20
FebDifference between Stored Procedure and Function in SQL Server
Stored Procedure and Function in SQL Server: An Overview
SQL Functions require at least one parameter and are not able to modify anything. Stored procedures don't require results to be returned, don't require any parameters, and can change database objects. Stored procedures interact with external systems and combine SQL queries into transactions.
In this SQL Server Tutorial, We will explore stored procedures vs functions. By 2027, 75% of tech recruiters will prioritize SQL Server expertise. Enroll in our Free SQL Server Courses Online with Certificate today!
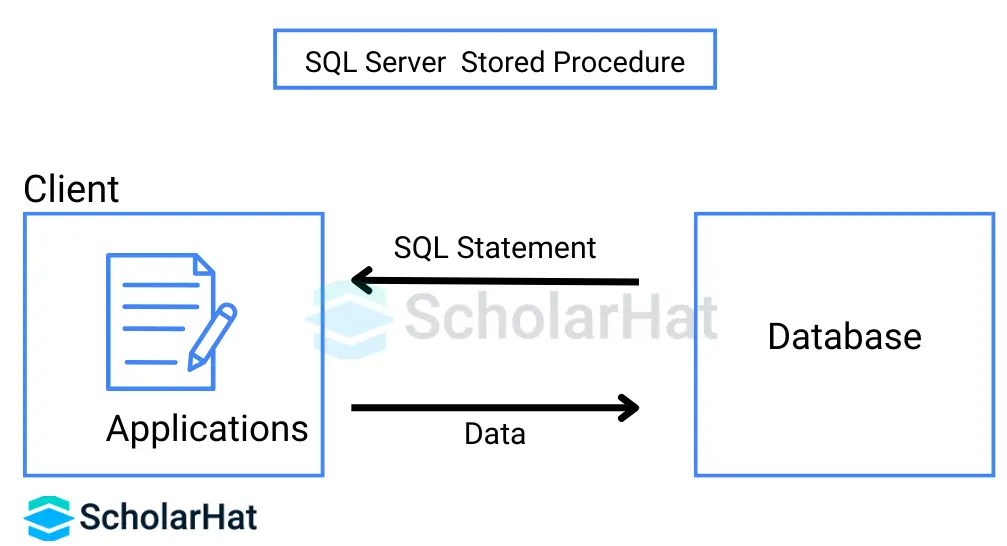
Stored Procedures
Precompiled SQL code constructs known as stored procedures are stored inside the database server and provide several benefits for database management, performance optimization, and security.
For more about stored procedure, please refer to the article Different Types of Stored Procedure.
Functions
A function is a reusable SQL procedure that takes parameters as inputs, executes SQL commands, and outputs either a single value or a table.
For more about functions, please refer to the article Different Types of Functions.
Read More - SQL Interview Questions And Answers For Experienced
Difference between Functions and Stored Procedures in SQL Server
| Function | Stored Procedure |
| Returns a single value, either as a table or as a scalar, always. | Can return zero, a single value, or several values. |
| Run-time compilation and execution occur for functions. | The database contains stored procedures that have been parsed and compiled. |
| Only Select statements are allowed. Updating and inserting DML statements are allowed. | Capable of carrying out any action on database objects, such as DML and select statements. |
| Only input parameters are permitted. Output parameters are not supported. | Both input and output parameters are supported. |
| Does not permit the usage of Try...Catch blocks are used to handle exceptions. | Allows the use of Try...Catch blocks are used to handle exceptions. |
| Transactions are not permitted within a function. | A stored procedure can contain transactions. |
| A function cannot call a stored procedure. | A stored procedure can be called a function. |
| A Select statement can invoke functions. | Stored procedures can't be accessed by Select/Where or Having statements. To run a stored procedure, use the Execute statement. |
| In JOIN clauses, functions can be used. | JOIN clauses can't use stored procedures. |
Read More - DBMS Interview Questions For Freshers
Advantages of Stored Procedure
- Programming in modules can be done using stored procedures. Stated differently, stored procedures are generated once, kept, and called as required. This facilitates quicker execution. Additionally, it boosts data security and decreases network traffic.
- Keeping up with the method on the server is far simpler than keeping copies on many client computers because the script is only kept in one location.
- Stored procedures can be developed with any Java-integrated development environment (IDE). After that, it can be implemented at any network architectural level.
- Scalability is increased by stored procedures because they separate server-side application operations.
Advantages of Function
- By placing functions where they belong, you can shorten the duration of your source program. When it comes to microcomputers with limited storage, this element is important.
- Functions are more easily recognized, isolated, and investigated further; iii) They can be utilized in several different programs. C programmers don't have to start from scratch; instead, they might expand on the work of others.
- Allows for top-down modular programming. This type of programming addresses the low-level specifics of each Function after resolving the problem's overall high-level logic. You don't need to be concerned about the internal workings of the Function if you simply utilize it programmatically. Take printf() as an example.
- Functions are helpful for the modularity of code. Stated differently, every code block is divided into independent units that carry out distinct functions. This greatly simplifies the implementation and debugging of each block.
Benefits of User-Defined Functions
- Modular programming: You can create the function once, store it in the database, and call it any number of times in your program. User-defined functions can be modified independently of the program source code.
- Faster execution: Similar to stored procedures, Transact-SQL user-defined functions reduce the compilation cost of Transact-SQL code by caching the plans and reusing them for repeated executions. This means the user-defined function doesn't need to be reparsed and reoptimized with each use resulting in much faster execution times.
- Reduce network traffic: An operation that filters data based on some complex constraint that can't be expressed in a single scalar expression can be expressed as a function. The function can then be invoked in the WHERE clause to reduce the number of rows sent to the client.
Summary
In conclusion, stored procedures perform larger activities and can modify data, whereas functions focus on computations and data retrieval, providing flexibility in SQL statements. Understanding their differences is critical for efficient database creation.
80% of full-stack roles now require .NET expertise. Don’t miss out—join our Full Stack .NET developer course and future-proof your career!
FAQs
Take our Sqlserver skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.