15
MarException Handling in C# - Types, Examples, and Practical Guide
Exception Handling in C#
Exception handling in C# is a technique to handle errors when you execute any program. It supports the developers in recognizing and managing unforeseen circumstances, keeping the software from crashing. C# assists in making sure that mistakes are handled gracefully and resources are managed appropriately by employing try, catch, and, finally, blocks.
This C# Tutorial guides you to learn what the exception in C# is, exception handling in C#, exceptions in C#, user-defined exceptions, and many more. Certified C# professionals earn 20% more than non-certified peers. Get your Free C Sharp Course with Certification today!
What is the Exception in C#?
In C#, an exception is an error that happens during the execution of a program, disrupting its normal flow. Exceptions in C# help in identifying issues like invalid input or missing files, and they can be handled using try, catch, and finally blocks to prevent the program from crashing.
How do we handle exceptions in C#?
For handling the exceptions in C#, we use some of the most important blocks of code with keywords that are:
| Keywords | Explanation |
| try | Used to specify a try block. Contains the code that might throw an exception. |
| catch | used in catch block definitions. The exception which the try block threw is caught by this block. |
| finally | Used for finally block definition. The default code is stored in this block. |
| throw | Used for manually throwing exceptions. |
Example
// C# program to show how
// Exceptions occur in a program
using System;
class ScholarHat {
static void Main(string[] args)
{
// An array of 4 indexes
int[] arr = { 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 };
// Displaying array values
for (int i = 0; i < arr.Length; i++) {
Console.WriteLine(arr[i]);
}
// Try to access invalid index of array
Console.WriteLine(arr[7]);
}
}Output
Exception
In this example, an array has only a maximum of 4 indexes. If we want to print the 7th indexed element, it throws an exception.
1. Exception Handling Using try-catch Block
Try-catch blocks in C# are used to manage errors that could arise while a program is running. The code in the catch block is run when an exception is raised in order to address the problem politely and prevent the application from crashing.
Syntax
try
{
// Code that may throw an exception
}
catch (ExceptionType ex)
{
// Code to handle the exception
// 'ex' is the exception object that holds details about the error
}Example
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
// Code that may throw an exception
int numerator = 10;
int denominator = 0; // This will cause a DivideByZeroException
int result = numerator / denominator;
Console.WriteLine("Result: " + result);
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
// Handling the exception
Console.WriteLine("Error: Cannot divide by zero.");
Console.WriteLine("Exception Message: " + ex.Message);
}
// Additional code continues here if needed
Console.WriteLine("Program continues even after the exception.");
}
}Output
Error: Cannot divide by zero.
Exception Message: Attempted to divide by zero.
Program continues even after the exception.
Explanation
- The code that divides by zero in the try block has the potential to throw an exception.
- The catch block outputs an error message when it captures the thrown exception.
- The fact that the application continues to function after the catch block indicates that the exception was handled without causing a crash.
2. Exception Handling Using try-catch and 'finally' Block
The try-catch block in C# may be used to manage exceptions and capture and handle mistakes elegantly. The final block can also be used to run code that has to run, such as resource releases or file closures, whether or not an error occurs.
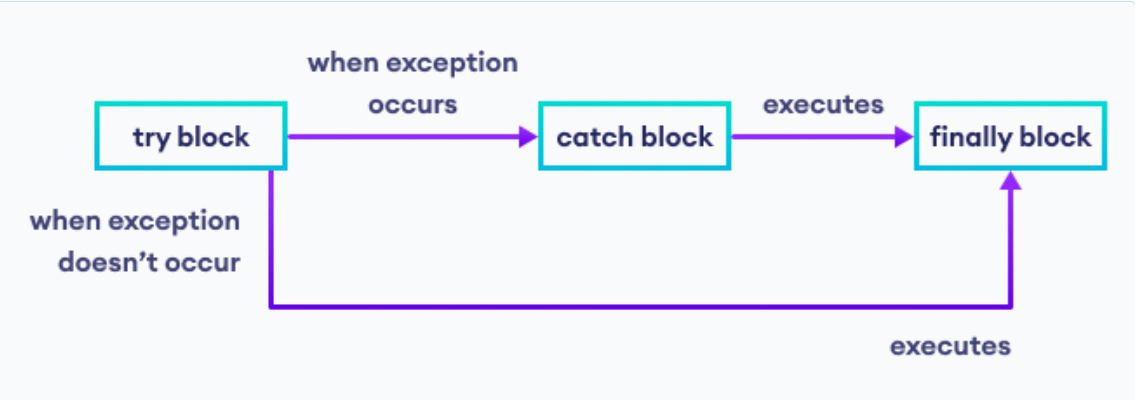
Syntax
try
{
// Code that may throw an exception
}
catch (ExceptionType ex)
{
// Code to handle the exception
// 'ex' is the exception object that holds details about the error
}
finally
{
// Code that will always execute, whether an exception is thrown or not
// Typically used for resource cleanup
}Example
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
// Code that may throw an exception
int numerator = 10;
int denominator = 0; // This will cause a DivideByZeroException
int result = numerator / denominator;
Console.WriteLine("Result: " + result);
}
catch (DivideByZeroException ex)
{
// Handling the exception
Console.WriteLine("Error: Cannot divide by zero.");
Console.WriteLine("Exception Message: " + ex.Message);
}
finally
{
// This code will always run
Console.WriteLine("Execution of the try-catch block is complete.");
}
Console.WriteLine("Program continues...");
}
}Output
Error: Cannot divide by zero.
