13
FebRedux in React - React Redux Tutorial with Example
React-Redux is a JavaScript state management library that works seamlessly with React applications. It helps you manage your application's state in a predictable and centralized way. With Redux, you can build applications that behave consistently across different environments—whether it's client, server, or native. It also makes your apps easier to test and ensures a clear data flow.
Curious about how Redux can improve your web development skills? In this React Tutorial, we’ll explore the ins and outs of React Redux. You will able to know about what is react redux and more on. React.js is the #1 framework for modern web apps. Don’t stay stuck with outdated skills—Enroll now in our free react js certification and level up!

What is Redux in React?
Redux is a state management library commonly used with React to manage the state of an application efficiently. React only supports component level state management. React redux allows any component to access the state at any time.
- It provides a centralized store for your application state, ensuring that your components can access the necessary data consistently.
- With Redux, you can predictably manage complex application states, making debugging and testing easier.
- It makes it easier to manage state and data. As the complexity of our application increases.
- At the start, it is hard to understand but it helps to build complex applications. In the beginning, it feels like a lot of work, but it is really helpful.
Why Use Redux in React?
- Predictability: The flow of data is predictable because of the unidirectional data flow, making it easier to debug and test your application.
- Scalability: Redux helps manage state effectively in large and complex applications.
- Consistency: By maintaining a single source of truth, Redux ensures that the state is consistent across your application.
- Debugging Tools: Tools like Redux DevTools allow you to inspect actions and state changes in real time, making debugging straightforward.
- Integration with Libraries: Redux can easily integrate with other libraries like React Router, enabling smooth navigation and state management.

Key Features of Redux
1.Single Source of Truth
- Redux maintains a single store for the entire application, which holds the complete state tree.
- This ensures consistency in the data used across components.
- The entire application state is stored in a single JavaScript object called the store.
2. Immutable State (Read-Only)
- The state in Redux is read-only and can only be changed through actions and reducers, making it predictable and easier to debug.
3. Actions
- Actions are plain JavaScript objects that describe what should be done to update the state, ensuring clear communication between components and the store.
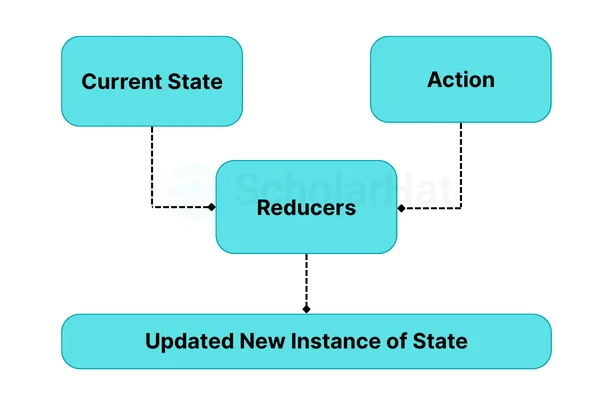
4. Reducers
- Reducers are pure functions responsible for updating the state based on the dispatched actions.
- It takes the current state and an action as arguments and returns a new state.
5. Middleware
- With middleware like Redux Thunk or Redux Saga, you can handle asynchronous operations and side effects in Redux.
Principles of React Redux
The three core principles of Redux are essential to its design and functionality. Let's break them down:
1. Single Source of Truth
The entire state of your application is stored in a single object tree within a single store. This centralized approach makes it easier to:
- Debug or inspect your application.
- Track changes efficiently, improving your development cycle.
- Persist the app’s navigation state for a seamless experience.
2. State Is Read-Only
In Redux, the only way to change the state is by initiating an action, which is an object that describes what happened. This principle ensures:
- Nothing, like network callbacks or views, can directly modify the state.
- Actions are just plain objects that can be logged, serialized, stored, and replayed for debugging or testing.
3. Changes are Made with Pure Functions
To update the state, you write pure functions known as reducers. These functions ensure:
- Reducers return new state objects rather than mutating the previous state, ensuring immutability.
- You can start with a single reducer, and as the app grows, split it into smaller, manageable reducers.
- Since reducers are just functions, you can control the order in which they are called, pass additional data, and even create reusable reducers.
Redux Architecture
Have you ever struggled with managing the React state in a large application? That's where Redux comes in! It's a unidirectional data flow architecture that helps you handle your app's state predictably. With Redux, you can ensure clear state management and seamless synchronization across all your components.
