15
FebContext in React
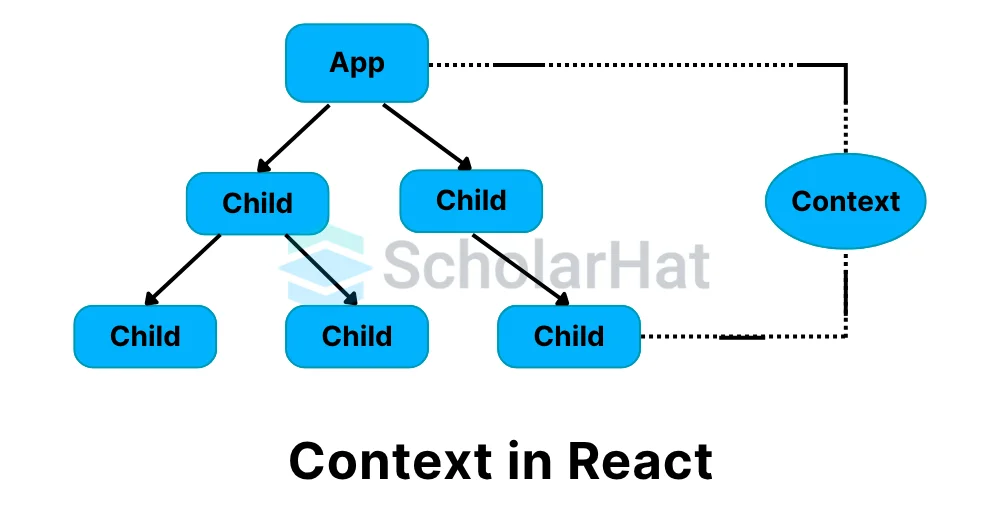
Context in React allows data to be passed through the component tree without manually prop-drilling at each level. It serves as a way to share 'global' or 'contextual' data within an app, such as the current user, theme preferences, or language settings.
In this React Tutorial, we'll cover what React Context is, when and when not to use it, its main benefits, and how to implement it step by step. You'll also discover best practices for effective usage and find helpful resources for further learning. React.js developers earn 50% more than basic JavaScript coders. Don’t wait—enroll in our free react js course with certificate and unlock your earning potential!
What is the context in React?
Context in React is a technique that makes it easy to share data across different parts of your app without having to pass it manually through every component. It’s useful for sharing things like the current user, theme (dark or light), or language settings with any component that needs them.
For a React application, it serves as a global state management system, enabling data to be shared and consumed by components at various levels of the component tree.
Read More - Top 50 Most Asked React Interview Questions & Answers
When to Use React Context?
When you have data that several components at various levels of the component tree need access to, the React context is most helpful. It is made to manage data that a tree of React components would deem to be "global." Data that can be stored in React context includes some examples such as:
- Theme information, including dark or light mode
- User information, such as the authenticated user at the moment
- Location-specific information, like user language and location
You can avoid the trouble of passing props through intermediary components that don't directly use the data by utilizing React Context. Instead, you can just use the context store to get the data in the components that require it.
The Benefits of React Context
React context is an effective tool for managing state in React apps due to a number of features it offers:
- Data sharing is made simple: You can avoid having to provide props via numerous tiers of components by utilizing React Context. This streamlines the code and makes it simpler for components to share data.
- Reduced Prop Drilling: Prop drilling, which is the practice of passing props through numerous intermediary components, can exacerbate the complexity and maintenance challenges of the code. React Context does away with the necessity for prop digging by offering a central location where all components may access data.
- Better Organisation of the Code: By separating responsibilities and maintaining relevant data in a single context store, React Context helps you better organize your code. The data is now simpler to manage & update as necessary.
- Improving Performance: Only the components that rely on the context data are re-rendered when the data changes, since React Context is performance-optimized. This enhances the performance of your application as a whole.
Read More - React developer salary in India
How to Use React Context
There are four key steps to using React Context:
- Create Context in React: Utilizing React's createContext function, you must first create a Context in React. By doing this, a context object that may be used to read and save data is created.
- Provide Context: The context must next be given to the components that will use the data. The component that serves as the context provider, React, is wrapped around the component or component tree to accomplish this. The data is transferred from the provider component to the consuming components using a value prop.
- Consume Context: You must utilize the context consumer react component to have access to the context's data. You can use the data within your components by consuming it through this component. Both the render props pattern and the useContext hook can be used to obtain the data.
- Update Context (If Necessary): You can adjust the context provider's value to reflect any necessary updates to the context's data. The components that rely on the context data will then be rendered again as a result.
When Not to Use React Context:
Even though React Context has numerous advantages, it might not be appropriate in all situations. The following situations suggest that React Context may not be the best option:
- Small Programmes: Using React Context could be overkill if you're developing a tiny application with a simple component hierarchy and few data exchange requirements. Manually passing props is frequently easier and more effective in these situations.
