13
FebSpring Boot Roadmap 2025: The Ultimate Guide to Mastering Spring Boot
Spring Boot Roadmap, If you have ever dreamed of building powerful Java applications without getting lost in endless XML configurations, this journey is for you. Spring Boot is the fast lane on the Spring Framework highway. It reduces complexities, automates setup, and allows you to focus on writing code that truly matters. However, mastering Spring Boot isn’t just about learning annotations and dependencies. It’s also about seeing the bigger picture and understanding how all the pieces fit together, from your first “Hello World” to deploying enterprise-grade microservices.
In this Spring Boot roadmap, we’ll walk step-by-step through the essential skills, tools, and concepts you need to become a confident Spring Boot developer, whether you’re just starting or looking to improve your skills in architecture design.
Why Learn Spring Boot?

Spring Boot’s popularity stems from its ability to simplify Java development while meeting modern enterprise needs. Spring Boot is in high demand for building scalable, cloud-native applications, offering excellent career opportunities and a supportive community. Here’s why mastering Spring Boot right now is a smart career move:
1. Market Demand:
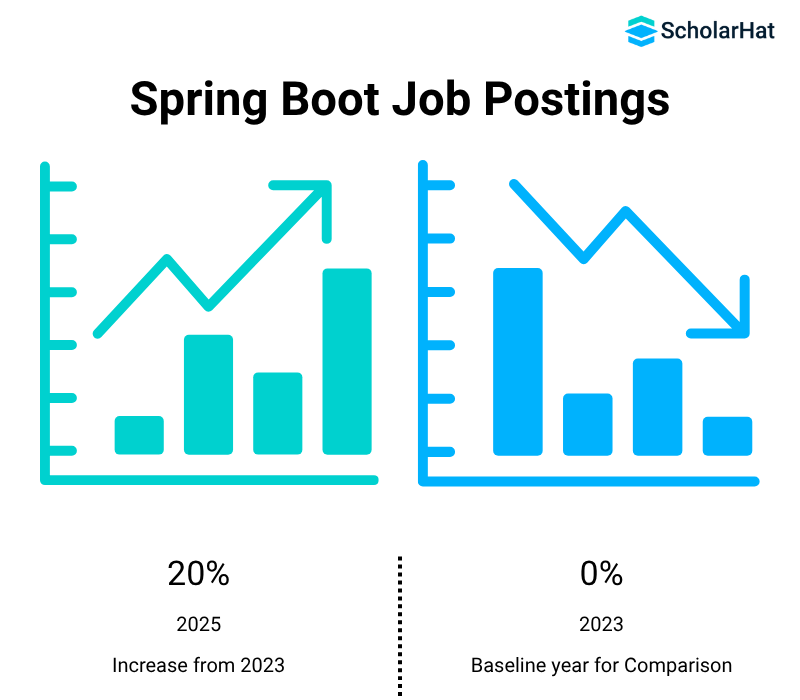
LinkedIn data shows a 20% increase in Spring Boot job postings from 2023 to 2025, with roles offering competitive salaries, often exceeding six figures for experienced developers. Companies like Amazon, Google, and startups rely on Spring Boot for scalable systems.
2. Technical Advantages:
Spring Boot’s auto-configuration eliminates boilerplate code, while starter dependencies streamline setup. Its seamless integration with cloud platforms (AWS, Azure, GCP) makes it ideal for modern architectures.
3. Ecosystem & Community:
The Spring ecosystem, including Spring Security and Spring Data, is backed by a vibrant community. Extensive documentation, forums, and conferences like SpringOne ensure you’re never stuck.
4.Trends:
Innovations like GraalVM for native compilation, AI-driven code generation (e.g., GitHub Copilot), and Kubernetes for microservices deployment keep Spring Boot at the forefront of backend development.
