30
JanWhat is Arrays in C++ | Types of Arrays in C++ ( With Examples )
Arrays in C++: An Overview
What is an Array in C++ Programming?
Anarray in C++ programming language is a powerful data structure that allows users to store and manipulate a collection of elements, all of the same data typein a single variable. Simply, it is a collection of elements of the same data type.Arrays are the derived data type in C++ that can store values of both - fundamental data types like int, and char; and derived data types like pointers, and structure. The values get stored at contagious memory locations that can be accessed with their index number.
Syntax
dataType arrayName[arraySize];Example
int a[5];
Here, an integer type array a is declared with the size 5. It can store 5 integer values.
Types of Arrays in C++
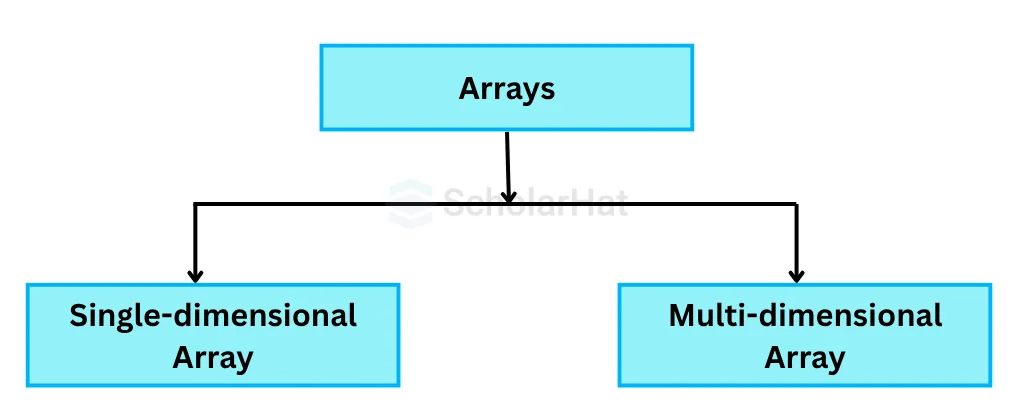
There are two types of array in C++, which are:
- Single-dimensional array: It is a collection of elements of the same data typestored in a contiguous block of memory.
- Multi-dimensional array: It is an array that contains one or more arrays as its elements. We will see this in the next section multidimensional arrays in C++.
In this tutorial, we will cover all the aspects of a Single dimensional array and in brief about Multi-dimensional arrays.
Read More - C++ Interview Interview Questions and Answers
Array Initialization in C++
- Initialize at the time of declaration using
{}.int a[5] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- Initialize an array without specifying its size at declaration time.
int a[] = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
Though we haven't specified the size, the compiler understands the size as 5 due to the initialization of 5 elements.
- Initialization by using the index of an element
int marks[5]; marks[0]=80; //the index of an array starts with 0. marks[1]=60; marks[2]=70; marks[3]=85; marks[4]=75; - What if the elements initialized are less than the size of the array declared?
Example
// store only 3 elements in the array int a[5] = {1, 2, 3};Here an array
aof size 5 is declared. We have initialized it with 3 elements only. In this case, the compiler assigns random values to the remaining places. Many a time, this random value is0.
