06
FebRouting in React using React-Router: Part1
Routing in React allows you to navigate between different components (pages) of your application without reloading the entire page. This is essential for building Single Page Applications (SPAs). React Router works like a GPS in the world of Web Development. Routing is a kind of mechanism by which users can navigate through different URLs available in a whole web application.
In this React Tutorial, we will try to learn about What is Routing and How to use React Routing with Examples. Mastering React.js opens doors to remote jobs and global opportunities. Don’t wait—enroll in our Free React Course now and get started!
What is Routing?
Routing is one of the important concepts in terms of features while developing Single Page Application (SPA). Using routing we can load the view partially without loading the webpage again from the server which makes our web app very much faster in terms of performance.
- Enables multi-page navigation in a SPA.
- Enhances user experience by avoiding full-page reloads.
- Lets you build complex apps like dashboards, blogs, e-commerce stores, etc.
React Router:
- React Router is a standard library for creating dynamic routes and navigation in React JS Applications.
- It allows you to manage navigation in your app by defining routes that connect the URL paths to specific components.
How to Install and Create a New React App
Step 1:To install and create a new react app, we need to install it in our React application by using the below-given commands.
bashnpm install create-react-app
Step 2:So when you execute the above command using a command prompt or power shell, now we can create a new reactjs app using the following command.
bashcreate-react-app react-routing-with-bootstrap4
Step 3: When we run the above command, you can see that our project will be created and run the application by using the following npm command.
bashnpm start
A new window into our default system browser will automatically open and a new window and you can see that our application is up and running somewhat as a given snapshot.
Read More - React Interview Questions For Freshers
React-router: Add Routing to the React App
Now we have a new project created with the name "react-routing-with-bootstrap4", and when you open the package.json file, it will look like this.
{
"name": "react-routing-with-bootstrap4",
"version": "0.1.0",
"private": true,
"dependencies": {
"react": "^16.5.1",
"react-dom": "^16.5.1",
"react-scripts": "1.1.5"
},
"scripts": {
"start": "react-scripts start",
"build": "react-scripts build",
"test": "react-scripts test --env=jsdom",
"eject": "react-scripts eject"
}
}Step 4: So as you can see in the above code snippet, we don't have the package installed called “react-router”, which is used to implement routing in react applications.
When we create a new react app, it will not be installed automatically into our project but if you want to use this package or are unable to find this package in your package.json then you can use the below npm command.
bashnpm install react-router
Step 5: There is a package named react-router-dom which indirectly depends on react-router, and in this article, we are going to use this package, in order to use it, execute the below npm command.
bashnpm install react-router-dom
Step 6: To design our page, we are going to use an additional third-party package of Bootstrap which is called react-bootstrapwhich provides different bootstrap-based components for the React application, just install the package using the below command.
bashnpm install react-bootstrap
So far we have covered the introduction part and also the installation part, now it’s time to implement a simple routine procedure.
Read More - React JS Roadmap 2024
Steps to Configure Routing in React
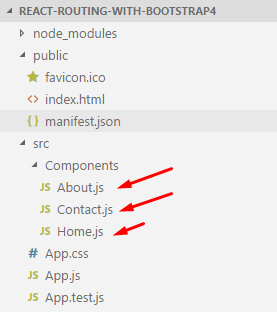
Step 1: Create Component Pages
In this simple yet effective example, we are going to work with the three different pages as Dashboard, About Us, and Contact Us. And for that, let's create a new folder inside the /src directory in React application and create three different files as given below.
- Home.js
- About.js
- Contact.js
And in these files, we are just showing static messages, and going to export these components, for that open the respective file and paste the following code snippets.
Home.jsimport React from 'react';
const Home = () => (
<div>
<h1>This Is From Dashboard Page</h1>
</div>
)
export default Home;import React from 'react';
const About = () => (
<div>
<h1>This Is From About Us Page</h1>
</div>
)
export default About;import React from 'react';
const Contact = () => (
<div>
<h1>This Is From Contact Us Page</h1>
</div>
)
export default Contact;So these three files are acts as the different independent pages just to see the routing in action by going from one page to another, the very next step is to design our user interface, and for design purposes, we have used react-bootstrap components such as Navbar, Nav, MenuItem as explained into the second step.
Step 2: Update App.js with React-Bootstrap Navbar
After creating all those files, it’s time to implement the user interface part in which we are going to implement navigations using react-bootstrap design components. Open App.js and paste the following code snippet.