Spring Boot Roadmap Step-by-step 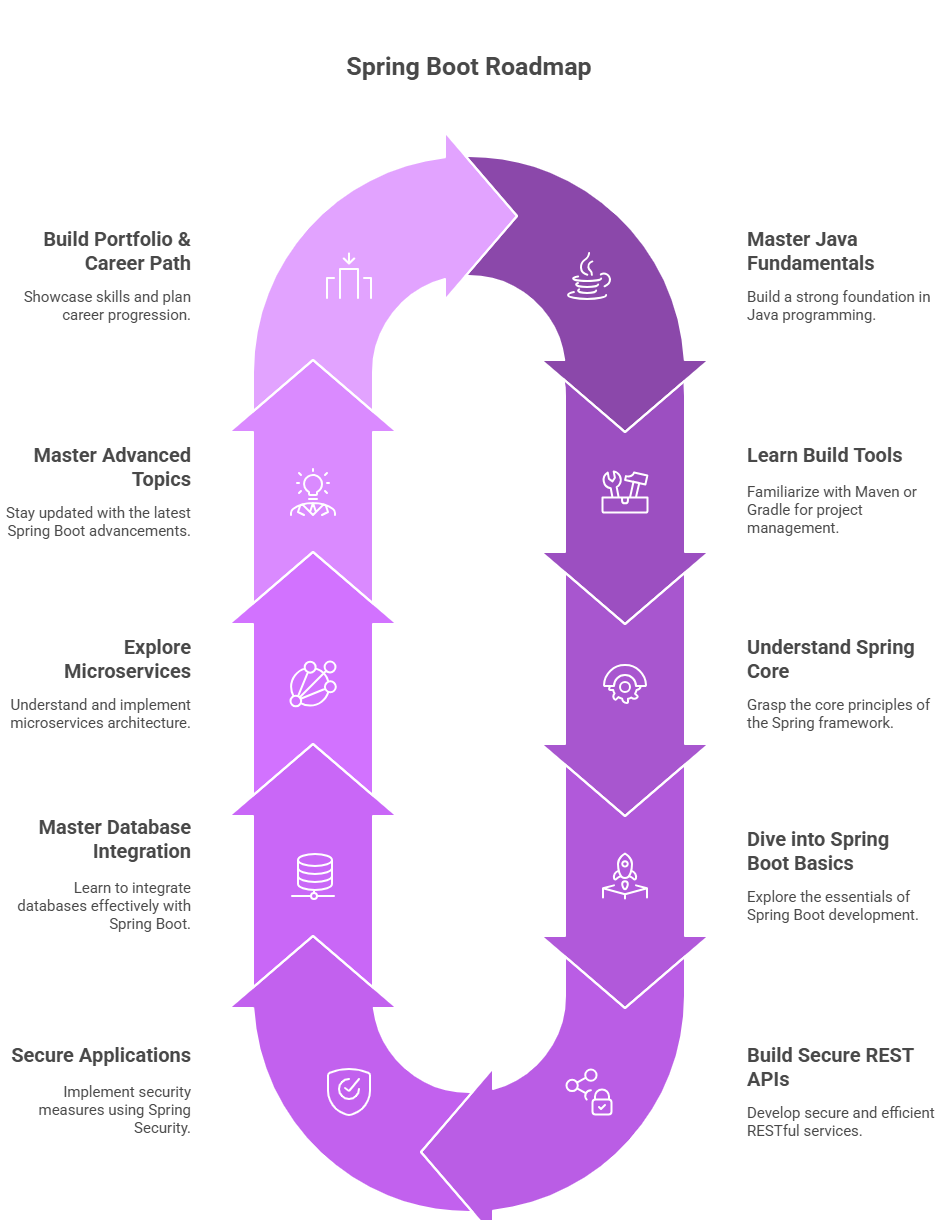
Step 1: Master Java Fundamentals
Spring Boot is built on Java, so a solid foundation in Java programming is non-negotiable. Focus on Java 17 or 21 (Long Term Support versions) to leverage modern features and ensure compatibility with Spring Boot.
Key Java Concepts
- Object-Oriented Programming (OOP): classes, objects, inheritance, polymorphism, and encapsulation. These concepts underpin Spring Boot’s dependency injection and bean management.