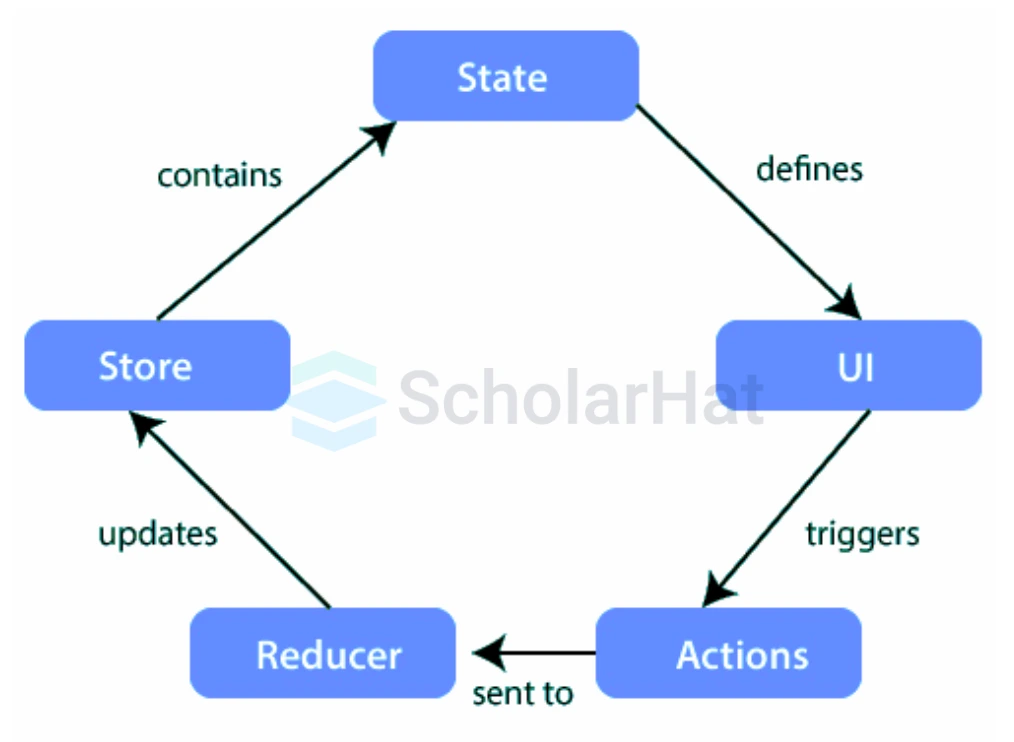
Key Components of Redux Architecture
1. Store
The store is like the brain of your application. It holds all the state in one centralized location, making it easy to manage. Here’s how you create one:
const store = createStore(reducer);2. Actions
Actions are like messengers that describe what happened in your app. They're plain JavaScript objects. Here’s an example:
const incrementAction = { type: 'INCREMENT', payload: 1 };3. Reducers
Reducers are where the magic happens! They’re pure functions that decide how your state should change. Check out this example:
const counterReducer = (state = 0, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return state + action.payload;
case 'DECREMENT':
return state - action.payload;
default:
return state;
}
};4. Dispatch
Think of dispatch as the postman for your actions. It sends the action to the store, which then triggers the reducers. Here’s how you do it:
store.dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT', payload: 1 });5. Selectors
Selectors are your best friends when it comes to retrieving specific data from the state. Here’s an example:
const selectCounter = (state) => state.counter;Read More - React Interview Questions for Freshers
Benefits of Using React Redux in Web Development
React Redux offers a powerful way to manage the state of your application efficiently, especially for large-scale applications. It helps in maintaining a predictable state and simplifies debugging and testing.
1. Centralized State Management
With Redux, all your application’s state lives in a single store. This makes it easier to manage and debug since you know exactly where to look when something goes wrong.
2. Predictable State Updates
Redux uses pure functions (reducers) to handle state changes, ensuring they’re predictable and consistent. This makes your app behavior more reliable.
3. Debugging and Testing Made Easy
Redux’s developer tools allow you to track every action and state change in your app. You can even time-travel through state changes, making it easier to debug and test.
4. Reusable Code
Actions and reducers can be reused across different parts of your app, reducing code duplication and improving maintainability.
5. Better Scalability
As your app grows, Redux provides a robust structure to handle increased complexity. It’s especially helpful for large-scale applications with multiple interacting components.