Accessing Array Elements in C++
To access the array elements, use theindex number of the required element. The array index starts with 0. The index of the last element is n-1.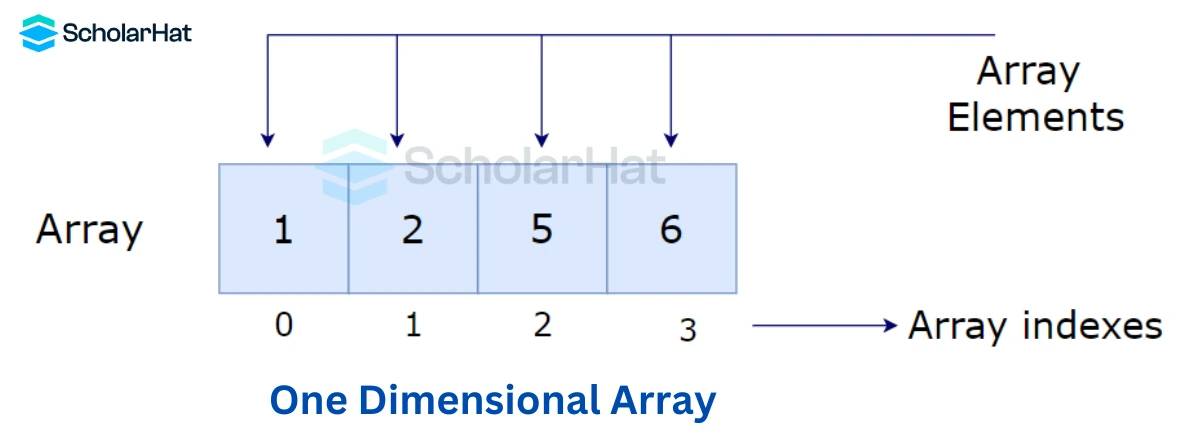
Example in C++ Compiler
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[] = {25, 50, 75, 100};
cout << a[0] << '\n';
cout << a[1] << '\n';
cout << a[2] << '\n';
cout << a[3] << '\n';
return 0;
} Output
25
50
75
100
Remember that when you access an unavailable element in an array, the program may result in an unexpected output (undefined behavior). Sometimes you might get an error and some other times your program may run correctly.
Changing the Elements of an Array in C++
To change the value of a specific element, refer to theindex number:Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int a[] = {25, 50, 75, 100, 45};
a[3] = 60;
cout << a[3] << '\n';
return 0;
}
Output
60
Traversing an Array in C++
- To traverse an array, for loop is used.
Example
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string fruits[5] = {"Apple", "Mango", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes"}; for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) { cout << fruits[i] << '\n'; } return 0; }In the above code, we have created a string
array,fruits. We are printing all the fruit names along with itsindexinside thefruitsarrayusingforloop.Output
Apple Mango Banana Orange Grapes - We have seen the
for-each loopin the loops in C++ programming section. This loop is used exclusively to traverse through elements in anarray. In this loop, we don't need to specify the number of iterations given by the size of the array.Example
#include <iostream> using namespace std; int main() { string fruits[5] = {"Apple", "Mango", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes"}; for (string i : fruits) { cout << i << "\n"; } return 0; }Output
Apple Mango Banana Orange Grapes - If we haven't specified the size of the
arrayduring declaration, we can use thesizeof()operator to traverse through thearrayExample in C++ Online Editor
#include <iostream> #include <string> using namespace std; int main() { string fruits[5] = {"Apple", "Mango", "Banana", "Orange", "Grapes"}; for (int i = 0; i < sizeof(fruits) / sizeof(string); i++) { cout << fruits[i] << '\n'; } return 0; }Output
Apple Mango Banana Orange Grapes
Input and Output Array Elements in C++
We can use thecin function to take inputs of an array from the user.Example in C++ Editor
// Program to take values of the array from the user and print the array
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int a[5];
cout << "Enter the values of an integer array:" << endl;
// Taking input and storing it in an array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cin >> a[i];
}
cout << "Displaying integers:" << endl;
// Printing elements of the array
for (int i = 0; i < 5; ++i) {
cout << a[i] << endl;
}
return 0;
}
The above code uses the for loop to take input values for an array a. After storing the elements in an array, it again uses the for loop to print all of them.
Output
Enter the values of an integer array:
1
2
3
4
5
Displaying integers:
1
2
3
4
5
Multidimensional Arrays in C++
1. Two Dimensional Arrays in C++
In this type of array, two indexes are there to describe each element, the first index represents a row, and the second index represents a column.