<import React from 'react';>
<import './App.css';>
<!-- React-Bootstrap components -->
<import { Navbar, Nav, Container } from 'react-bootstrap';>
<!-- React Router components -->
<import { BrowserRouter as Router, Routes, Route, Link } from 'react-router-dom';>
<!-- Custom components -->
<import Home from './Components/Home';>
<import About from './Components/About';>
<import Contact from './Components/Contact';>
<function App() {>
<return (
<Router>
<div className="App">
<Navbar bg="dark" variant="dark" expand="lg">
<Container>
<Navbar.Brand as={Link} to="/">Routing With React-Router</Navbar.Brand>
<Navbar.Toggle aria-controls="basic-navbar-nav" />
<Navbar.Collapse id="basic-navbar-nav">
<Nav className="me-auto">
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/">Dashboard</Nav.Link>
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/about">About Us</Nav.Link>
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/contact">Contact Us</Nav.Link>
</Nav>
</Navbar.Collapse>
</Container>
</Navbar>
<Container className="mt-4">
<Routes>
<Route path="/" element={<Home />} />
<Route path="/about" element={<About />} />
<Route path="/contact" element={<Contact />} />
</Routes>
</Container>
</div>
</Router>
);>
<}>
<export default App;>
Here in this code snippet, we have used different markups to implement routing, let’s see about each of them in detail as given below.
React Routing with React-Bootstrap – Key Components Explained
Navbar, Nav, Container :
jsx<!-- React-Bootstrap components -->
<import { Navbar, Nav, Container } from 'react-bootstrap';>
Container: Provides Bootstrap padding and centering for layout.
Navbar: A bootstrap component that is used to implement a navigation bar into our application.
<Navbar bg="dark" variant="dark" expand="lg">
...
</Navbar>Nav: It contains the list of navigation links. Holds the navigation links inside the navbar.
<Nav className="me-auto">
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/">Dashboard</Nav.Link>
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/about">About Us</Nav.Link>
<Nav.Link as={Link} to="/contact">Contact Us</Nav.Link>
</Nav>
<!-- React Router components -->
<import { BrowserRouter as Router, Routes, Route, Link } from 'react-router-dom';>
Link: This isa router API that allows accessing navigation throughout the application.
Route: The route is one of the most important parts/components in react-router and it is used to render the user interface when any location matches. Defines a path and what component to render at that path.
| Component | Source | Purpose |
| Router | React Router | Enables client-side navigation without page reload |
| Routes / Route | React Router | Define and match paths to components. |
| Link | React Router | Navigates within the app without reloading the page |
| Navbar | React Bootstrap | Creates a responsive top navigation bar |
| Nav/ Nav.Link | React Bootstrap | Contains and styles navigation links |
| Container | React Bootstrap | Adds consistent layout padding/margin |
Note
We have used react-bootstrap in our react application, for that we need to include two different style sheets, please find the below code snippet.
Public/Index.html <!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="utf-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1, shrink-to-fit=no">
<meta name="theme-color" content="#000000">
<link rel="manifest" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/manifest.json">
<link rel="shortcut icon" href="%PUBLIC_URL%/favicon.ico">
<!-- Bootstrap CDN Files -->
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap.min.css" integrity="sha384-BVYiiSIFeK1dGmJRAkycuHAHRg32OmUcww7on3RYdg4Va+PmSTsz/K68vbdEjh4u"
crossorigin="anonymous">
<link rel="stylesheet" href="https://maxcdn.bootstrapcdn.com/bootstrap/3.3.7/css/bootstrap-theme.min.css" integrity="sha384-rHyoN1iRsVXV4nD0JutlnGaslCJuC7uwjduW9SVrLvRYooPp2bWYgmgJQIXwl/Sp"
crossorigin="anonymous">
<!-- End -->
<title>React App</title>
</head>
<body>
<noscript>
You need to enable JavaScript to run this app.
</noscript>
<div id="root"></div>
</body>
</html>Primarily I have included two different bootstrap CDN and the version is 3.3.7, still, we can use bootstrap 4 as well, for that just we need to search for the latest CDN files for that and include them into our main index.html file. We are done with the user interface part so far, our next step is very much important so let’s have a look.
Step 3: Why UI Alone Won’t Work Without <BrowserRouter>
We are done with the UI part, but it won’t work as expected because we have not configured our app component with the router configuration, so for that, we need to use a router API called <BrowserRouter> as explained below.
What is <BrowserRouter>?
<BrowserRouter> is a router component from react-router-dom that enables client-side routing using the HTML5 History API. It allows you to:
- Navigate between pages without refreshing the browser
- Update the URL in the address bar
- Maintain page state efficiently
HTML5 History API Methods Used by React Router:
| Method | Description |
| pushState() | Pushes a new entry into the browser history (used for navigation) |
| replaceState() | Replaces the current entry in the history stack |
| popstate event | Triggered when the active history entry changes (e.g., using back/forward) |
These events are used to manage the different routing activity using state and update accordingly, and every time it manages its own history object for each of them.