- Java 17/21 LTS: Understand new features like records (for concise data classes), sealed classes (for restricted inheritance), and pattern matching for cleaner code.
- Exception Handling: Learn try-catch blocks, custom exceptions, and try-with-resources to handle errors gracefully in Spring Boot applications.
- Lambdas & Streams: Embrace functional programming with Java 8+ features to process data efficiently, a must for modern Spring Boot apps.
- Multithreading: Grasp thread safety, synchronization, and the Executor framework to build scalable, high-performance applications.
Practical Tips
- Build small projects like a task manager app to apply OOP and streams.
- Use IntelliJ IDEA for code completion and debugging to accelerate learning.
- Practice writing clean, maintainable code following SOLID principles.
Resources
- Oracle Java Tutorials
- Book: “Effective Java” by Joshua Bloch
- Java OOP Guide
| Feature | Java 17 | Java 21 |
| Records | Introduced for data classes | Enhanced with new patterns |
| Sealed Classes | Supported | improved with pattern matching |
| Pattern Matching | Basic Support | Advanced switch expression |
What Java skills do I need for Spring Boot?
Master OOP, exception handling, lambdas, streams, and multithreading in Java 17 or 21 to build robust Spring Boot applications.
Step 2: Learn Build Tools – Maven or Gradle
Build tools like Maven and Gradle are essential for managing dependencies, building projects, and deploying Spring Boot applications.
Key Skills
- Maven: Understand the pom.xml file, dependency scopes (compile, runtime, test), and plugins for tasks like testing and packaging.
- Gradle: Learn the build.gradle file, task customization, and dependency management for more complex projects.
- CI/CD Integration: Configure builds for tools like Jenkins or GitHub Actions to automate testing and deployment.
Practical Tips
- Start with Maven for its simplicity, then explore Gradle for flexibility in larger projects.
- Create a sample Spring Boot project using spring-boot-starter-web to practice dependency management.
- Use mvn clean install or gradle build to understand the build process.
Resources
1. What is Maven?
Maven is a build automation and project management tool primarily for Java projects. It uses an XML file named pom.xml to describe the project, its dependencies, plugins, and the build lifecycle.
- Convention over configuration (standard project layout).
- Dependency management using repositories (local and remote).
- Uses lifecycle phases like compile, test, package, install, deploy.
- Extensible via plugins (compiler, surefire, shade, etc.).
How Maven works (step-by-step)
- Reads pom.xml: project coordinates, dependencies, plugins, and build configuration.
- Resolve dependencies: checks the local repository (typically ~/.m2), then remote repositories (Maven Central or private repos).
- Download missing artifacts: caches them locally for reuse.
- Execute lifecycle phases: runs phases in order (validate → compile → test → package → install → deploy).
- Produce output: final artifact(s) such as a .jar or .war.
Maven architecture (brief)
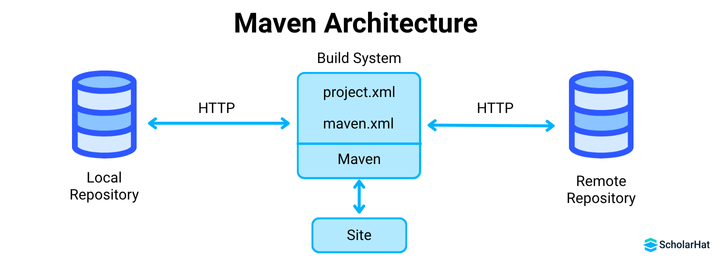
- POM (Project Object Model) — central XML configuration.
- Repositories — local and remote artifact storage.
- Build lifecycle — ordered phases representing the build process.
- Plugins — perform specific build tasks.
2. What is Gradle?
Gradle is a modern build automation tool that is flexible and fast. It uses a domain-specific language (Groovy or Kotlin) in files like build.gradle or build.gradle.kts. Gradle supports many languages and platforms (Java, Kotlin, Android, C/C++, Python, and more).
- Task-based execution model.
- Incremental builds and build caching for speed.
