30
JanJump statements in C++: break statement
Jump Statements in C++: An Overview
Jump statements are control flow statements that let you change the order in which programs execute. These statements provide flexibility and control over program logic to the programmer.jump statements and explains the break statement in detail. For more insights, you can even check our C++ Online Course Free. Types of Jump Statements C++
jump statements in C++ language:breakcontinuegotoreturn
In the below section, we will discuss the first kind of jump statement i.e. the break statement in C++. The other jump statements will be discussed subsequently in the next sections.
Break Statement in C++
If you remember we already came across thebreak statement while learning the switch statement. We used to check each case in switch and after finding the correct match used to get out using break.- It is one of the most used jump statements.
- In C++,
breakis used to prematurely exit from alooporswitchstatement, before the block has been fully executed. - As soon as a
breakstatement is encountered inside a loop, the loop terminates immediately, and control is transferred to the next statement outside the loop.
Syntax
//loop or switch case
break;Example
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i == 5)
{
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- The above C++ code in C++ Compiler iterates from 1 to 10 using a
for loop. It determines whether the value ofiinside the loop equals 5. - It outputs numbers from 1 to 4 (inclusive) as a result
- When
i=5, thebreakstatement is executed, which abruptly ends the loop.
Output
1
2
3
4
Read More - Advanced C++ Interview Interview Questions and Answers
Where to use break statements in C++?
- break statement in
switchcase - break statement in a
loop
- break statement in switch case in C++
break statement is used inside a switch statement to terminate the execution of the enclosing switch statement and exit the block of code. When a break statement is encountered inside a switch block, the control flow is transferred to the end of the switch block, and the remaining case statements are skipped.You have already executed this while learning the switch case in C++.
Syntax
switch (expression) {
case 1:
// code to be executed if expression is equal to 1
break;
case 2:
// code to be executed if expression is equal to 2
break;
case 3:
// code to be executed if expression is equal to 3
break;
default:
// code to be executed if expression doesn't match any case
break;
}
- break statement in a loop in C++
We will see here, how to use the break statement in all three types of loops as well as in nested loop.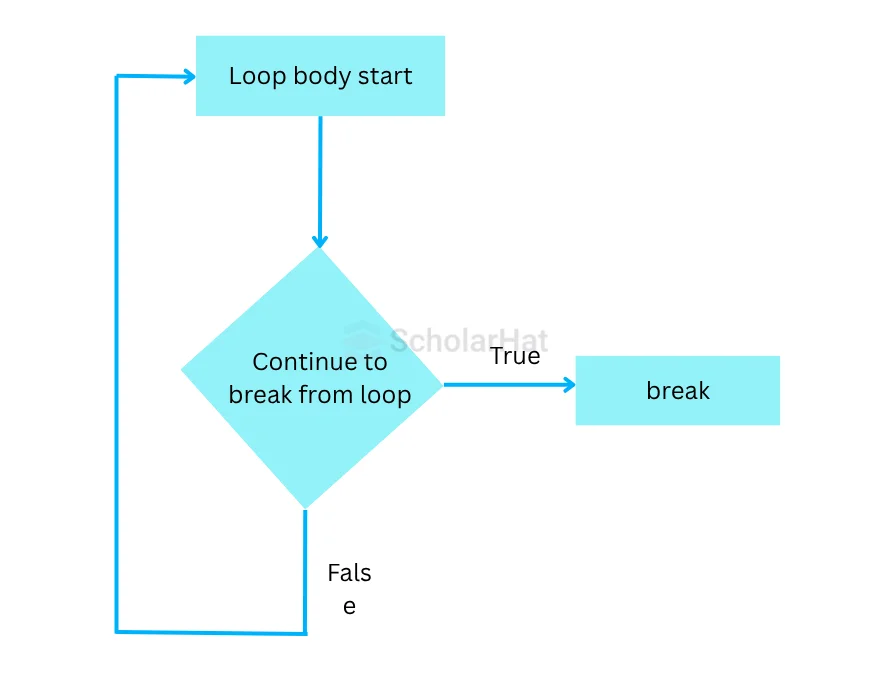
- Break statement in a for loop
The break statement can be used anywhere inside the for loop's body. When executed, it immediately terminates the loop, and control is transferred to the statement following the loop.This example that you have already executed above is an example of a break statement in a for loop.
Example of break statement in a for loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
if (i == 5)
{
break;
}
cout << i << endl;
}
return 0;
}
- The above C++ code in C++ Editor iterates from 1 to 10 using a
forloop. It determines whether the value ofiinside the loop equals 5. - It outputs numbers from 1 to 4 (inclusive) as a result.
- When
i=5, thebreakstatement is executed, which abruptly ends the loop.
Output
1
2
3
4
Break statement in a while loop
Example of break statement in a while loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int i = 0;
while (true) {
cout << i << endl;
i++;
if (i == 5)
break;
}
cout << "The loop terminates" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
Here the loop would have become an infinite one had the break statement not been there. When i becomes 5, the control comes out of the otherwise infinite whileloop.
Output
0
1
2
3
4
The loop terminates
Break statement in a do...while loop
Example of break statement in a do...while loop
#include <iostream>
int main() {
int n = 1, i, choice;
do {
i = 1;
while (i <= 10) {
std::cout << n << " X " << i << " = " << n * i << std::endl;
i++;
}
std::cout << "Do you want to further print the table of " << n + 1 << ", enter any non-zero value to continue: ";
std::cin >> choice;
if (choice == 0) {
break;
}
n++;
} while (true);
return 0;
}
Output
1 X 1 = 1
1 X 2 = 2
1 X 3 = 3
1 X 4 = 4
1 X 5 = 5
1 X 6 = 6
1 X 7 = 7
1 X 8 = 8
1 X 9 = 9
1 X 10 = 10
Do you want to further print the table of 2, enter any non-zero value to continue: 1
2 X 1 = 2
2 X 2 = 4
2 X 3 = 6
2 X 4 = 8
2 X 5 = 10
2 X 6 = 12
2 X 7 = 14
2 X 8 = 16
2 X 9 = 18
2 X 10 = 20
Do you want to further print the table of 3, enter any non-zero value to continue: 0
break statement in a nested loop
break statement terminates the innermost loop when it is used in the nested loop.Example of break statement in a nested loop
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
int number;
int sum = 0;
// first loop
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
// second loop
for (int j = 1; j <= 5; j++) {
if (i == 2) {
break;
}
cout << "i = " << i << ", j = " << j << endl;
}
}
return 0;
}
In the above code in C++ Online Compiler, when i becomes 2, the inner forloop terminates and does not print the output at i=2. The outer for loop iterates 5 times while the inner one skips the iteration at i=2 and continues the remaining iterations.
Output
i = 1, j = 1
i = 1, j = 2
i = 1, j = 3
i = 1, j = 4
i = 1, j = 5
i = 3, j = 1
i = 3, j = 2
i = 3, j = 3
i = 3, j = 4
i = 3, j = 5
i = 4, j = 1
i = 4, j = 2
i = 4, j = 3
i = 4, j = 4
i = 4, j = 5
i = 5, j = 1
i = 5, j = 2
i = 5, j = 3
i = 5, j = 4
i = 5, j = 5
Summary
break statement in C++. We saw its uses in all kinds of scenarios in a comprehensive manner. If you want to go to the next level, consider enrolling in our C++ Training,