Exception Message: Attempted to divide by zero.
Execution of the try-catch block is complete.
Program continues...
Explanation
- try block: The code inside the try block attempts to divide by zero, which causes a DivideByZeroException.
- catch block: The catch block catches the exception and prints an error message. This prevents the program from crashing.
- finally block: The finally block runs after the try-catch, regardless of whether an exception occurred. In this case, it prints that the execution is complete.
3. Multiple try-catch Block
Multiple try-catch blocks can be used in C# to manage separate code segments that can generate exceptions. You can handle distinct exceptions individually since each try-catch block has the ability to capture certain exceptions on its own.
Syntax
try
{
// Code that may throw multiple types of exceptions
}
catch (ExceptionType1 ex1)
{
// Handle the first type of exception
}
catch (ExceptionType2 ex2)
{
// Handle the second type of exception
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle any other exceptions
}
finally
{
// Code that will always execute, whether an exception occurred or not
}Example
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
// Code that may throw exceptions
string input = "abc";
int number = int.Parse(input); // This will throw FormatException
int[] numbers = { 1, 2, 3 };
Console.WriteLine(numbers[5]); // This will throw IndexOutOfRangeException
}
catch (FormatException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: Invalid format. Cannot convert string to integer.");
Console.WriteLine("Exception Message: " + ex.Message);
}
catch (IndexOutOfRangeException ex)
{
Console.WriteLine("Error: Array index out of bounds.");
Console.WriteLine("Exception Message: " + ex.Message);
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// This will catch any other types of exceptions
Console.WriteLine("An unexpected error occurred.");
Console.WriteLine("Exception Message: " + ex.Message);
}
finally
{
// This block always runs, regardless of whether an exception occurred
Console.WriteLine("Execution of the try-catch block is complete.");
}
Console.WriteLine("Program continues...");
}
}Output
Error: Invalid format. Cannot convert string to integer.
Exception Message: The input string 'abc' was not in a correct format.
Execution of the try-catch block is complete.
Program continues...
Explanation
- try Block: This block contains code that can raise exceptions, as when it tries to access an incorrect array index or convert a string to an integer.
- Particular catch Blocks: Provides particular error messages by handling FormatException and IndexOutOfRangeException independently.
- finally Block: This block always runs after the try-catch block, making sure that, in the event of an exception, cleanup or final messages are written.
4. Use the throw keyword in try-catch Block
The throw keyword may be used in catch blocks to rethrow an exception, or it can be used to explicitly raise an exception in try blocks. Custom error handling and control flow in exception management are made possible by this.
Syntax
try
{
// Code that may throw exceptions
throw new Exception("Custom exception message.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle the exception
Console.WriteLine("Caught an exception: " + ex.Message);
throw; // Rethrow the caught exception
}
finally
{
// Cleanup code that always runs
Console.WriteLine("Execution of the try-catch block is complete.");
}Example
using System;
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
// Call a method that may throw an exception
ThrowException();
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle the exception from the method
Console.WriteLine("Caught an exception in Main: " + ex.Message);
}
finally
{
// This block always runs
Console.WriteLine("Execution of the try-catch block is complete.");
}
Console.WriteLine("Program continues...");
}
static void ThrowException()
{
try
{
// Manually throw an exception
throw new Exception("An error occurred in the try block.");
}
catch (Exception ex)
{
// Handle the exception
Console.WriteLine("Caught an exception in ThrowException: " + ex.Message);
throw; // Rethrow the exception for further handling
}
finally
{
// This block always runs
Console.WriteLine("Execution of the ThrowException method is complete.");
}
}
}Output
Caught an exception in ThrowException: An error occurred in the try block.
