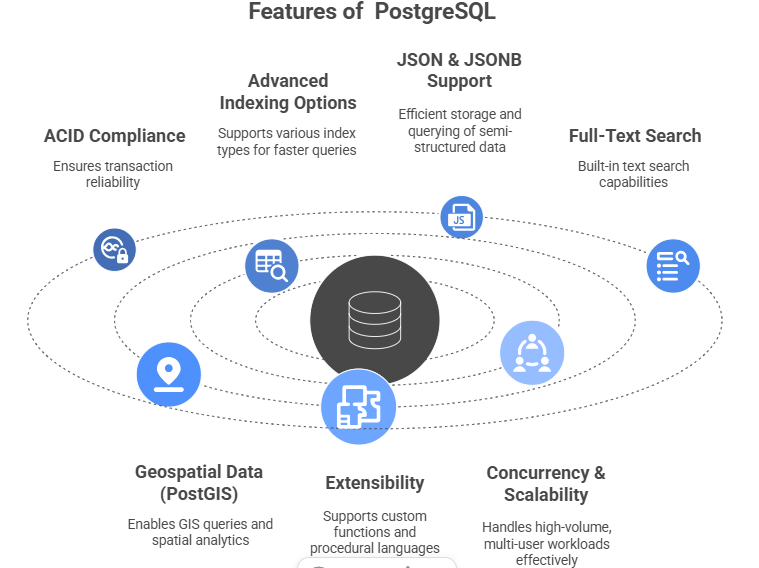
- ACID Compliance: Guarantees transaction reliability, ensuring that operations are atomic, consistent, isolated, and durable.
- Advanced Indexing Options: Supports B-Tree, Hash Table, GiST, GIN, BRIN indexes for faster query performance.
- JSON & JSONB Support: Efficient storage and querying of semi-structured data for modern applications.
- Full-Text Search: Built-in text search capabilities for blogs, content management systems, and search engines.
- Geospatial Data (PostGIS): Enables GIS queries, mapping, and spatial analytics.
- Extensibility: Supports custom functions, types, and procedural languages like PL/pgSQL, Python, and Perl.
- Concurrency & Scalability: Handles high-volume, multi-user workloads effectively using MVCC (Multi-Version Concurrency Control).
Why Learn PostgreSQL in 2025?
- Open Source and Free: PostgreSQL is completely free and backed by a strong developer community.
- Advanced Features: Supports transactions, triggers, views, stored procedures, and full ACID compliance.
- Cross-Platform: Runs on Windows, Linux, and macOS.
- Scalability and Performance: Handles massive datasets with ease.
- Extensible Architecture: Allows users to define custom functions and data types.
History of PostgreSQL
PostgreSQL originated from the Ingres project at UC Berkeley in the 1970s, led by Professor Michael Stonebraker.
PostgreSQL History Table:
| Year | Development |
| 1970s | Development of the Ingres Project at UC Berkeley by Prof. Michael Stonebraker. |
| 1986 | Launch of the POSTGRES (Post-Ingres) project to add advanced database features. |
| 1989 | First version of POSTGRES released. |
| 1994 | POSTGRES 4.2 made open source. |
| 1995 | Added SQL support and renamed the project to PostgreSQL. |
| 1996 | Official open-source release of PostgreSQL 6.0. |
| 2000s | Introduction of enterprise features like MVCC, replication, and point-in-time recovery. |
| 2010s | Added JSON support, PostGIS, and cloud compatibility. |
| 2020s | PostgreSQL becomes one of the most popular open-source databases globally, powering enterprise and cloud applications. |
Prerequisites for Learning PostgreSQL
- Familiarity with computers and basic command-line usage.
- Prior programming is not mandatory but helpful.
- Understanding of relational database concepts.
- Basic SQL knowledge is beneficial. Beginners can start with tutorials on SELECT, INSERT, and JOIN.
- Text Editor: VS Code, Sublime Text, or Atom.
- Terminal / Command Line Access: To interact with PostgreSQL server.
- Optional GUI: pgAdmin, DBeaver, or TablePlus for easier database management
Installation and Setup
1. Windows
- Download PostgreSQL installer from official site.
- Run the installer and follow instructions.
- Set up the default user (postgres) and password.
- Verify installation using pgAdmin or psql in terminal.
2. macOS
Homebrew Installation:
brew install postgresql
brew services start postgresql
Postgres.app: GUI-based, drag-and-drop setup for immediate use.
3. Linux
Debian/Ubuntu:
sudo apt update
sudo apt install postgresql postgresql-contrib
sudo systemctl start postgresql
CentOS/RedHat:
sudo yum install postgresql-server postgresql-contrib
sudo postgresql-setup initdb
sudo systemctl start postgresql
4. Docker Setup
Run PostgreSQL in a container:
docker run --name postgres-container -e POSTGRES_PASSWORD=yourpassword -p 5432:5432 -d postgres
5. Verifying Installation
Start the PostgreSQL server:
pg_ctl -D /usr/local/var/postgres start # macOS
sudo service postgresql start # Linux
Connect and create your first database:
psql -U postgres
CREATE DATABASE mydb;
6. Common Pitfalls
- Connection issues: Firewall or port conflicts.
- Authentication errors: Ensure correct password and user setup.
- Configuration issues: Misconfigured pg_hba.conf can block access.
How to Start Learning PostgreSQL from Basics
1. Understand Database Fundamentals
- Begin with the basics of databases what they are, how data is stored, and how SQL (Structured Query Language) works.
- This foundation will help you understand PostgreSQL more easily.
2. Install PostgreSQL
- Download and install PostgreSQL from the official PostgreSQL website.
- The installation includes pgAdmin, a graphical tool that helps you manage your databases visually.
3. Learn Basic SQL Commands
- CREATE DATABASE, CREATE TABLE: for database and table creation
- INSERT, SELECT, UPDATE, DELETE: for data manipulation
- WHERE, ORDER BY, GROUP BY: for filtering and organizing data
4. Explore PostgreSQL’s psql Tool
- Use the psql command-line interface to interact with your database directly.
- Learn essential commands like \l (list databases), \c (connect), and \dt (list tables).
5. Work on Real Projects
6. Learn Advanced Features
- Joins and subqueries
- Indexing and optimization
- Views, triggers, and stored procedures
- Backup and restore operations
7. Use Online Resources
- PostgreSQL Official Docs
- YouTube tutorials and PostgreSQL courses on platforms like Scholarhat ,Coursera or more.
8. Practice Regularly
Conclusion
Learning PostgreSQL is a valuable step toward mastering modern data management and database development. With its powerful features, open-source flexibility, and strong community support, PostgreSQL is ideal for both beginners and professionals. By understanding SQL fundamentals, practicing real-world examples, and exploring advanced concepts, you can quickly build a solid foundation.
Consistent learning and hands-on experience will help you become confident in handling complex databases and open up excellent career opportunities in data-driven fields. .NET full stack developers climb to senior roles 15% faster. Accelerate your growth with our .NET Full Stack Developer Course and unlock leadership positions!
FAQs
- Complex analytical queries
- Large-scale applications
- Full SQL standard compliance
- Strong ACID properties
- Support for stored procedures, triggers
- Powerful indexing & query optimization
- Role-based authentication
- Extensions like PostGIS (for Geospatial data)