6. Integration with React
React Redux provides easy integration between Redux and React, enabling components to access the state and dispatch actions effortlessly through hooks like useSelector and useDispatch.
7. Community Support
Redux has a vast community of developers and an extensive library of tools and middleware. You’ll find plenty of resources and plugins to enhance your app development process.
8. Separation of Concerns
Redux promotes a clear separation of concerns by dividing your logic into actions, reducers, and the store. This leads to better-organized and more maintainable code.
| Read More: React Interview Questions & Answers |
Installing React Redux
To integrate Redux with React, you need to install the required libraries. Follow this step-by-step guide to get started:
1. Prerequisites
Ensure that you have Node.js and npm (or Yarn) installed. If you haven't set up a React app yet, you can create one by running the following commands:
npx create-react-app my-app
cd my-app2. Install Redux and React-Redux
To install Redux and React-Redux, run the following command:
npm install redux react-reduxIf you're using Yarn, use the following command:
yarn add redux react-redux3. Install Redux Toolkit (Optional but Recommended)
Redux Toolkit simplifies Redux usage. Install it by running:
npm install @reduxjs/toolkitAlternatively, using Yarn:
yarn add @reduxjs/toolkit4. Verify Installation
To confirm that the libraries are installed correctly, check the package.json file. It should contain entries like these:
{
"dependencies": {
"react-redux": "^8.x.x",
"redux": "^4.x.x",
"@reduxjs/toolkit": "^1.x.x"
}
}5. Next Steps
Once the installation is complete, you can follow these steps to set up Redux in your React application:
- Set up the Redux Store: Create a
store.jsfile and define the store. - Wrap Your App in the Redux Provider: Use the
Providercomponent fromreact-reduxto make the store available to your components. - Connect Components to Redux: Use hooks like
useSelectoranduseDispatchto interact with the store.
For detailed examples, visit the official Redux documentation:
React Redux tutorial: Setting up a basic project
Let's first put up a simple project before we get into the fundamental ideas of React Redux. You must have Node.js & npm installed on your computer to follow along with this tutorial.
- Create a new directory for your project to begin with, then use the command line to enter it.
- To start a new npm project, enter the following command:
npm init npm install react react-dom redux react-redux- In the project's root directory, make a new file called index.js, and then add the following code:
import React from 'react';
import ReactDOM from 'react-dom';
import { Provider } from 'react-redux';
import { createStore } from 'redux';
import App from './App';
import rootReducer from './reducers';
const store = createStore(rootReducer);
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);- In the project's root directory, create a new file called App.js, and then add the following code:
import React from 'react';
import { connect } from 'react-redux';
const App = (props) => {
return (
<div>
<h1>Welcome to React Redux Tutorial</h1>
<p>Current count: {props.count}</p>
<button onClick={props.increment}>Increment</button>
<button onClick={props.decrement}>Decrement</button>
</div>
);
};
const mapStateToProps = (state) => {
return {
count: state.count,
};
};
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => {
return {
increment: () => dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' }),
decrement: () => dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' }),
};
};
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(App);- In the project's root directory, create a new file called reducers.js, and then add the following code:
const initialState = {
count: 0,
};
const rootReducer = (state = initialState, action) => {
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { count: state.count + 1 };
case 'DECREMENT':
return { count: state.count - 1 };
default:
return state;
}
};
export default rootReducer;- Finally, add the following code to an HTML file called index.html in the root directory:
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>React Redux Tutorial</title>
</head>
<body>
<div id="root"></div>
<script src="index.js"></script>
</body>
</html>| Read More: React Developer Salary |
Understanding the Core Concepts of React Redux
To use React Redux effectively, it's crucial to understand its core concepts:
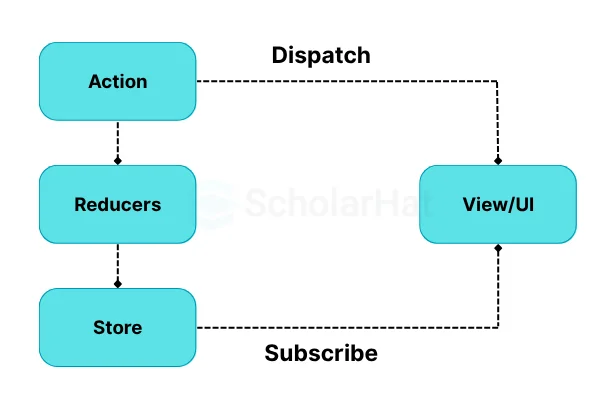
- Store: The store is the foundation of React Redux. It holds the application's state. You can create a store using the Redux library's
createStoremethod.