- Applications with High Performance: Using React Context may have an impact on performance if your application needs regular modifications to the context data & has a lot of components that rely on the context. A more optimized state management system, such as Redux, may be a preferable option in these circumstances.
- Management of Complex States: Using a specialized state management library like Redux can give you access to more sophisticated capabilities and more effective state management tools if your application needs extensive state management, such as time-travel debugging or undo/redo capability.
Context.Provider
Context provider React is a component that serves to provide context to its child components. It serves as the React context API's primary component. The data that will be shared with the child components is submitted as a value prop to the provider component. Any sort of data, including a string, an object, or an array, can be the value prop.
Here is a simple example using the context provider React:
import React, { createContext } from 'react';
// Step 1: Create Context in react
const MyContext = createContext();
// Step 2: Create a component that will provide the context values
const MyProvider = ({ children }) => {
const contextValue = 'Hello from Context!'; // The value you want to provide
return (
<MyContext.Provider value={contextValue}>
{children}
</MyContext.Provider>
);
};
// Step 3: Create a component that consumes the context values
const ChildComponent = () => {
return (
<MyContext.Consumer>
{contextValue => (
<div>{contextValue}</div>
)}
</MyContext.Consumer>
);
};
// Step 4: Use the components in your app
const App = () => {
return (
<MyProvider>
<ChildComponent />
</MyProvider>
);
};
export default App;In this example, we use the createContext() method, with the value "Hello from Context!" MyProvider encapsulates ChildComponent in MyContext.Provider. ChildComponent uses the context value using MyContext.Consumer and shows it. The app utilizes MyProvider to supply the context value, and ChildComponent displays "Hello from Context!" as a result. If you're looking to validate your React expertise, consider pursuing a React Certification to demonstrate your proficiency in React development.
Context.Consumer
Context Consumer React is a component that sticks to context changes. The nearest available context is consumed using it. A function is taken as a child by the consumer component, and this function returns a React node after receiving the current context value.
Here is a simple example using Context Consumer React:
import React, { createContext } from 'react';
// Step 1: Create a new context
const MyContext = createContext();
// Step 2: Create a component that consumes the context values
const ChildComponent = () => {
return (
<MyContext.Consumer>
{contextValue => (
<div>{contextValue}</div>
)}
</MyContext.Consumer>
);
};
// Step 3: Use the component in your app
const App = () => {
const contextValue = 'Hello from Context!'; // The value you want to provide
return (
<MyContext.Provider value={contextValue}>
<ChildComponent />
</MyContext.Provider>
);
};
export default App;In this example, a context is created, and a component that uses the context value is added. We access the value and render it in a <div> using MyContext.Consumer. MyContext.Provider in the App provides the context value 'Hello from Context!' so that the ChildComponent can show it.
Best Practices of React Context
Here are some guidelines for using React Context:
- Use context sparingly: Context should only be utilized when data is really global or deeply nested. Don't use it to pass information that can be handled via props.
- Limit context values: Performance problems may result from using large or complicated items as context values. Reduce context values as much as you can to reduce re-renders
- Set default values: To address situations where components are presented outside the context provider, set default settings for context.
- Separate context generation from usage: At higher levels of the component tree, create context and supply values. Only the values that the consuming components actually need should be accessed.
- Memorise context consumers: To avoid needless re-renders, memoize components that consume context values using techniques like React. memo or useMemo.
- Avoid excessive nesting: To increase readability and maintainability, avoid utilizing too much nesting. Keep the component tree flat when using context.
- Test context usage: By including the proper context values in tests to account for various scenarios, test context usage involves testing components that consume context.
- Document context usage: Clearly state the function, configuration, and application of context, along with desired outcomes. This aids other developers in effectively interpreting and utilizing context.
Conclusion
In this tutorial, we explored what React Context is, when and when not to use it, and how it helps manage global state in React applications. We covered its key benefits, including simplified data sharing, reduced prop drilling, and better code organization.
The average React.js developer earns ₹15–25 LPA, but seniors earn more. Don’t wait—Enroll in our Reactjs Certification Course and unlock top-tier roles!
FAQs
- Create context using React.createContext().
- Provide context using <Context.Provider> with a value prop.
- Consume context using either useContext() or <Context.Consumer>.
- Update context by changing the value in the provider, which re-renders consuming components.
- You're building small apps with simple data needs.
- Your app has high-performance requirements and updates frequently.
- You need complex state management features like time-travel debugging or middleware—in such cases, use Redux or other libraries.
- Use Context only for truly global or deeply nested data.
- Keep context values minimal and focused to prevent unnecessary re-renders.
- Memoize consuming components using React.memo() or useMemo().
- Set default values for robustness.
- Document the purpose and usage of each context for better maintainability.
Take our React skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.