15
MarTips to Optimize Your Angular App/Application
Angular App/Application Optimization: An Overview
Angular performance optimization comes into the picture as our Angular applications grow in size and complexity. Have you ever felt like your Angular app might use a boost? Whether you're a beginner or an experienced developer, this Angular tutorial is going to be a great help in optimizing your Angular Application. We have covered some of the best angular optimization techniques to help you figure out your problem and get the solution.
Read More: What is Angular?
How to Optimize Angular Application?
There are issues with Angular, like high bounce rate, in which a few factors could give you a quick idea if your application is struggling. You need to monitor your app's performance throughout its lifecycle to ensure its smooth running.
Optimization helps achieve better app performance and easier code maintenance. It is a process that must begin right from the time you start writing code for your app development. It becomes really difficult to optimize the application that already exists.
There are hundreds of performance optimization techniques and there is no universal way to optimize your app. In the below section, we'll discuss how to improve the performance of the angular application with the help of some performance optimization techniques.
Angular Optimization Techniques
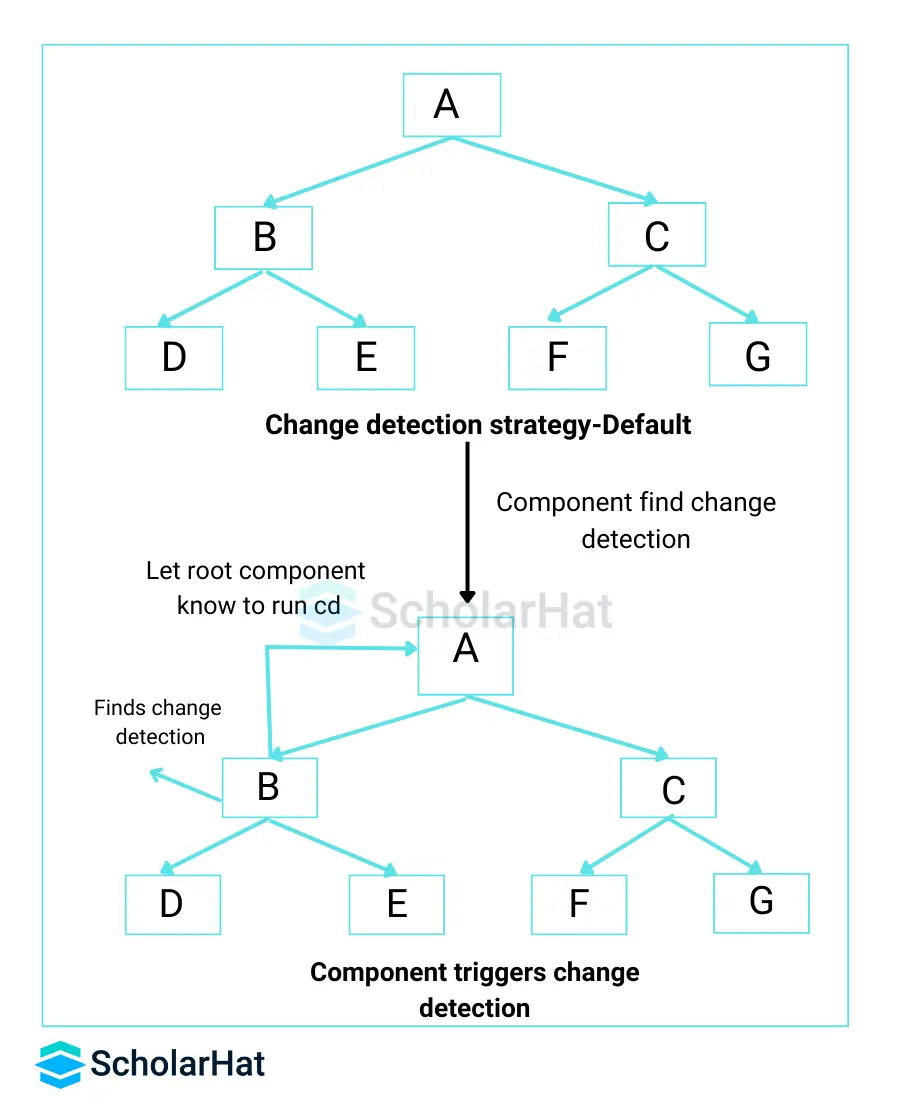
1. Controlling Change Detection:
- To update bindings on a page, Angular uses unidirectional data flow.
- The method by which Angular changes model values on the view is known as change detection.
- There are two primary methods:
- Default: Change detection is enabled by default for all components, even if the binding hasn't changed. This is inefficient.
- OnPush: Only detects changes in components with altered bindings. This is more efficient, but it must be handled with care.
