27
FebData Types in Python - 8 Data Types in Python With Examples
Data types in Python are categories that define what kind of value a variable can hold. They help the computer understand how to use and store the data properly. Common data types include integers (whole numbers like 10), floats (decimal numbers like 3.14), strings (text like "hello"), and booleans (True or False).
Besides these, Python has special data types to store many values together. Lists hold ordered items that can change, tuples are like lists but cannot be changed, and dictionaries store data as key-value pairs for quick access. Knowing data types is important because it helps you write clear and error-free programs.
In this Python tutorial, we’ll explore the most commonly used data types in Python and provide practical insights into their applications. 90% of self-taught coders struggle to land jobs. Enroll in our Free Python Course with Certification to gain industry-ready skills, and the competitive edge you need to stand out and get hired.
What are the Data Types in Python?
The data type in Python tells us what kind of value a variable in Python can hold. They help the Python interpreter understand how to handle and process the data. Using the correct data types in Python makes your code more accurate and easier to work with.
Key Features of Data Types in Python
- Dynamically Typed: You don’t need to declare the data type of a variable. Python automatically understands it when you assign a value.
- Built-in Data Types: Python provides many built-in data types, such as int, float, str, bool, list, tuple, dict, and set.
- Flexible and Easy to Use: You can easily switch between data types using built-in functions like int(), str(), or list().
- Supports Type Conversion:Python allows changing the data type of a value (for example, from string to integer) using type casting.
- Memory Efficient: Python manages memory for data types automatically, so you don’t have to worry about memory allocation.
- Object-Oriented: All data types in Python are treated as objects, which means they come with built-in functions and properties.
Understanding the different data types in Python is important for writing correct and flexible code. This section will explain the different data types in Python, how they work, and where to use each type in real programs.
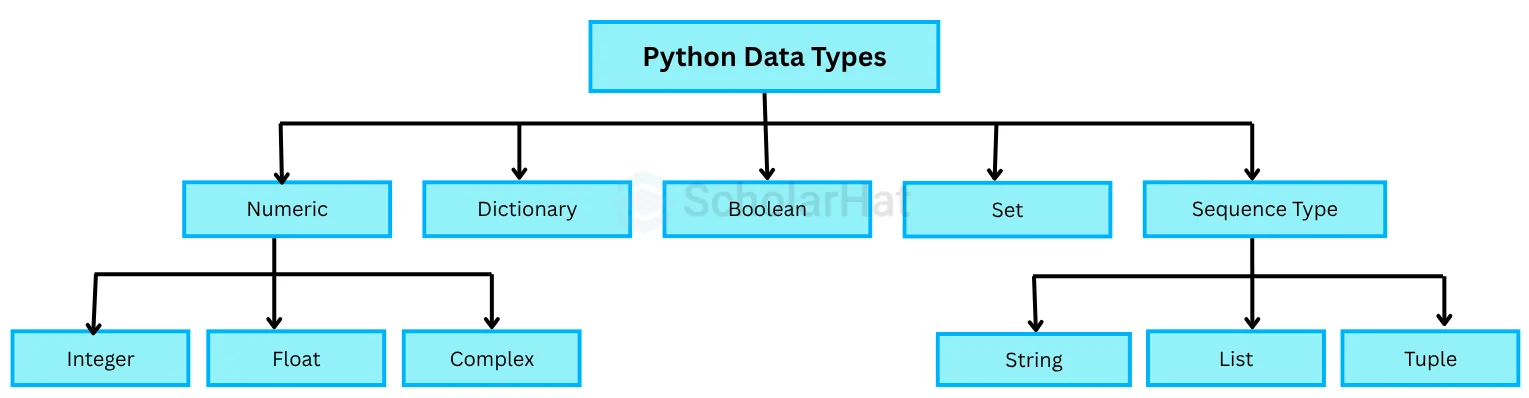
1. Numeric Data Types in Python
When you work with numbers in Python, you use numeric data types in Python. They let you handle different types of numeric values like whole numbers, decimals, or even complex numbers. Let's learn the numeric data types in Python:
- int: Used for whole numbers. These are signed integers like 10, -5, or 0.
- long: Python 2 supports long integers, which can represent vast numbers, including octal and hexadecimal. (In Python 3, all integers are of type int.)
- float: Used for decimal numbers, like 3.14 or -0.99.
- complex: Represents numbers with a real and imaginary part, like 3+4j.
Example
# integer variable.
a=150
print("The type of variable having value", a, " is ", type(a))
# float variable.
b=20.846
print("The type of variable having value", b, " is ", type(b))
# complex variable.
c=18+3j
print("The type of variable having value", c, " is ", type(c))
Output
The type of variable having value 150 is <class 'int'>
The type of variable having value 20.846 is <class 'float'>
The type of variable having value (18+3j) is <class 'complex'>Explanation
- The program defines three variables: a, b, and c, with integer, float, and complex values, respectively.
- The type() function is used to determine the data type of each variable.
- It prints the variable's value and its corresponding data type to the console.
- This helps in understanding how Python recognizes and categorizes different types of data.