Execution of the ThrowException method is complete.
Caught an exception in Main: An error occurred in the try block.
Execution of the try-catch block is complete.
Program continues...
Explanation
- try Block: An exception is manually thrown using the throw keyword.
- catch Block: The thrown exception is caught, and its message is printed. The exception is then rethrown using throw; allowing it to propagate further if necessary.
- finally Block: Executes after the try and catch, ensuring that cleanup actions or final messages are always executed.
User-Defined Exceptions in C#
In C#, you may construct a custom error type called a user-defined exception to reflect certain issues in your program. By doing this, you can manage errors in a way that makes sense for your application and give more understandable notifications when something goes wrong.
Example
using System;
// Define a custom exception class
public class InvalidAgeException : Exception
{
public InvalidAgeException(string message) : base(message) { }
}
class Program
{
static void Main()
{
try
{
int age = -1; // Let's say someone entered an invalid age
if (age < 0)
{
throw new InvalidAgeException("Age cannot be negative."); // Throwing the custom exception
}
Console.WriteLine("Your age is: " + age);
}
catch (InvalidAgeException ex)
{
// Catching and handling the custom exception
Console.WriteLine("Caught an invalid age exception: " + ex.Message);
}
Console.WriteLine("Program continues..."); // Program keeps running
}
} Output
Caught an invalid age exception: Age cannot be negative.
Program continues...
Explanation
- Creating the Custom Exception: In this step, we construct the InvalidAgeException, a brand-new category of errors. This indicates that the age that was entered is incorrect.
- Using the Exception: This exception is thrown (or created) by the software if the user inputs a negative age. Next, we intercept it to provide a useful alert that reads, "Age cannot be negative."
- Proceeding with the Program: The software keeps operating without crashing after processing the exception.
Some Most Important .NET Exceptions in C#
Here, we will explain some of the most important .NET exceptions that are described below:
| Exception | Description |
| System.NullReferenceException | Thrown when trying to access a member of a null object. |
| System.ArgumentException | Thrown when one of the arguments provided to a method is not valid. |
| System.IndexOutOfRangeException | Thrown when trying to access an index outside the bounds of an array. |
| System.DivideByZeroException | Thrown when attempting to divide by zero. |
| System.IO.FileNotFoundException | Thrown when trying to access a file that does not exist. |
| System.FormatException | Thrown when an argument is not in the expected format. |
| System.InvalidOperationException | Thrown when a method call is invalid for the object's current state. |
| System.OutOfMemoryException | Thrown when there is not enough memory to continue execution. |
| System.UnauthorizedAccessException | Thrown when trying to access a resource without necessary permissions. |
| System.TimeoutException | Thrown when an operation exceeds the allowed time limit. |
Difference Between Error and Exception in C#
Here, we will understand the difference between errors and exceptions in C# that are below:
| Factors | Error | Exceptions |
| Definition | Errors are significant problems that arise in software and frequently point to a fault with the application or environment. | Events that happen while a program is running and indicate that something unexpected happened are known as exceptions, but they are often manageable. |
| Nature | Errors are usually fatal and can cause the program to stop running entirely. | Exceptions can be caught and handled within the program, allowing it to continue running. |
| Type | Common types of errors include syntax errors, runtime errors, and logical errors. | Exceptions include specific issues like NullReferenceException, DivideByZeroException, and user-defined exceptions. |
| Handling | Errors typically require fixing the code or addressing environmental issues, and they often cannot be handled within the program. | Exceptions can be managed using try-catch blocks, allowing developers to implement custom error handling. |
| Example | Exceptions can be managed using try-catch blocks, allowing developers to implement custom error handling. | An exception occurs when trying to access a file that doesn't exist, which can be handled gracefully in the code. |
Conclusion
In conclusion, exception handling in C# is an essential part of writing robust and reliable applications. By using techniques like try-catch blocks, developers can gracefully manage errors and provide meaningful feedback to users, making the software experience smoother. Overall, effective exception handling in C# not only helps identify and fix issues but also ensures that applications run smoothly without crashing.
Over 10,000 companies seek certified .NET full stack developers in India. Start your journey with our full stack .NET developer course and seize top opportunities!
FAQs
Take our Csharp skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.