- Highly customizable via plugins and scripts.
- Works with Maven and Ivy repositories.
How Gradle works (step-by-step)
- Reads the build script: build.gradle or build.gradle.kts describing plugins, dependencies, and tasks.
- Initialization: evaluates settings (multi-project builds, included builds).
- Configuration: creates and configures tasks and builds a task graph based on dependencies between tasks.
- Execution: runs only the required tasks in the correct order incremental checks avoid re-running unchanged tasks.
- Produce output: artifacts like .jar, .war, Android APK/AAB, or other deliverables.
Gradle architecture (brief)
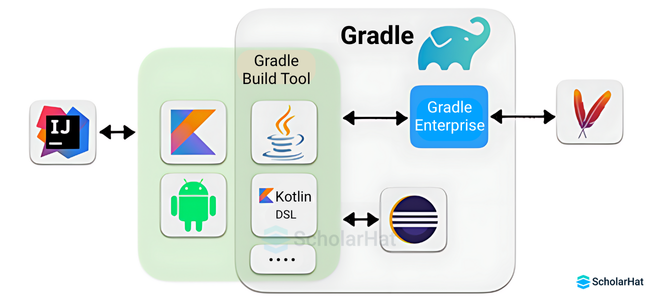
- Build scripts — Groovy or Kotlin DSL.
- Tasks — smallest unit of work (compile, test, package).
- Plugins — add capabilities (Java plugin, Android plugin, Spring Boot plugin).
- Daemon — background process that speeds up subsequent builds.
| Ask Yourself Question: Which build tool is best for Spring Boot? |
| Ans: Maven is beginner-friendly with simpler configuration, while Gradle offers flexibility for complex Spring Boot projects. |
Step 3: Understand Spring Core
Spring Core is the foundation of Spring Boot, providing dependency injection (DI) and inversion of control (IoC) to manage application components.
Key Concepts
- Dependency Injection (DI): Learn constructor, setter, and field injection. Constructor injection is preferred for immutability and testability.
- Inversion of Control (IoC): Understand how the Spring container (ApplicationContext) manages object lifecycles, reducing manual instantiation.
- Bean Lifecycle: Study bean creation, initialization, and destruction to customize behavior.
- Annotations: Use @Component, @Service, @Repository, and @Configuration to define and manage beans.
Practical Tips
- Build a simple Spring application without Boot to grasp manual configuration.
- Experiment with @Autowired for dependency injection and @Bean for custom bean definitions.
- Explore ApplicationContext to understand how Spring manages beans.
| Ask Yourself Question: What is Spring Core in Spring Boot? |
| Ans: Spring Core provides dependency injection and bean management, the foundation for Spring Boot’s auto-configuration and application logic. |
Step 4: Learn Spring Boot Basics
Spring Boot simplifies Spring development with auto-configuration, starter dependencies, and production-ready features.
Key Features
- Auto-Configuration: Automatically configures beans based on classpath dependencies, reducing manual setup.
- Starter Dependencies: Use curated libraries like spring-boot-starter-web for web apps or spring-boot-starter-data-jpa for database access.
- Profiles & Properties: Manage environment-specific configurations with application.properties or application.yml files.
- Actuator: Monitor application health, metrics, and configuration via endpoints like /actuator/health.
Practical Tips
- Create a “Hello World” REST API using spring-boot-starter-web and test it with Postman.
- Experiment with application.yml to configure different profiles (dev, prod, test).
- Enable Actuator to monitor a sample app’s metrics.
Code snippet of a Spring Boot REST controller for a Hello World API
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String sayHello() {
return "Hello, Spring Boot!";
}
}
Step 5: Build Secure REST APIs
Key Skills
- Controllers: Use @RestController and @RequestMapping to define endpoints for GET, POST, PUT, and DELETE operations.
- Data Transfer Objects (DTOs): Design DTOs to control data exchange and maintain API contracts.
- Validation: Apply Bean Validation annotations (@NotNull, @Size) to ensure data integrity.