To enable OnPush change detection, define this strategy in the component decorator:
import { ChangeDetectionStrategy, Component, Input } from '@angular/core'; @Component({ selector: 'app-user-list', templateUrl: './user-list.component.html', changeDetection: ChangeDetectionStrategy.OnPush }) export class UserListComponent { @Input() users$: any[]; trackByFn(index: number, item: any): any { return item.id; } }
- Detaching components from the change detector tree: You can detach components that don't need constant updates to improve performance. Use the ChangeDetectorRef to detach and reattach components as needed.
abstract class ChangeDetectorRef { abstract markForCheck(): void abstract detach(): void abstract detectChanges(): void abstract checkNoChanges(): void abstract reattach(): void }
2. Lazy Loading
Loading the entire application at once can result in a longer initial loading time, affecting the perceived performance of your application. Lazy loading in angular is a technique that allows you to load modules on demand. This can improve performance by reducing the initial bundle size and only loading the modules that are needed for the current page.
To set up lazy loading, create a separate module for each feature or section of your application and use the loadChildren property in the routing configuration:
const routes: Routes = [
// Normal eager-loaded route
{ path: 'home', component: HomeComponent },
// Lazy-loaded route
{ path: 'lazy', loadChildren: () => import('./lazy/lazy.module').then(m => m.LazyModule) },
];Read More: Top 50+ Angular Interview Questions & Answers
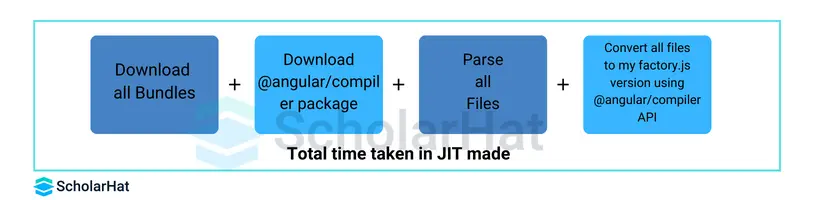
3. AOT compilation mode
- Angular can be used in two ways:
- Just in Time (JIT): JIT (Just in Time) compiles files in the browser. This can be time-consuming.
- Ahead of Time (AOT): Compiles files ahead of time (AOT) before deployment. This is quicker.
- AOT mode also avoids sending the @angular/compiler package, which reduces the size of the initial bundle.
- AOT mode improves performance but is incompatible with dynamically loaded components.
To enable AoT compilation, add the following to your angular.json file:
"build": {
"builder": "@angular-devkit/build-angular:browser",
"options": {
"aot": true
}
}
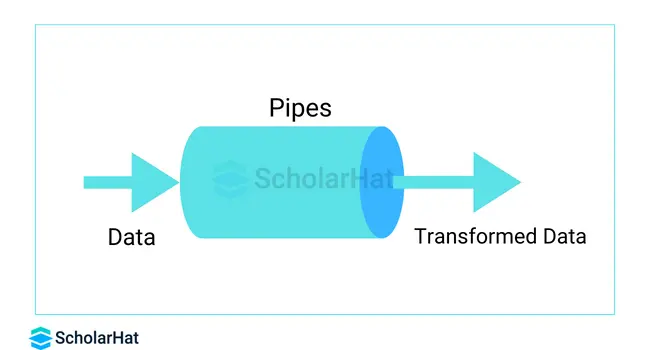
4. Use Pure Pipes
- Angular Pipes are used to format data in the user interface.
- Because pure pipes always provide the same output for the same input, Angular can cache the results.
- This can enhance performance by eliminating redundant calculations.
- When possible, use pure pipes to improve caching and efficiency.
@Pipe({
name: ‘filterPipe’,
pure: true
})
export class FilterPipe {}
5. Use the TrackBy Function
The TrackBy function allows you to track changes in a list of items. It lets you define a function that identifies unique objects in a collection. This can improve performance by reducing the number of change detection cycles.