2. Sequence Data Type in Python
A sequence data type in Python is like a line of items arranged in a specific order. You can go through each item one by one, and you can also get any item using its position (index).
In Python, there are three main sequence types:
- String Data Type
- List Data Type
- Tuple Data Type
2. Python String Data Type
A string is a collection of characters enclosed in single, double, or even triple quotes. Key features of the String data type in Python:
- Immutable: Once you create a string, you can’t change its content.
- Multi-line Support: Use triple quotes (''' or """) for strings that span multiple lines.
- Indexing and Slicing: Access individual characters or parts of the string using indices.
- String Methods: Python offers built-in methods like lower(), upper(), and replace() for string manipulation.
Example
str = 'Hello World!'
print (str) # Prints complete string
print (str[0]) # Prints first character of the string
print (str[2:5]) # Prints characters starting from 3rd to 5th
print (str[2:]) # Prints string stating from 3rd character
print (str * 2) # Prints string two times
print (str + "TEST") # Prints concatenated stringOutput
Hello World!
H
llo
llo World!
Hello World!Hello World!
Hello World!TEST
Explanation
- The program demonstrates string operations in Python.
- It shows how to print the complete string, access specific characters, extract substrings using slicing in Python, repeat the string, and concatenate it with another string using the string in Python.
3. Python List Data Type
When you need to store multiple items in a single variable, you’ll use the list data type in Python. A list can hold items of different data types in Python, and you can easily modify, add, or remove elements. You can explore how to work with lists in Python. You can create a list in Python by placing items inside square brackets [], separated by commas.
Example
list = [ 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2 ]
tinylist = [123, 'Scholar-Hat']
print (list) # Prints complete list
print (list[0]) # Prints first element of the list
print (list[1:3]) # Prints elements starting from 2nd till 3rd
print (list[2:]) # Prints elements starting from 3rd element
print (tinylist * 2) # Prints list two times
print (list + tinylist) # Prints concatenated listsOutput
['abcd', 786, 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2]
abcd
[786, 2.23]
[2.23, ‘Scholar-Hat', 70.2]
[123, 'Scholar-Hat', 123, 'john']
['abcd', 786, 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2, 123, 'Scholar-Hat']
Explanation
- This program demonstrates various list operations in Python, including printing the entire list, accessing specific elements, slicing the list, repeating elements, and concatenating two lists.
- It uses two lists, list and finalist, and performs various operations like slicing and concatenation.
How will you access items in the List?
In Python, if you want to get something from a list, you can just use its position. If you count from the front (starting at 0), that's called positive indexing. But if you count from the back (starting at -1), that's negative indexing; it's like reading from the end.
Example
fruits = ["apple", "banana", "mango"]
print(fruits[0]) # apple (counting from the front)
print(fruits[-1]) # mango (counting from the back) Output
apple
mango4. Python Tuple Data Type
A tuple in Python is one of the data types that represents an ordered list of elements, just like a list. However, unlike lists, tuples are immutable, meaning that once created, they cannot be changed.
- You can create a tuple by placing items inside round brackets (), separated by commas.
- Tuples are ordered and unchangeable, meaning you can't change their values after creating them.
Example
tuple = ( 'abcd', 786 , 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2 )
tinytuple = (123, 'Scholar-Hat')
print (tuple) # Prints the complete tuple
print (tuple[0]) # Prints first element of the tuple
print (tuple[1:3]) # Prints elements of the tuple starting from 2nd till 3rd
print (tuple[2:]) # Prints elements of the tuple starting from 3rd element
print (tinytuple * 2) # Prints the contents of the tuple twice
print (tuple + tinytuple) # Prints concatenated tuplesOutput
('abcd', 786, 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2)
abcd
(786, 2.23)
(2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2)
(123, ‘Scholar-Hat', 123, 'Scholar-Hat')
('abcd', 786, 2.23, 'Scholar-Hat', 70.2, 123, 'Scholar-Hat')
Explanation
- The program defines two tuples, tuple and tinytuple, containing mixed data types.
- Considering both tuples, we just perform the operations on the tuple data types in Python.
How will you access items in a tuple?
You can access items in a tuple just like a list, by using index numbers. Indexes start from 0, and you can also use negative numbers to access items from the end.
fruits = ("apple", "banana", "mango")
# Access using positive index
print(fruits[0]) # Output: apple
# Access using negative index
print(fruits[-1]) # Output: mango Output
apple
mango5. Python Range Data Type
The range data type in Python represents a sequence of numbers commonly used in loops in Python. It generates numbers starting from a given value up to, but not including, another value. As one of the useful data types in Python, it’s very convenient when you need to iterate over a specific range of values without manually creating a list.
Key Features of Python Range
- Efficient: It generates numbers on the fly, which is memory efficient compared to lists.
- Supports Indexing: You can access individual elements of a range using indexing.
- Customizable: You can specify the start, stop, and step values when creating a range.
- Used in Loops: Commonly used in Python for loops to iterate over a sequence of numbers.