- Exception Handling: Use @ExceptionHandler for consistent error responses with appropriate HTTP status codes.
- Rate Limiting: Implement tools like Bucket4j to protect APIs from abuse.
Practical Tips
- Build a CRUD API for a blog application (create, read, update, delete posts).
- Use Swagger/OpenAPI to document your API endpoints for better usability.
- Test APIs with Postman or curl to validate functionality.
Step 6: Secure Applications with Spring Security
Security is critical for protecting APIs and user data. Spring Security provides robust tools to secure Spring Boot applications.
Key Concepts
- Authentication: Implement form-based login, JWT, or OAuth2 for user verification.
- Authorization: Use role-based access control with @PreAuthorize to restrict access.
- Custom Filters: Create filters for logging, monitoring, or custom security logic.
Practical Tips
- Integrate OAuth2 with Google for social login to enhance user experience.
- Secure a REST API with JWT authentication using libraries like JJWT.
- Test security with tools like Postman to ensure endpoints are protected.
Step 7: Master Database Integration
Most Spring Boot applications interact with databases for data storage and retrieval. Spring Data simplifies this process.
Key Skills
- Spring Data JPA: Create repository interfaces for CRUD operations and query derivation.
- Custom Queries: Write JPQL or native SQL queries for complex requirements.
- Transaction Management: Use declarative (@Transactional) or programmatic transactions for data consistency.
- Database Migrations: Use Flyway or Liquibase to manage schema changes.
Step 8: Explore Microservices Architecture
Microservices enable scalable, maintainable applications by breaking them into small, independent services.
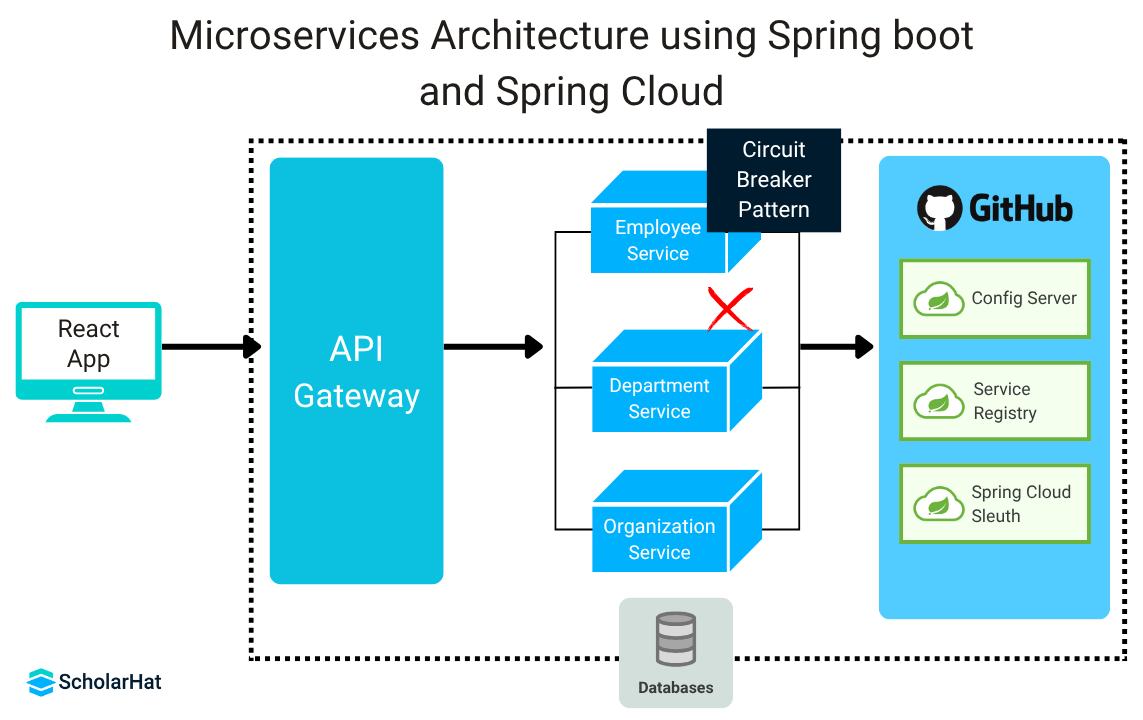
Key Concepts
- Spring Cloud: Use Gateway for routing, Config for centralized configuration, Circuit Breaker for fault tolerance, and Sleuth for distributed tracing.