Configuration in index.js
To configure BrowserRouter, we need to import the API from the package react-router-dom like this.
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';And the complete code will look like this for the file index.js.
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import './index.css';
import App from './App';
import registerServiceWorker from './registerServiceWorker';
import { BrowserRouter } from 'react-router-dom';
ReactDOM.render(
<BrowserRouter>
<App />
</BrowserRouter>, document.getElementById('root'));
registerServiceWorker();
Running the App
Now we are done with most of the primary settings required for the routing, and in order to test how routing works so for that, we need to run the application using the below npm command into the command prompt.
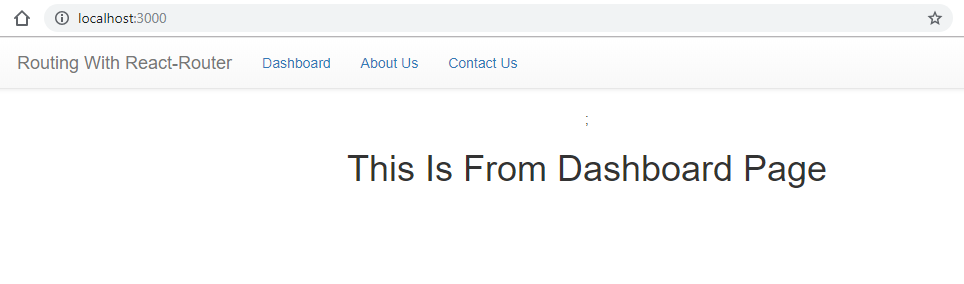
Npm startHow it works..
DashboardWhen we execute our application, at that time the first page will appear as Dashboard (Home) page, and you can see the output as given below.
When we click on the About us link, the about us page from the respective routing configuration will be redirected.
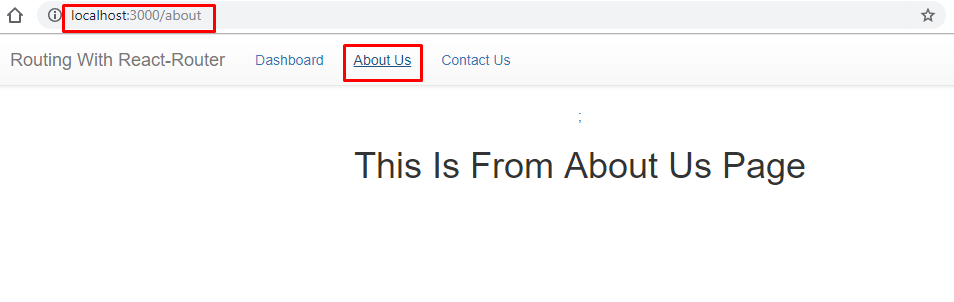
The third page is for contact us and you can see the output as given below.
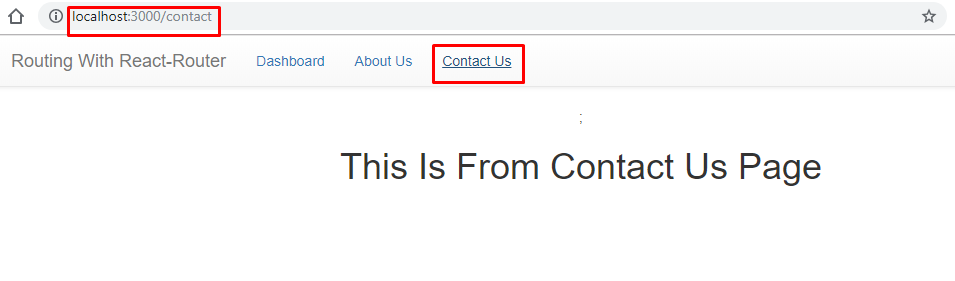
That's a wrap, we have created a straightforward React application using the routing configuration to showcase how multiple components can be configured with the routing and redirect can be done, and for the exercise, you can enhance this example by creating nested routing, parameterized routing or the hash-based routing configuration.
Summary
React Routing allows developers to create a multi-page experience in a single-page application (SPA) without refreshing the browser. By integrating react-router-dom with react-bootstrap, you can build dynamic, responsive, and navigable UIs easily.
React.js experts are landing ₹20–30 LPA roles while others struggle. Upgrade your skills with our React JS Online Training and secure your future.
Read More: Start your Dream Career with React Development
Take our React skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.