Example
for i in range(1, 5):
print(i)Output
1
2
3
46. Python Dictionary Data Type
A dictionary data type in Python is a collection of key-value pairs. It allows you to store data in a way that associates a unique key with a corresponding value. As one of the most powerful data types in Python, it’s beneficial to look up data based on a unique identifier quickly.
Key Features of Python Dictionaries
- Unordered: The items in a dictionary are not stored in any particular order.
- Mutable: You can modify, add, or remove key-value pairs after the dictionary is created.
- Unique Keys: Each key in a dictionary is unique, and it maps to a specific value.
- Efficient Lookup: You can quickly retrieve the value associated with a key.
Example
dict = {}
dict['one'] = "This is one"
dict[2] = "This is two"
tinydict = {'name': 'Scholar-Hat','code':6734, 'dept': 'sales'}
print (dict['one']) # Prints value for 'one' key
print (dict[2]) # Prints value for 2 key
print (tinydict) # Prints complete dictionary
print (tinydict.keys()) # Prints all the keys
print (tinydict.values()) # Prints all the valuesOutput
This is one
This is two
{'name': 'Scholar-Hat', 'code': 6734, 'dept': 'sales'}
dict_keys(['name', 'code', 'dept'])
dict_values(['Scholar-Hat', 6734, 'sales'])Explanation
- This program creates two dictionaries, dict, and tinydict, with key-value pairs.
- And we did print operations on these dictionary data types in Python.
7. Python Boolean Data Type
The boolean data type in Python represents one of two possible values: True or False. It is one of the most important data types in Python, especially for conditional statements, where decisions are made based on whether a condition is true or false. As a part of the core data types in Python, it plays a key role in controlling the flow of a program.
Key Features of Python Booleans
- True or False: The two boolean values are True and False.
- Conditional Logic: Used extensively in if and while statements to control program flow.
- Result of Comparisons: Comparisons between values often result in a Boolean value.
- Logical Operations: You can use logical operators in Python like and, or, and not with boolean values.
Example
a = True
# display the value of a
print(a)
# display the data type of a
print(type(a))Output
true
<class 'bool'>Explanation
- This program defines a variable a and assigns it the boolean value True.
- print(a): Displays the value of a, which is True.
- print(type(a)): Displays the data type of a, which is <class 'bool'>.
8. Python Set Data Type
A set is one of the data types in Python that stores an unordered collection of unique elements. It’s a very handy data type in Python when you need to store values without duplicates and perform operations like union, intersection, and difference. Among the many data types in Python, sets are efficient when you want each element to be unique and easy to work with.
Key Features of Python Sets
- Unordered: Sets do not maintain any order of elements.
- Unique Elements: A set automatically removes duplicate values, so each element is unique.
- Mutable: You can add or remove elements from a set after it is created.
- Supports Set Operations: Python sets support operations like union(), intersection(), and difference().
Example of Set Data Type in Python
my_set = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5}
print(my_set)Output
{1, 2, 3, 4, 5}Explanation
- This program defines a set my_set containing the elements 1, 2, 3, 4, 5.
- print(my_set): Displays the content of the set my_set.
- Since sets are unordered collections, the elements might appear in any order when printed.
Data Type Conversion Function in Python
The data types in Python can be changed from one type to another using built-in conversion functions. This process is called type casting or type conversion. For example, you can convert an integer to a string using str() or a float to an integer using int().
Reasons why data type conversion is helpful in Python:
- It helps you work with different data types in Python without errors.
- It makes your code more flexible and reusable by handling different input types.
- It is essential when reading data from files, user input, or performing calculations.
- Understanding this helps you switch between various data types in Python easily.
Example
a = str(1) # a will be "1"
b = str(2.2) # b will be "2.2"
c = str("3.3") # c will be "3.3"
print (a)
print (b)
print (c)Output
1
2.2
3.3Explanation
- This program converts different data types into strings using the str() function.
How do you check the data type in Python?
To check the data types in Python, you can use the built-in type() function. It tells you what kind of data types in Python a value or variable has. This is very helpful when working with different data types in Python, especially when you're not sure what kind of data you're dealing with.
Example:
value = 10
print(type(value))
Output
<class 'int'>Explanation
- This code creates a variable value with the number 10 and uses print(type(value)) to display its data type, which is <class 'int'> (an integer).
Conclusion
Now you’ve learned the basics of data types in Python, and that’s a big step for writing better code. Each data type is helpful in its own way, and knowing how to use them makes your work easier. Keep practicing with different data types in Python, and don’t worry if you make mistakes; that’s how you learn.
Single-skill coders are losing out to full-stack pros. Upgrade with our Full-Stack Python Developer Certification Training to level up!
If you are preparing for the Python Interview Questions and Answers Book, this Python Interview Questions and Answers Book can really help you. It has simple questions and answers that are easy to understand. Download and read it for free today!
Test your skills with the following MCQs 🎯
Test your knowledge of Python data types and strengthen your foundation in programming!
Q 1: Which of the following is an immutable data type?
FAQs
Take our Python skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.