- Design Patterns: Learn Aggregator, CQRS, SAGA, and Event Sourcing for microservices design.
- Service Discovery: Implement Eureka for dynamic service registration and discovery.
Practical Tips
- Build a microservices-based e-commerce system with separate services for users, products, and orders.
- Use Spring Cloud Gateway to route requests to appropriate services.
- Monitor microservices with Sleuth and Zipkin for distributed tracing.
Step 9: Advanced Topics for 2025
Stay ahead by mastering cutting-edge features and trends in Spring Boot development.
Key Areas
- Reactive Programming: Use Spring WebFlux for non-blocking, high-concurrency apps with Project Reactor (Mono, Flux).
- GraphQL: Implement flexible APIs with Spring GraphQL for efficient data querying.
- Messaging: Integrate Apache Kafka for real-time data streaming and processing.
- Cloud Deployment: Deploy to AWS, Azure, or GCP using Kubernetes for orchestration.
- Native Compilation: Use GraalVM to create native images for faster startup and lower memory usage.
- Generative AI: Leverage tools like GitHub Copilot to accelerate Spring Boot code generation and debugging.
Practical Tips
- Build a reactive API with WebFlux and MongoDB for a real-time dashboard.
- Deploy a Spring Boot app to Kubernetes using a Dockerfile and Helm charts.
Step 10: Build a Portfolio & Career Path
A strong portfolio and strategic career planning are key to landing Spring Boot developer roles.
Key Steps
- Build Projects: Create a blog app, e-commerce system, or task manager to showcase skills.
- Open Source: Contribute to Spring Boot projects on GitHub to gain experience and visibility.
- Documentation: Write clear READMEs and technical blogs to explain your projects.
Career Tips
- Certifications: Earn the Spring Professional Certification from Pivotal to validate your skills.
- Networking: Join Spring forums, attend SpringOne, and engage on Stack Overflow.
- Job Applications: Highlight Spring Boot skills on LinkedIn and tailor resumes to job descriptions.
Bonus Tip : Learn Essential Developer Tools
Mastering developer tools enhances productivity and collaboration in Spring Boot development.
Key Tools
- Git: Use for version control, branching, and CI/CD integration with GitHub Actions.
- IDE: Leverage IntelliJ IDEA for code completion, refactoring, and Spring Boot-specific plugins.
- Linux: Learn shell scripting for server management and deployment automation.
Practical Tips
- Master Git commands like git branch, git merge, and git rebase.
- Customize IntelliJ with plugins like Spring Boot Assistant for faster development.
- Write shell scripts to automate deployment tasks on Linux servers.
Why Learning Spring Boot after Java makes sense?
- Java foundation is required: Spring Boot is a Java-based framework, so you must be comfortable with OOP concepts, Java syntax, collections, exceptions, and streams before jumping in.
- Rapid application development: Spring Boot removes a lot of boilerplate from traditional Spring, so you can quickly create production-ready applications.
- In-demand skill: Many enterprise-level applications and microservices today are built using Spring Boot.
- Hands-on learning: It forces you to apply Java in a practical, real-world project setting.
Conclusion
Congratulations on exploring the Spring Boot Roadmap! From mastering Java fundamentals to building microservices and embracing advanced topics like reactive programming and GraalVM, this guide equips you to become a proficient Spring Boot developer. Start small with a “Hello World” API, build portfolio projects, and engage with the vibrant Spring community to accelerate your learning. If you have no clue where to start just start with our Java Online Course Free With Certificate. Or if you are already a professional and want to upgrade your career with spring boot then, have a look into Java Solution Architect Certification Training.