- Immutable State: In React Redux, the state is read-only and must not be directly modified. Instead, state changes are triggered by actions, which are simple JavaScript objects describing the type of change required.
- Reducers: Reducers are pure functions that handle state changes. They take the current state and an action as inputs and return a new state. Reducers must not modify the existing state object but should always return a new one.
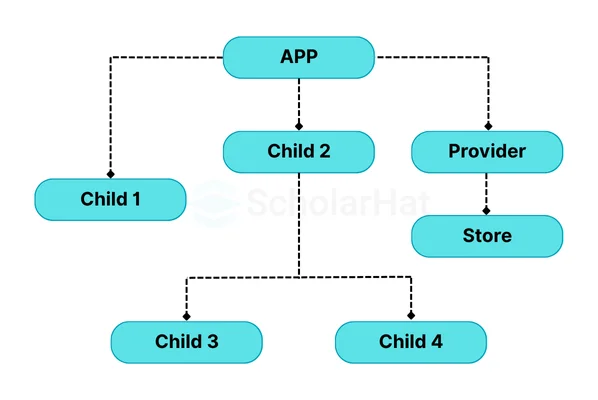
- Provider: The Provider component in React Redux ensures the application's store is available to all components. By wrapping the root component with the Provider and passing the store as a prop, all child components can access the store seamlessly.
Container Component vs Presentational Component
The concept of Container Components and Presentational Components in React Redux helps separate UI rendering from state management:
| Aspect | Container Component | Presentational Component |
| Purpose | Handles application logic and data fetching. | Focuses on rendering the user interface (UI). |
| Concern | Concerned with how things work (behavior). | Concerned with how things look (appearance). |
| State Management | Manages and stores the state. | Receives state and data via props from container components. |
| Dependencies | Often connected to external APIs, Redux, or Context for data handling. | Minimal or no dependency on external libraries or data sources. |
| Reusability | Typically specific to a domain or application. | Highly reusable for rendering similar UI. |
| Props Usage | Passes props to presentational components for rendering. | Receives props and uses them to render the UI. |
| Logic | Includes logic for event handling, data transformation, and API calls. | Avoids any business logic; and focuses on rendering. |
| UI Rendering | Rarely contains UI-related code but may include minimal structure. | Primarily responsible for UI and styling. |
| Testing | Requires integration tests due to its business logic. | It can be easily tested through unit tests. |
| Example | A component fetching user data from an API and passing it to a child component for display. | A component displaying user details like name, email, and profile picture. |
Container Component
The container component is responsible for managing the state and logic of the application. It fetches data, processes it if needed, and passes it down to presentational components as props.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import UserDetails from './UserDetails';
const UserContainer = () => {
const [user, setUser] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
fetch('/api/user')
.then((response) => response.json())
.then((data) => setUser(data));
}, []);
return ;
};
export default UserContainer;
Presentational Component
The presentational component is responsible for rendering the UI. It receives data as props from the container component and focuses on how the information is displayed to the user.
const UserDetails = ({ user }) => {
if (!user) return Loading...;
return (
{user.name}
{user.email}
);
};
export default UserDetails;
- Presentational Components: These components handle UI rendering and user input. They typically receive data and callbacks through props and are generally stateless. Their focus is on appearance, and they do not interact with Redux or the application's state.
- Container Components: These components are connected to the Redux store. They manage the application's state and behavior, passing data and callbacks to presentational components. Container components interact directly with the Redux store to ensure functionality.
- Separating container and presentational components improves reusability and maintainability. Presentational components can be reused across the application, while container components provide centralized state management.
Utilizing High-Order Components in React
High-order components (HOCs) in React are powerful tools for component composition and code reuse:
- What Are HOCs: HOCs are functions that take a component as input and return a new component with added functionality. They enable us to enhance existing components without modifying them directly.
- Using HOCs in React Redux: HOCs are often used to provide components with access to the Redux store and state. This is commonly achieved using React Redux's
connectmethod, which is itself a HOC. - Connect Function: The
connectfunction in React Redux accepts two optional arguments:- mapStateToProps: Maps the Redux store's state to the component's props, allowing the component to access the necessary data.
- mapDispatchToProps: Maps the
dispatchfunction to the component's props, enabling the component to dispatch actions to the Redux store.