To use the TrackBy function, add the following to your component:
<ul>
<li *ngFor="let item of items; trackBy: trackByFn">{{ item }}</li>
</ul>
trackByFn(index: number, item: any): number {
return index;
}
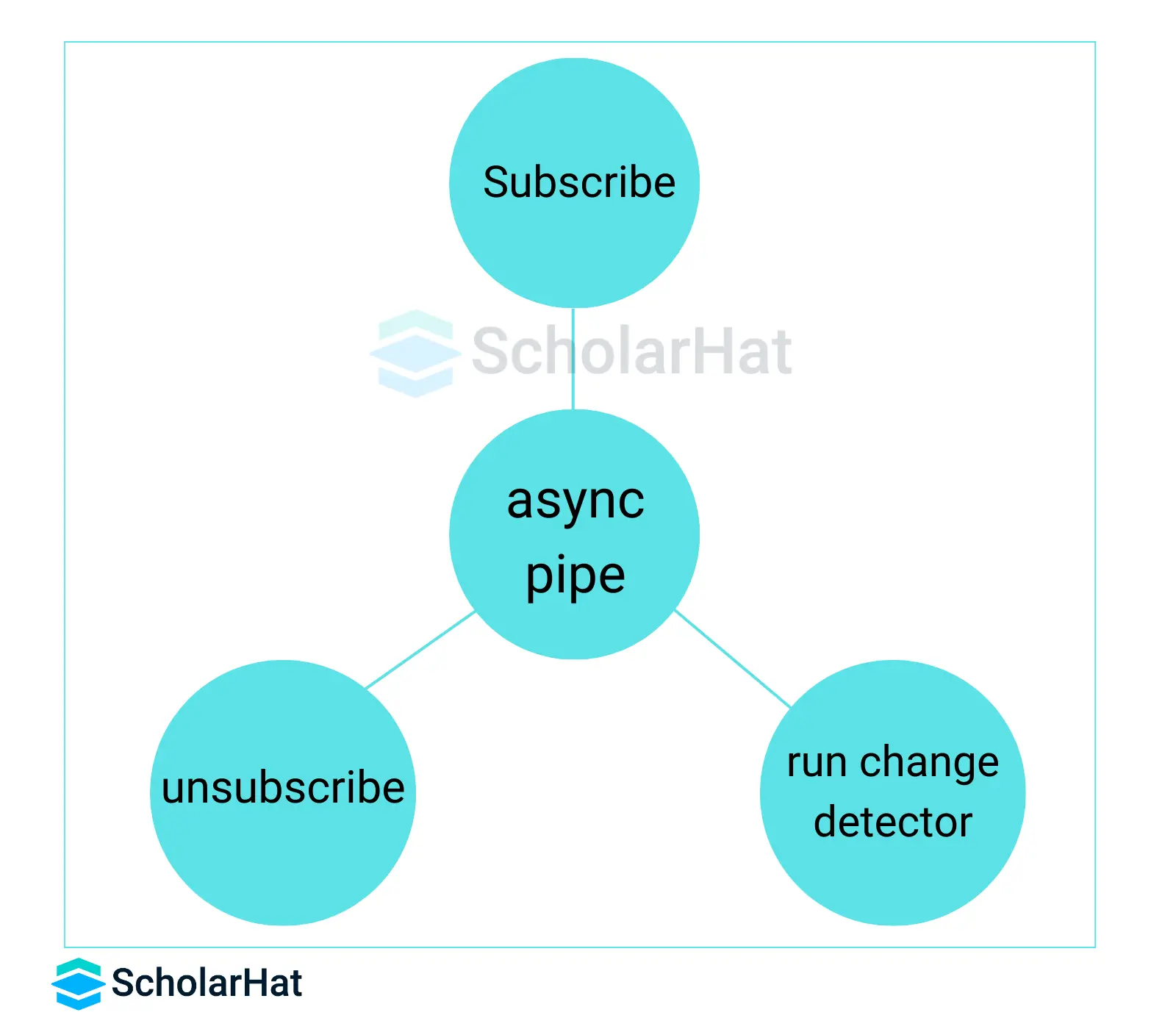
6. Use the Async Pipe
The async pipe allows subscribing to Observable directly from the template. This can improve performance by reducing the number of change detection cycles.
<div *ngIf="observable | async as value">{{ value }}</div>
7. Unsubscribing Observables
Though Observables help to handle asynchronous operations in Angular applications, unsubscribing them can result in memory leaks.
To unsubscribe from observables, add the following to your component:
ngOnInit() {
this.subscription = this.observable.subscribe((value) => {
// Do something with value
});
}
ngOnDestroy() {
this.subscription.unsubscribe();
}
8. Tree shaking
<listing>
ng build –prod
<listing>
9. Preloading Modules
Preloading overcomes the drawbacks of lazy loading. With preloading the router loads all the modules in the background beforehand while the user interacts with only the lazy loaded modules.
abstract class PreloadingStrategy {
abstract preload(route: Route, fn: () => Observable):
Observable
}
10. Angular Checklist
The Angular Checklist is a tool that analyzes your application and provides a list of optimizations that you can make.
11. Server-Side Rendering (SSR) with Angular Universal
Server-side rendering (SSR) is a process that involves rendering pages on the server, resulting in initial HTML content that contains the initial page state. Once the HTML content is delivered to a browser, Angular initializes the application and utilizes the data contained within the HTML.
Angular Universal is a server-side rendering solution. It allows rendering the angular applications on the server before sending them to the client.
To implement SSR with Angular Universal:
Ng add @nguniversal/express-engine
11. Minimize Requests and Payloads
Reducing the number of network requests and optimizing the payloads can significantly improve the performance of your Angular application. Avoid sending unnecessary data in API responses and consider using compression techniques, such as Gzip, to reduce payload size.
Read More:
Summary
This article provides seven tips for optimizing your Angular app: Control change detection, use lazy loading, select AOT compilation, exploit pure pipes, track ngFor items, examine service workers,and server-side rendering. These changes will improve performance, improve the user experience, and will make your app shine!
FAQs
Take our Angular skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.