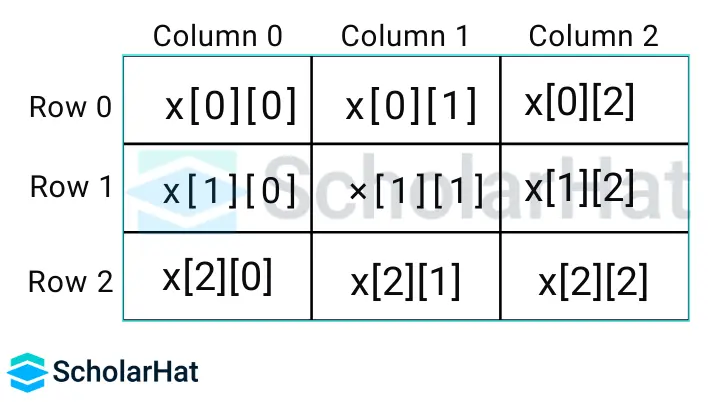
Syntax of a 2D Array
data_Type array_name[m][n];
Here,
- m: row number
- n: column number
Example of a 2D array in C++
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[6][6];
// Initialization
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
arr[i][j] = i + j;
}
}
for (int i = 0; i < 6; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 6; j++) {
cout << arr[i][j] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
0 1 2 3 4 5
1 2 3 4 5 6
2 3 4 5 6 7
3 4 5 6 7 8
4 5 6 7 8 9
5 6 7 8 9 10
2. Three Dimensional Arrays in C++
The 3D array uses three dimensions. There are three indices—the row index, column index, and depth index to uniquely identify each element in a 3D array.
Syntax of a 3D Array
data_Type array_name[d][r][c];
Here,
- d: Number of 2D arrays or depth of array.
- r: Number of rows in each 2D array.
- c: Number of columns in each 2D array.
Example of a 3D array in C++ Online Compiler
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int arr[3][3][3];
// initializing the array
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j < 4; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k < 4; k++) {
arr[i][j][k] = i + j + k;
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i < 4; i++) {
cout << i << "st layer:" << endl;
for (int j = 1; j < 4; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k < 4; k++) {
cout << arr[i][j][k] << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
Output
1st layer:
3 4 5
4 5 6
5 6 7
2st layer:
4 5 6
5 6 7
6 7 8
3st layer:
5 6 7
6 7 8
7 8 9
Advantages of an Array in C++
- Efficient memory usage: Arrays in C++ use contiguous memory locations to store the elements, thus making it efficient to allocate and access data.
- Easy access to elements: Elements in an array can be accessed using their
index, making it easy to retrieve specific data from the array. - Better performance: Accessing elements in an array using an
indexis faster than using other data structures likelinked listsortrees. This is because the index provides direct access to the memory location where the element is stored. - Flexibility: Arrays in C++ can be used to store different types of data, including
integers,characters, andstrings. - Easy to implement algorithms: Many algorithms in computer science use arrays, making it easy to implement these algorithms in C++.
- Compatible with other data structures: Arrays can be used in conjunction with other data structures in C++, such as
stacksandqueues, to implement complex data structures and algorithms. - Easy to pass to functions: Arrays can be easily passed as arguments to functions in C++, making it easy to manipulate large amounts of data efficiently.
Disadvantages of an Array in C++
- Fixed-size: Arrays in C++ have a fixed size determined at the time of declaration. There is no dynamic increase in the size of an array.
- Memory allocation: Arrays in C++ are allocated in contiguous memory blocks. If the array is very large, there may not be enough contiguous memory available for allocation.
- No bounds checking: C++ does not perform any bounds checking on arrays, so it is possible to access memory outside of the bounds of the array. This can lead to segmentation faults or other memory-related errors.
- Limited flexibility: Arrays in C++ have limited flexibility due to fixed size and dimensions. This makes it difficult to implement certain algorithms and data structures that require dynamic resizing and manipulation.
- Inefficient for insertion and deletion: Inserting or deleting elements from an array in C++ can be inefficient, as it requires shifting all the elements after the insertion or deletion point to make room or fill in the gap. This can be time-consuming, especially for large arrays.
Summary
The array in C++ is a useful data structure for representing a sequence of elements. By using an array, you can easily store and access data in a structurally consistent way. It is very important to understand how an array works in C++ to use it to its full potential. This will help make your code more efficient and improve your skills as a programmer.90% of tech giants prefer React.js experts for high-impact roles. Enroll in our React Certification Course today or risk being overlooked.