- By leveraging HOCs and their
connectfunction, we can enhance our components' functionality, making them more flexible and reusable.
Using React Redux MapStateToProps and MapDispatchToProps
- The utilities mapStateToProps, and mapDispatchToProps tie components to the Redux store, making state management efficient.
- mapStateToProps: This function uses the Redux store’s state as input and maps it to the component’s props, enabling the component to access necessary data.
const mapStateToProps = (state) => ({
count: state.count,
});The example above maps the state’s count value to the component’s count prop.
- mapDispatchToProps: This function maps the dispatch function to the component’s props, allowing it to trigger actions in the Redux store.
const mapDispatchToProps = (dispatch) => ({
increment: () => dispatch({ type: 'INCREMENT' }),
decrement: () => dispatch({ type: 'DECREMENT' }),
});In the above example, the increment and decrement functions dispatch the INCREMENT and DECREMENT actions, respectively.
Real-World Examples of React Redux
React Redux is widely used in various applications for efficient state management:
- E-commerce Sites: React Redux handles user authentication, shopping cart state, and order tracking, providing a seamless user experience.
- Social Media Applications: It enables real-time updates for posts, comments, and notifications, making it ideal for interactive user interfaces.
- Dashboard and Analytics Tools: React Redux efficiently manages dynamic data and real-time visualizations required for dashboards and analytics.
Real-World Example: Shopping Cart Application
Consider a shopping cart application:
- Store: Manages the cart's state, including items and total price.
- Action:
{ type: 'ADD_TO_CART', payload: { itemId: 1, quantity: 2 } } - Reducer:
const cartReducer = (state = [], action) => { switch (action.type) { case 'ADD_TO_CART': return [...state, action.payload]; default: return state; } }; - Dispatch: Triggering actions updates the state through the reducer.
- View: The cart’s UI dynamically updates to reflect the new state.
These examples demonstrate how React Redux simplifies state management for complex applications. For in-depth training, consider enrolling in the Best React JS Course.
Best Practices for Using React Redux
Follow these best practices to write clean and maintainable React Redux code:
- Normalize State: Keep the Redux store's state normalized. Avoid deeply nested objects and arrays for better performance and simpler management.
- Use Selectors: Encapsulate state access logic with selectors. This improves code readability and keeps components independent of the state structure.
- Prevent Unnecessary Re-renders: Minimize re-renders by using techniques like
shouldComponentUpdateor memoization in container components. - Separate Business Logic from Presentation: Maintain clear boundaries between business logic and UI rendering. This enhances code reusability and testability.
- Follow Naming Conventions: Use consistent naming for actions, reducers, and selectors to improve code readability and teamwork.
Summary
This article provides a comprehensive guide to React Redux, covering everything you need to know for your interviews. We start with the core concepts like actions and reducers, and the store moves to more complex topics like middleware, state management, and connecting React with Redux. Each section is filled with practical interview questions and answers to give you the confidence to tackle any React Redux-related question in your interview. We also covered the best practices for using Redux in your React applications, how to manage the global state efficiently, and the common pitfalls to avoid when integrating Redux into your projects.
75% of front-end jobs will demand React.js mastery. Don’t be left behind—enroll in our Best React JS Course now!
Test Your Knowledge on React Redux!
Q 1: What is Redux used for in a React application?
- (a) To manage side-effects in React components
- (b) To manage the global state of an application
- (c) To improve the performance of React components
- (d) To replace React Context API
Explanation: Redux is a state management library that helps you manage the global state of your application, making it easier to share state between different components.
Q 2: Which of the following is not a part of the Redux flow?
- (a) Actions
- (b) Reducers
- (c) Store
- (d) Views
Q 3: What does the `connect` function do in React Redux?
- (a) It connects Redux with the React component
- (b) It dispatches actions to Redux store
- (c) It helps in accessing the store's state
- (d) All of the above
Q 4: What is the purpose of the `Provider` component in React Redux?
- (a) To provide the Redux store to React components
- (b) To connect components to the Redux store
- (c) To dispatch actions to the store
- (d) To manage the global state
Q 5: What is the role of a reducer in Redux?
- (a) To define the initial state of the application
- (b) To manage side effects like API calls
- (c) To update the state based on actions
- (d) To return the store
FAQs
Take our React skill challenge to evaluate yourself!

In less than 5 minutes, with our skill challenge, you can identify your knowledge gaps and strengths in a given skill.